Python Numpy 位运算符和用于执行位运算的函数。它们是 `bitwise_and`、`&`、`bitwise_or`、`|`、`invert`(位非)、`left_shift`、`<<`、`right_shift` 和 `>>`。这些位运算符会比较两个值的二进制表示并返回结果。
您还可以将这些 Python Numpy 位运算符和函数用作比较运算符。我的意思是,将每个项与一个条件进行比较。
Python Numpy 位与运算符
Python Numpy 位与运算符 `bitwise_and` 函数在两个位值都返回 true 时返回 true,否则返回 false。在我们进行实际示例之前,让我通过下面的程序向您展示此位与运算背后的真值表。
import numpy as np
print('----and Example----')
print('True & True = ', (True & True))
print('True & False = ', (True & False))
print('False & True = ', (False & True))
print('False & False = ', (False & False))
print('\n----bitwise_and Function Example----')
print('True bitwise_and True = ', np.bitwise_and(True, True))
print('True bitwise_and False = ', np.bitwise_and(True, False))
print('False bitwise_and True = ', np.bitwise_and(False, True))
print('False bitwise_and False = ', np.bitwise_and(False, False))
Numpy 数组位与运算符输出
----and Example----
True & True = True
True & False = False
False & True = False
False & False = False
----bitwise_and Function Example----
True bitwise_and True = True
True bitwise_and False = False
False bitwise_and True = False
False bitwise_and False = False在此示例中,我们声明了两个整数变量并对它们使用了位与运算。首先,它将它们转换为二进制格式,然后比较 a 的每个位与 b。这里,12 = 00001100,25 = 00011001,因此 00001100 & 00011001 返回 00001000,即 8。
import numpy as np
a = 12
b = 25
print('Binary Value of 12 = ', bin(a))
print('Binary Value of 25 = ', bin(b))
print('\nBinary Value of 12 = ', np.binary_repr(a))
print('Binary Value of 25 = ', np.binary_repr(b))
print('\nBitwise and Operator Result = ', a & b)
print('bitwise_and Function Result = ', np.bitwise_and(a, b))
位与运算输出
Binary Value of 12 = 0b1100
Binary Value of 25 = 0b11001
Binary Value of 12 = 1100
Binary Value of 25 = 11001
Bitwise and Operator Result = 8
bitwise_and Function Result = 8在上面的 Python 示例中,我们将此 Numpy `bitwise_and` 用于单个值。让我尝试将此位与运算符和函数用于两个数组。这意味着 arr1 中的单个元素与 arr2 执行二进制与运算,并返回 `bitwise_and` 结果。
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([2, 12, 9, 12, 17, 11])
print(arr1)
arr2 = np.array([14, 13, 65, 25, 42, 65])
print(arr2)
print('\nNumpy Bitwise and Operator Result = ', (arr1 & arr2))
print('Numpy bitwise_and Function Result = ', np.bitwise_and(arr1, arr2))
print()
x = np.random.randint(1, 20, size = (3, 7))
print(x)
y = np.random.randint(50, 125, size = (3, 7))
print(y)
print('\n---Numpy Bitwise and Operator Result---\n', (x & y))
print('---Numpy bitwise_and Function Result---\n ', np.bitwise_and(x, y))
位与运算输出
[ 2 12 9 12 17 11]
[14 13 65 25 42 65]
Numpy Bitwise and Operator Result = [ 2 12 1 8 0 1]
Numpy bitwise_and Function Result = [ 2 12 1 8 0 1]
[[18 1 11 10 5 14 6]
[13 6 3 14 3 7 6]
[10 14 18 12 4 19 6]]
[[121 86 73 98 73 96 82]
[ 72 119 113 103 110 65 120]
[ 55 77 75 72 59 64 113]]
---Numpy Bitwise and Operator Result---
[[16 0 9 2 1 0 2]
[ 8 6 1 6 2 1 0]
[ 2 12 2 8 0 0 0]]
---Numpy bitwise_and Function Result---
[[16 0 9 2 1 0 2]
[ 8 6 1 6 2 1 0]
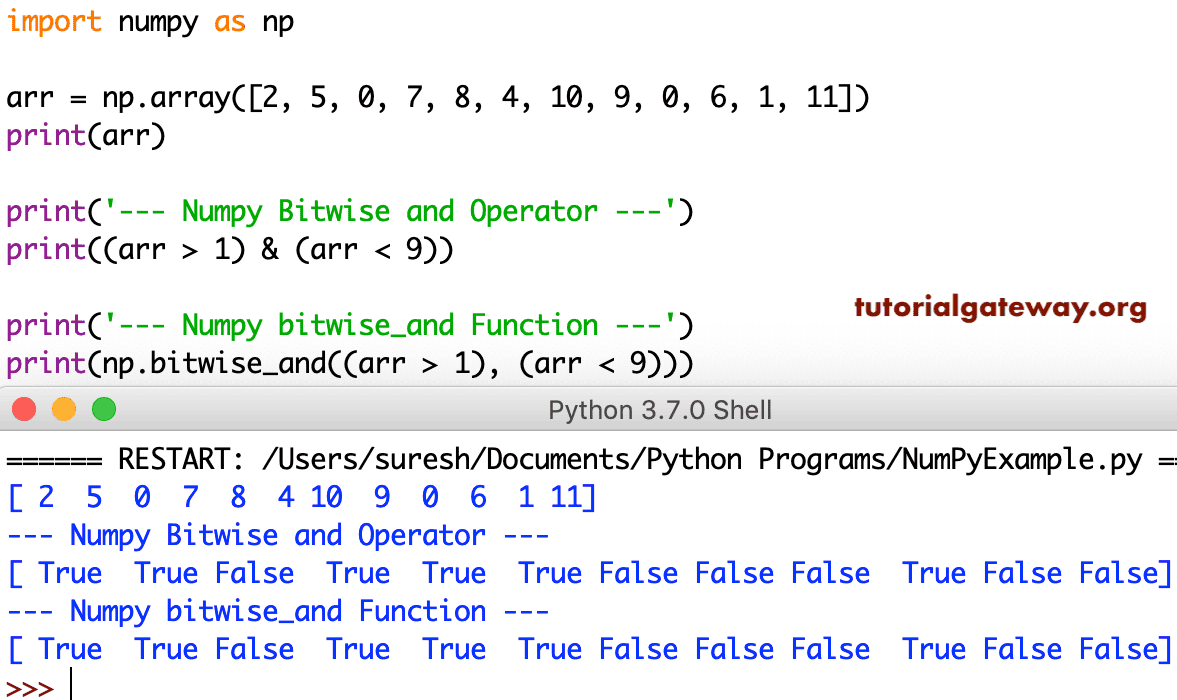
