Python tan 数学函数用于计算指定表达式的三角函数正切值。在本节中,我们将通过一个示例展示如何使用 tan 函数。
三角函数正切背后的数学公式是:对边长度 / 斜边长度。Python math tan 函数的语法是:
math.tan(number);
Number:可以是您想计算正切值的数字或有效的数值表达式。
- 如果 number 参数是正数或负数,math tan 函数将返回正切值。
- 如果 number 参数不是数字,则返回 TypeError。
Python tan 函数示例
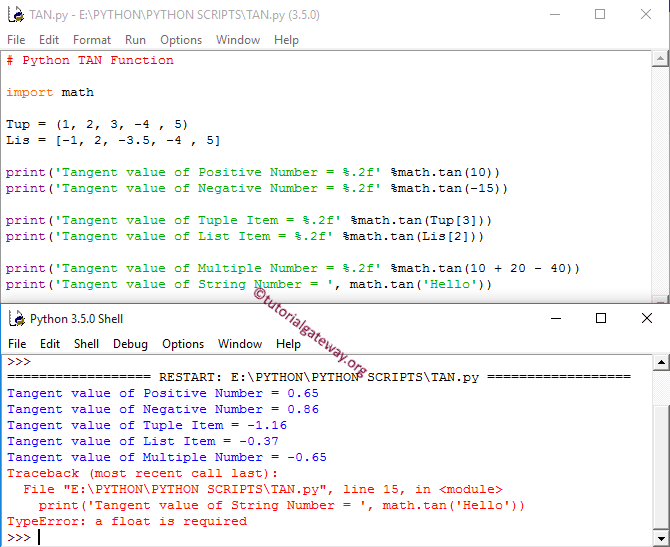
tan 函数允许您计算数值的三角函数正切值。在此示例中,我们将计算不同数据类型的正切值并显示输出。
首先,我们使用一些随机值声明了 列表 和元组。接下来,我们对正整数和负整数使用了 tan 函数。前两个语句计算相应值的正切值。
接下来,我们对 元组 和列表项使用了该函数。如果您查看下面的屏幕截图,它在它们上面运行完美。接下来,我们对多个数字使用了此 数学方法。
在最后一个语句中,我们尝试对字符串数据使用 tan 函数,该函数返回 TypeError 作为输出。请参阅 atan 文章,以查找指定 Python 表达式的反正切值。
import math
Tup = (1, 2, 3, -4 , 5)
Lis = [-1, 2, -3.5, -4 , 5]
print('Tangent value of Positive Number = %.2f' %math.tan(10))
print('Tangent value of Negative Number = %.2f' %math.tan(-15))
print('Tangent value of Tuple Item = %.2f' %math.tan(Tup[3]))
print('Tangent value of List Item = %.2f' %math.tan(Lis[2]))
print('Tangent value of Multiple Number = %.2f' %math.tan(10 + 20 - 40))
print('Tangent value of String Number = ', math.tan('Hello'))