编写一个 Python 程序,使用 min 函数、for 循环和 sort 函数以及实际示例来查找列表中的最小数字。min() 函数返回最小值,sort() 函数按升序对列表进行排序,第一个值将是最小值。
Python 程序查找列表中的最小数字
在此示例中,我们声明了一个包含随机整数值的列表。 min 函数返回 List 中的最小值。
a = [10, 50, 60, 80, 20, 15] print(min(a))
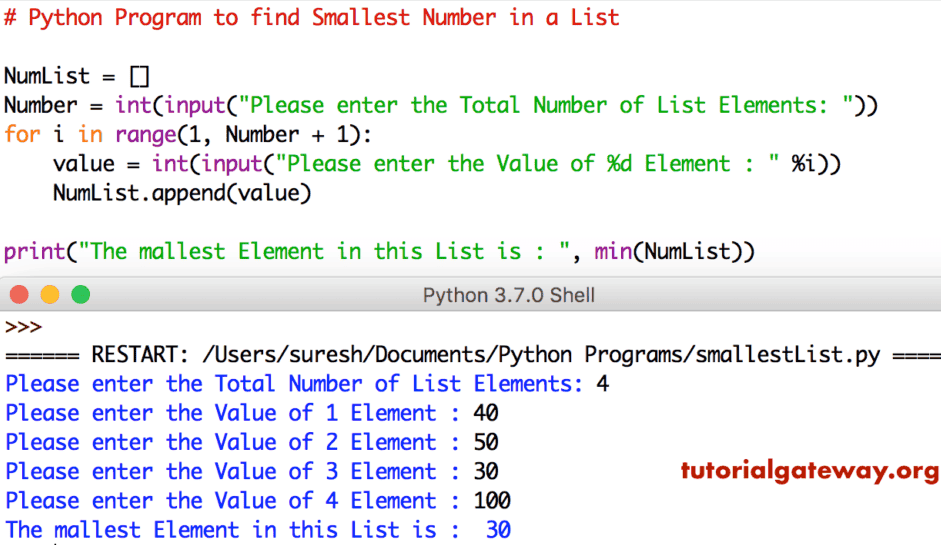
10这个 Python 程序与上面的程序相同。但这次,我们允许用户输入列表的长度。接下来,我们使用 For Loop 将数字添加到 Python 列表中。
NumList = []
Number = int(input("Please enter the Total Number of List Elements: "))
for i in range(1, Number + 1):
value = int(input("Please enter the Value of %d Element : " %i))
NumList.append(value)
print("The Smallest Element in this List is : ", min(NumList))
Python 程序使用 sort 函数查找列表中的最小数字
sort 函数按升序对列表元素进行排序。接下来,我们使用索引位置 0 来打印列表中的第一个元素。
a = [100, 50, 60, 80, 20, 15] a.sort() print(a[0])
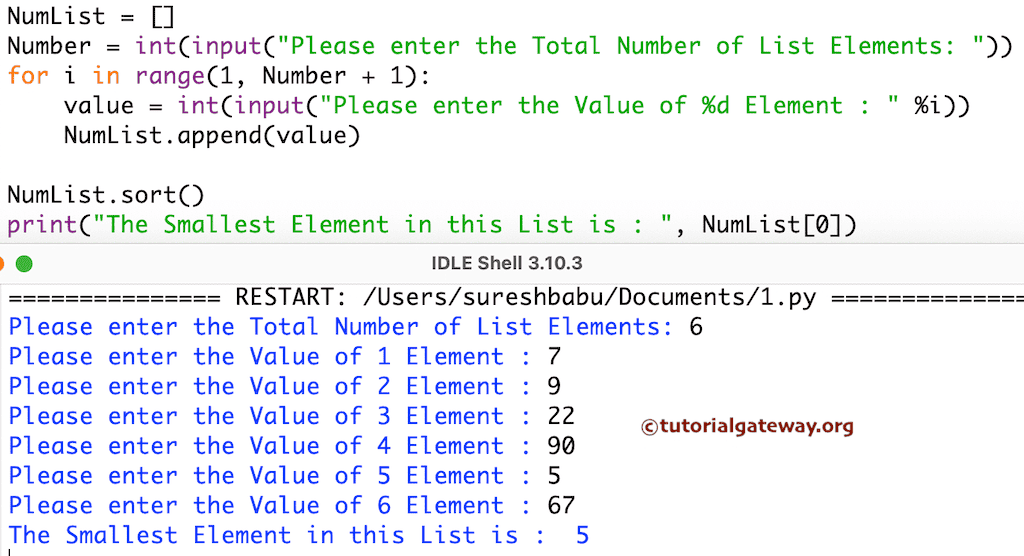
20这个列表的最小数字与上面相同。但这次,我们允许用户输入他们的列表项。
NumList = []
Number = int(input("Please enter the Total Number of List Elements: "))
for i in range(1, Number + 1):
value = int(input("Please enter the Value of %d Element : " %i))
NumList.append(value)
NumList.sort()
print("The Smallest Element in this List is : ", NumList[0])
Python 程序使用 for 循环查找列表中的最小数字
下面的程序使用 for 循环迭代列表项。接下来,它将每个项与最小项进行比较,即第一个列表值。如果任何元素小于第一个值,则它是列表中的最小数字。
a = [7, 6, 8, 2, 10, 5]
smallest = a[0]
i = 0
for n in a:
if n < smallest:
smallest = n
i = a.index(n)
print(smallest, "available in", i)