[ 2 12 2 8 0 0 0]]到目前为止,我们一直在使用 Numpy 位与运算执行位运算。但是,您也可以使用它们执行比较运算。让我使用此位与运算来检查该项是否大于 1 且小于 9。如果条件为 True,则返回 True,否则返回 False。
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([2, 5, 0, 7, 8, 4, 10, 9, 0, 6, 1, 11])
print(arr)
print('--- Numpy Bitwise and Operator ---')
print((arr > 1) & (arr < 9))
print('--- Numpy bitwise_and Function ---')
print(np.bitwise_and((arr > 1), (arr < 9)))
在这里,我们使用 `bitwise_and` 函数和位与运算符对多维数组执行比较。
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.randn(3, 5)
print(arr)
print('--- Two Dimensional Numpy Bitwise and Operator ---')
print((arr > 0) & (arr < 0.5))
print('--- Two Dimensional Numpy bitwise_and Function ---')
print(np.bitwise_and((arr > 0), (arr < 0.5)))
arr2 = np.random.randint(1, 25, size = (2, 2, 4))
print('--- Three Dimensional Random Array ---')
print(arr2)
print('--- Three Dimensional Numpy Bitwise and Operator ---')
print((arr2 > 5) & (arr2 < 20))
print('--- Three Dimensional Numpy bitwise_and Function ---')
print(np.bitwise_and((arr2 > 5), (arr2 < 20)))
位与运算输出
[[-0.49370172 0.36784164 -0.5634175 -1.52734428 1.97063201]
[ 0.33895941 -0.07471463 2.26536834 -1.80136643 -0.06620597]
[-0.20766583 0.38012599 -0.85149217 0.01983919 -1.45677273]]
--- Two Dimensional Numpy Bitwise and Operator ---
[[False True False False False]
[ True False False False False]
[False True False True False]]
--- Two Dimensional Numpy bitwise_and Function ---
[[False True False False False]
[ True False False False False]
[False True False True False]]
--- Three Dimensional Random Array ---
[[[24 21 24 23]
[10 11 7 13]]
[[17 19 13 20]
[ 5 24 4 16]]]
--- Three Dimensional Numpy Bitwise and Operator ---
[[[False False False False]
[ True True True True]]
[[ True True True False]
[False False False True]]]
--- Three Dimensional Numpy bitwise_and Function ---
[[[False False False False]
[ True True True True]]
[[ True True True False]
[False False False True]]]Python Numpy 位或运算符
Python Numpy 位或运算符和 `bitwise_or` 函数在两个位值都返回 False 时返回 False,否则返回 True。让我通过下面的程序向您展示位或运算的真值表。
import numpy as np
print('----Bitwise or operator Example----')
print('True | True = ', (True | True))
print('True | False = ', (True | False))
print('False | True = ', (False | True))
print('False | False = ', (False | False))
print('\n----bitwise_or Function Example----')
print('True bitwise_or True = ', np.bitwise_or(True, True))
print('True bitwise_or False = ', np.bitwise_or(True, False))
print('False bitwise_or True = ', np.bitwise_or(False, True))
print('False bitwise_or False = ', np.bitwise_or(False, False))
位或运算输出
----Bitwise or operator Example----
True | True = True
True | False = True
False | True = True
False | False = False
----bitwise_or Function Example----
True bitwise_or True = True
True bitwise_or False = True
False bitwise_or True = True
False bitwise_or False = False在这里,我们声明了两个整数变量,并对它们使用了位或运算符和 `bitwise_or`。正如我们已经知道的,12 = 00001100,25 = 00011001,所以 00001100 | 00011001 返回 00011101,即 29。
import numpy as np
a = 12
b = 25
