编写一个 Python 程序,通过实际示例打印列表中的元素。
print 函数会自动打印 List 中的元素。
a = [10, 50, 60, 80, 20, 15]
print("Element in this List are : ")
print(a)
Element in this List are :
[10, 50, 60, 80, 20, 15]Python 打印列表元素示例程序
这个 python 程序与上面相同。但这次,我们使用 For Loop 来迭代列表中的每个元素,并打印该元素。这种方法非常适合使用此 Python 索引位置来修改单个项。
a = [10, 50, 60, 80, 20, 15]
print("Element in this List are : ")
for i in range(len(a)):
print("Element at Position %d = %d" %(i, a[i]))
Element in this List are :
Element at Position 0 = 10
Element at Position 1 = 50
Element at Position 2 = 60
Element at Position 3 = 80
Element at Position 4 = 20
Element at Position 5 = 15print 函数还会打印列表中的字符串元素。
Fruits = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Grape', 'Banana']
print("Element in this List are : ")
print(Fruits)
打印列表项的输出如下所示。
Element in this List are :
['Apple', 'Orange', 'Grape', 'Banana']这个列表项程序与上面相同。但是,我们使用了 For Loop 来迭代列表中的每个字符串元素。
Fruits = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Grape', 'Banana']
print("Element in this List are : ")
for fruit in Fruits:
print(fruit)
Element in this List are :
Apple
Orange
Grape
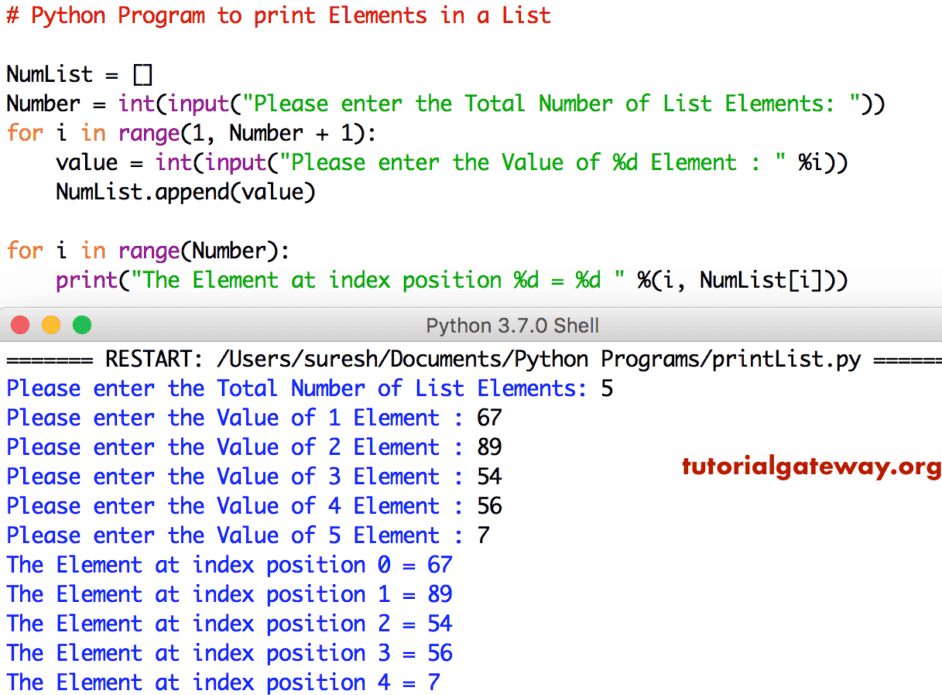
Banana这个 Python 程序允许用户输入任何整数值,该值是列表的长度。接下来,我们使用 For Loop 将数字添加到列表中。
NumList = []
Number = int(input("Please enter the Total Number of List Elements: "))
for i in range(1, Number + 1):
value = int(input("Please enter the Value of %d Element : " %i))
NumList.append(value)
for i in range(Number):
print("The Element at index position %d = %d " %(i, NumList[i]))