编写一个 Python 程序,使用 For Loop、While Loop 和 Functions 打印列表中的奇数,并附带实际示例。
在此 Python 程序中,我们使用 For Loop 迭代列表中的每个元素。我们在 for 循环中使用 If 语句来检查并打印奇数。
NumList = []
Number = int(input("Please enter the Total Number of List Elements: "))
for i in range(1, Number + 1):
value = int(input("Please enter the Value of %d Element : " %i))
NumList.append(value)
print("\nOdd Numbers in this List are : ")
for j in range(Number):
if(NumList[j] % 2 != 0):
print(NumList[j], end = ' ')
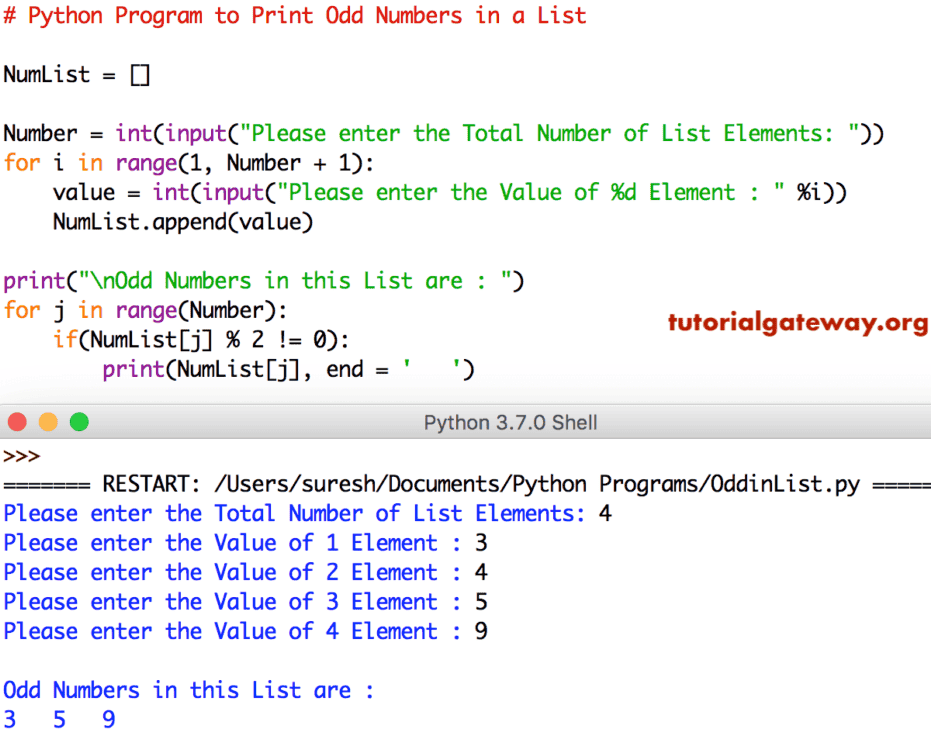
用户输入的 列表 元素 = [3, 4, 5, 9]。在此 Python 程序中,For Loop 迭代是
For循环 – 第一次迭代:for 0 in range(0, 4)
条件为 True。因此,它进入If 语句
if(NumList[0] % 2 != 0) => if(3 % 2 != 0) – 条件为 True
此数字被打印。
第二次迭代:for 1 in range(0, 4) – 条件为True
if(NumList[1] % 2 != 0) => if(4 % 2 != 0) – 条件为 False
此数字被跳过。
第三次迭代:for 2 in range(0, 4) – 条件为True
if(NumList[2] % 2 != 0) => if(5 % 2 != 0) – 条件为 True
此数字将打印。
第四次迭代:for 3 in range(0, 4) – 条件为True
if(9 % 2 != 0) – 条件为 True
此数字也被打印。
第五次迭代:for 4 in range(0, 4) – 条件为 False