print('Binary Value of 12 = ', np.binary_repr(a))
print('Binary Value of 25 = ', np.binary_repr(b))
print('Bitwise or Operator Result = ', a | b)
print('bitwise_or Function Result = ', np.bitwise_or(a, b))
Numpy 数组位或运算输出
Binary Value of 12 = 1100
Binary Value of 25 = 11001
Bitwise or Operator Result = 29
bitwise_or Function Result = 29在此示例中,我们在两个数组上使用 Numpy `bitwise_or` 函数和位或运算符。
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([2, 5, 0, 12, 8, 10])
print(arr1)
arr2 = np.array([12, 30, 6, 25, 12, 65])
print(arr2)
print('\nNumpy Bitwise or Operator Result = ', (arr1 | arr2))
print('Numpy bitwise_or Function Result = ', np.bitwise_or(arr1, arr2))
print()
x = np.random.randint(1, 15, size = (3, 5))
print(x)
y = np.random.randint(10, 25, size = (3, 5))
print(y)
print('\n---Numpy Bitwise or Operator Result---\n', (x | y))
print('---Numpy bitwise_or Function Result---\n ', np.bitwise_or(x, y))
Numpy 数组位或运算输出
[ 2 5 0 12 8 10]
[12 30 6 25 12 65]
Numpy Bitwise or Operator Result = [14 31 6 29 12 75]
Numpy bitwise_or Function Result = [14 31 6 29 12 75]
[[11 7 12 7 10]
[ 4 2 5 12 12]
[ 9 12 3 11 13]]
[[16 17 11 15 10]
[18 19 19 22 19]
[22 17 14 19 23]]
---Numpy Bitwise or Operator Result---
[[27 23 15 15 10]
[22 19 23 30 31]
[31 29 15 27 31]]
---Numpy bitwise_or Function Result---
[[27 23 15 15 10]
[22 19 23 30 31]
[31 29 15 27 31]]与位与运算类似,您也可以使用位或运算和 `bitwise_or` 函数来执行逻辑比较。让我使用此位或运算符来检查数组中的项是否小于 3 或大于 8。如果任一条件为 True,则返回 True,否则返回 False。
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([2, 5, 0, 7, 8, 4, 10, 9, 0, 6, 1, 11])
print(arr)
print('--- Numpy Bitwise or Operator ---')
print((arr < 3) | (arr > 8))
print('--- Numpy bitwise_or Function ---')
print(np.bitwise_or((arr < 3), (arr > 8)))
位或运算输出
[ 2 5 0 7 8 4 10 9 0 6 1 11]
--- Numpy Bitwise or Operator ---
[ True False True False False False True True True False True True]
--- Numpy bitwise_or Function ---
[ True False True False False False True True True False True True]在这里,我们使用 `bitwise_or` 和位或运算符对多维数组执行比较。
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.randn(3, 5)
print(arr)
print('--- Two Dimensional Numpy Bitwise or Operator ---')
print((arr < 0) | (arr > 1))
print('--- Two Dimensional Numpy bitwise_or Function ---')
print(np.bitwise_or((arr < 0), (arr > 1)))
arr2 = np.random.randint(1, 25, size = (2, 2, 4))
print('--- Three Dimensional Random Array ---')
print(arr2)
print('--- Three Dimensional Numpy Bitwise or Operator ---')
print((arr2 < 8) | (arr2 > 17))
print('--- Three Dimensional Numpy bitwise_or Function ---')
print(np.bitwise_or((arr2 < 8), (arr2 > 17)))
输出
[[ 1.04390004 0.66190755 0.27436456 -1.80262006 -0.263908 ]
[ 0.4266228 -0.08927048 0.48680432 -3.34951675 0.36628762]
[-1.41136647 -0.42538889 -1.88675276 -1.11568904 0.47588306]]
--- Two Dimensional Numpy Bitwise or Operator ---
[[ True False False True True]
[False True False True False]
[ True True True True False]]
--- Two Dimensional Numpy bitwise_or Function ---