2 available in 3在此 程序中,我们不使用任何内置函数,例如 sort 或 min 函数。
NumList = []
Number = int(input("Please enter the Total Number of List Elements: "))
for i in range(1, Number + 1):
value = int(input("Please enter the Value of %d Element : " %i))
NumList.append(value)
smallest = NumList[0]
for j in range(1, Number):
if(smallest > NumList[j]):
smallest = NumList[j]
position = j
print("The Smallest Element in this List is : ", smallest)
print("The Index position of the Smallest Element is : ", position)
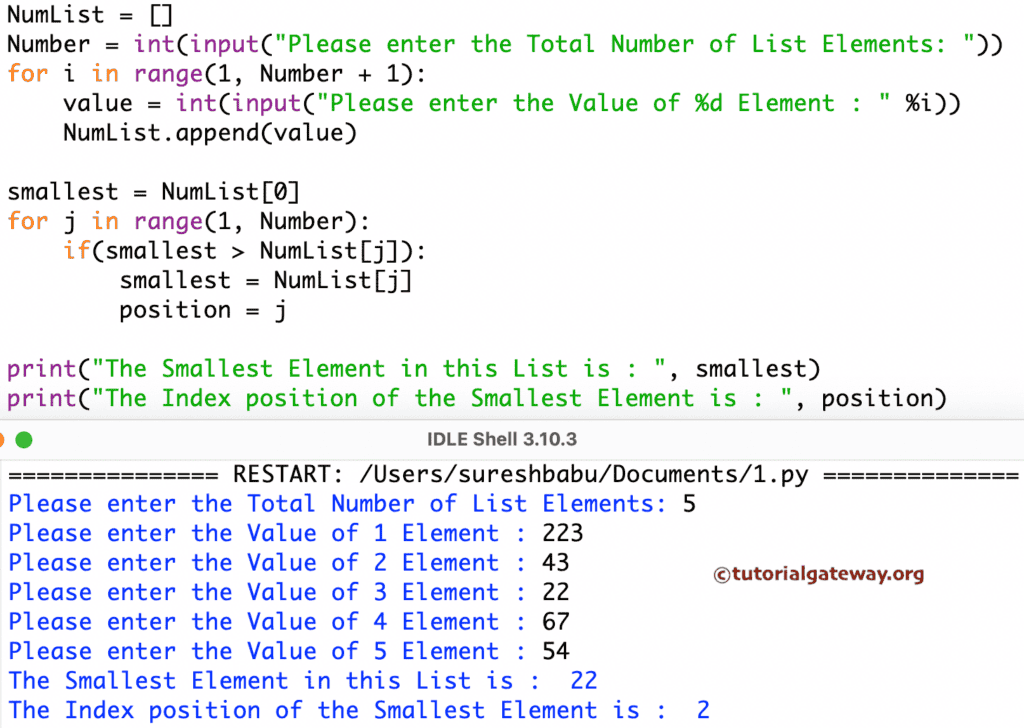
从上面的 Python 程序查找列表中的最小数字示例中,用户插入的值是
NumList[5] = {223, 43, 22, 67, 54}
smallest = NumList[0] = 223
第一次迭代 – for 1 in range(1, 5) – 条件为真。因此,它执行循环内的 If 语句,直到条件失败。
for 循环中的 if (smallest > NumList[j]) 为 True,因为 (223 > 43)。
smallest = NumList[1] => 43。
position = 1
第二次迭代: for 2 in range(1, 5) – 条件为真。
If (smallest > NumList[2]) = (43 > 22) – 条件为真。
smallest = NumList[2] => 22
Position = 2
第三次迭代: for 3 in range(1, 5) – 条件为真。
If (smallest > NumList[3]) = (22 > 67) – 条件为假
smallest = 22
Position = 2
第四次迭代: for 4 in range(1, 5) – 条件为真
If (22 > 54) – 条件为假
smallest = 22
Position = 2
第五次迭代: for 5 in range(1, 5) – 条件为假。因此,它退出循环。
如果您想使用 while loop 代码编写 Python 程序来查找列表中的最小数字,请将 for 循环替换为下面的代码。
j = 1
while j < Number:
if(smallest > NumList[j]):
smallest = NumList[j]
position = j
j = j + 1