因此,它会退出 Python For Loop。
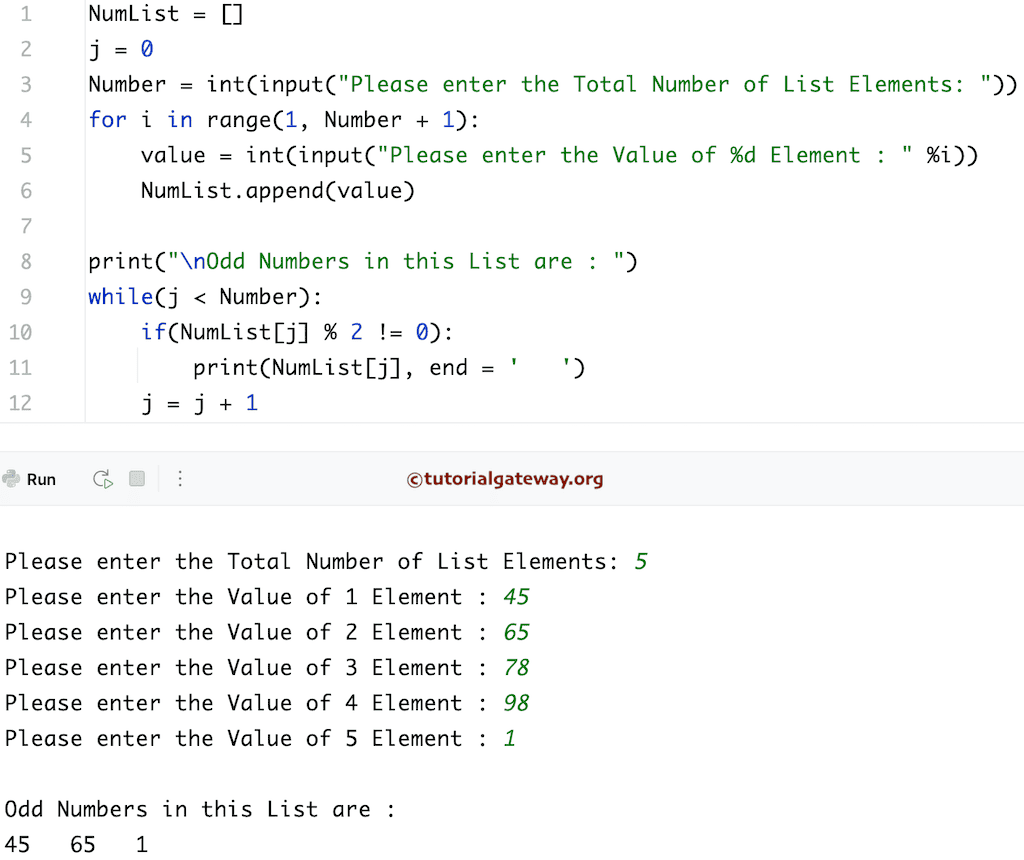
Python 程序:使用 While 循环打印列表中的奇数
这个列表中的奇数程序与上面相同。我们只是将 For Loop 替换为 While loop。
NumList = []
j = 0
Number = int(input("Please enter the Total Number of List Elements: "))
for i in range(1, Number + 1):
value = int(input("Please enter the Value of %d Element : " %i))
NumList.append(value)
print("\nOdd Numbers in this List are : ")
while(j < Number):
if(NumList[j] % 2 != 0):
print(NumList[j], end = ' ')
j = j + 1
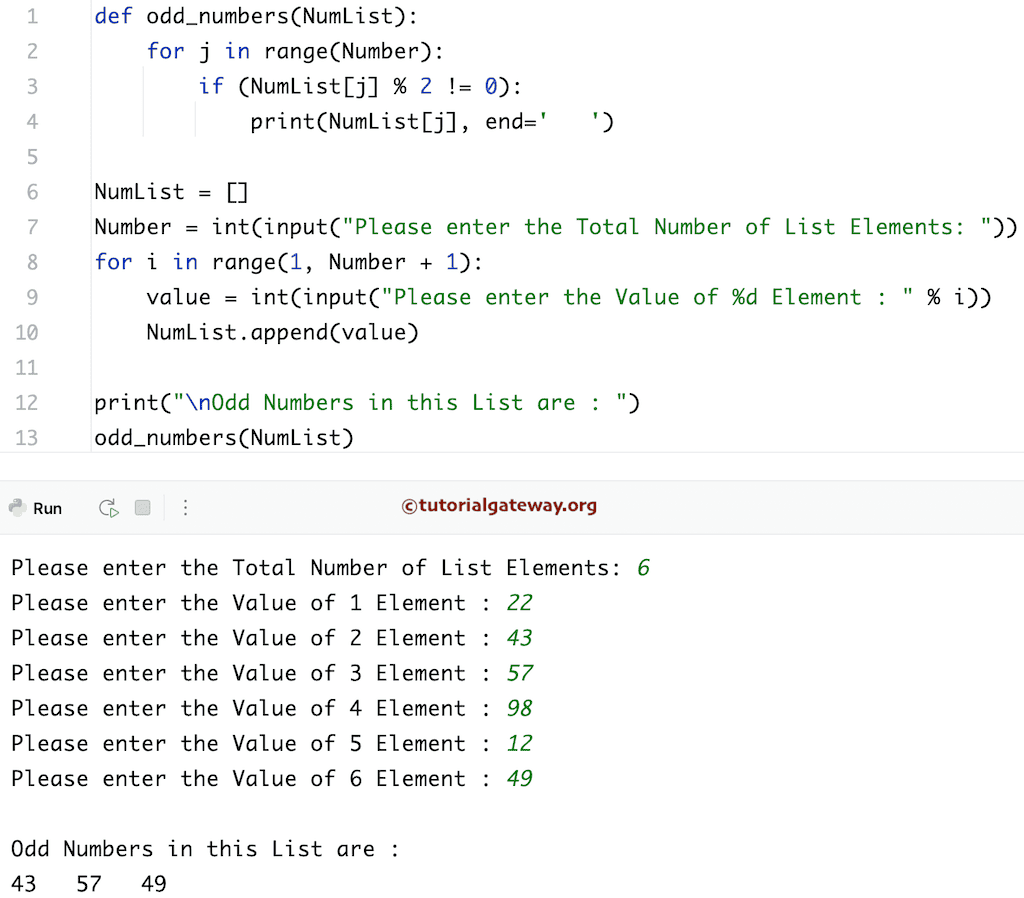
Python 程序:使用函数打印列表中的奇数
这些列表中的奇数程序与第一个示例相同。但是,我们使用 Functions 分离了逻辑。
def odd_numbers(NumList):
for j in range(Number):
if(NumList[j] % 2 != 0):
print(NumList[j], end = ' ')
NumList = []
Number = int(input("Please enter the Total Number of List Elements: "))
for i in range(1, Number + 1):
value = int(input("Please enter the Value of %d Element : " %i))
NumList.append(value)
print("\nOdd Numbers in this List are : ")
odd_numbers(NumList)