[[ True False False True True]
[False True False True False]
[ True True True True False]]
--- Three Dimensional Random Array ---
[[[ 8 17 10 5]
[ 9 16 10 23]]
[[11 11 6 10]
[ 9 4 6 15]]]
--- Three Dimensional Numpy Bitwise or Operator ---
[[[False False False True]
[False False False True]]
[[False False True False]
[False True True False]]]
--- Three Dimensional Numpy bitwise_or Function ---
[[[False False False True]
[False False False True]]
[[False False True False]
[False True True False]]]Python Numpy 左移运算符
Python Numpy 位左移运算符将二进制数向左移动指定的位数。例如,a<<1 或 `left_shift(a, 1)` 将 12 转换为二进制值,然后向左移动一位。a = 00001100<<1 = 00011000 = 24。如果 a<<2,则为 00110000。
import numpy as np
a = 12
b = 25
print('Binary Value of 12 = ', np.binary_repr(a))
print('Binary Value of 25 = ', np.binary_repr(b))
print('\nLeft Shift Operator Result = ', a << 1)
print('left_shift Function Result = ', np.left_shift(a, 1))
print('\nLeft Shift Operator Result = ', b << 1)
print('left_shift Function Result = ', np.left_shift(b, 1))
左移输出
Binary Value of 12 = 1100
Binary Value of 25 = 11001
Left Shift Operator Result = 24
left_shift Function Result = 24
Left Shift Operator Result = 50
left_shift Function Result = 50在此示例中,我们在数组上使用 Numpy `left_shift` 函数和左移运算符。第一个语句 (arr1 << 1) 将对数组中的每一项执行二进制左移一位。第二个语句 (arr1 << arr2) 根据 arr2 的项执行左移。我的意思是,2 << 1、12 << 2、9 << 3、12 << 4、17 << 5、11 << 6
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([2, 12, 9, 12, 17, 11])
print(arr1)
arr2 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
print(arr2)
print('\nNumpy Left Shift Operator Result = ', (arr1 << 1))
print('Numpy left_shift Function Result = ', np.left_shift(arr1, 1))
print('\nNumpy Left Shift Operator Result = ', (arr1 << arr2))
print('Numpy left_shift Function Result = ', np.left_shift(arr1, arr2))
print()
x = np.random.randint(1, 20, size = (3, 7))
print(x)
y = np.random.randint(1, 5, size = (3, 7))
print(y)
print('\n---Numpy Left Shift Operator Result---\n', (x << y))
print('---Numpy left_shift Function Result---\n ', np.left_shift(x, y))
左移输出
[ 2 12 9 12 17 11]
[1 2 3 4 5 6]
Numpy Left Shift Operator Result = [ 4 24 18 24 34 22]
Numpy left_shift Function Result = [ 4 24 18 24 34 22]
Numpy Left Shift Operator Result = [ 4 48 72 192 544 704]
Numpy left_shift Function Result = [ 4 48 72 192 544 704]
[[ 3 13 18 14 5 4 2]
[13 14 7 9 7 6 4]
[ 8 13 4 3 18 4 8]]
[[2 3 1 3 4 2 1]
[2 2 3 2 2 2 1]
[4 2 2 2 4 3 4]]
---Numpy Left Shift Operator Result---
[[ 12 104 36 112 80 16 4]
[ 52 56 56 36 28 24 8]
[128 52 16 12 288 32 128]]
---Numpy left_shift Function Result---
[[ 12 104 36 112 80 16 4]
[ 52 56 56 36 28 24 8]
[128 52 16 12 288 32 128]]Python Numpy 右移
Python Numpy 位右移运算符将二进制数向右移动给定的位数。例如 b>>1 或 `right_shift(b, 1)` 将 25 转换为二进制值,然后向右移动一位。b>>1 = 00011001>>1 = 00001100 = 12。
import numpy as np
a = 12
b = 25
print('Binary Value of 12 = ', np.binary_repr(a))
print('Binary Value of 25 = ', np.binary_repr(b))
print('\nRight Shift Operator Result = ', a >> 1)
print('right_shift Function Result = ', np.right_shift(a, 1))
print('\nRight Shift Operator Result = ', b >> 1)
print('right_shift Function Result = ', np.right_shift(b, 1))
Numpy 数组右移输出
Binary Value of 12 = 1100
Binary Value of 25 = 11001
Right Shift Operator Result = 6
right_shift Function Result = 6
Right Shift Operator Result = 12
right_shift Function Result = 12在这里,我们在数组上使用 Numpy `right_shift` 函数和右移运算符。第一个 Numpy 语句 (arr1 >> 1) 对数组中的每一项执行二进制右移一位。第二个语句 (arr1 >> arr2) 根据 arr2 的项执行右移。我的意思是,2 >> 1、12 >> 2、9 >> 3、12 >> 4、17 >> 5、11 >> 6
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([2, 12, 9, 12, 17, 11])
print(arr1)
arr2 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
print(arr2)
print('\nNumpy right Shift Operator Result = ', (arr1 >> 1))
print('Numpy right_shift Function Result = ', np.right_shift(arr1, 1))
print('\nNumpy right Shift Operator Result = ', (arr1 >> arr2))
print('Numpy right_shift Function Result = ', np.right_shift(arr1, arr2))
print()
x = np.random.randint(1, 20, size = (3, 7))
print(x)
y = np.random.randint(1, 5, size = (3, 7))
print(y)
print('\n---Numpy right Shift Operator Result---\n', (x >> y))
print('---Numpy right_shift Function Result---\n ', np.right_shift(x, y))
Numpy 数组右移输出
[ 2 12 9 12 17 11]
[1 2 3 4 5 6]
Numpy right Shift Operator Result = [1 6 4 6 8 5]
Numpy right_shift Function Result = [1 6 4 6 8 5]
Numpy right Shift Operator Result = [1 3 1 0 0 0]
Numpy right_shift Function Result = [1 3 1 0 0 0]
[[11 12 12 12 2 12 4]
[ 1 14 14 14 17 12 2]
[12 11 10 12 2 9 11]]
[[3 3 1 1 3 3 3]
[4 4 4 1 2 4 4]
[1 3 1 2 4 3 1]]
---Numpy right Shift Operator Result---
[[1 1 6 6 0 1 0]
[0 0 0 7 4 0 0]
[6 1 5 3 0 1 5]]
---Numpy right_shift Function Result---
[[1 1 6 6 0 1 0]
[0 0 0 7 4 0 0]
[6 1 5 3 0 1 5]]Python Numpy 翻转
Python Numpy `invert` 函数与位非运算符相同。我们通过下面显示的 Python 示例来展示这一点。
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([10], dtype = np.uint8)
print(arr1)
print('Invert Value of arr1 = ', np.invert(arr1))
print('Binary Representation of arr1 = ', np.binary_repr(10, 8))
print('Binary Representation of x = ', np.binary_repr(245, 8))
arr2 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], dtype = np.uint8)
print(arr2)
print('Invert Value of arr1 = ', np.invert(arr2))
for x in arr2:
print('Binary Value of arr2 =', np.binary_repr(x, 8))
print('Binary Representation of 254 = ', np.binary_repr(254, 8))
print('Binary Representation of 253 = ', np.binary_repr(253, 8))
print('Binary Representation of 252 = ', np.binary_repr(252, 8))
print('Binary Representation of 251 = ', np.binary_repr(251, 8))
print('Binary Representation of 250 = ', np.binary_repr(250, 8))
print('Binary Representation of 249 = ', np.binary_repr(249, 8))
Python Numpy 数组翻转函数
[10]
Invert Value of arr1 = [245]
Binary Representation of arr1 = 00001010
Binary Representation of x = 11110101
[1 2 3 4 5 6]
Invert Value of arr1 = [254 253 252 251 250 249]
Binary Value of arr2 = 00000001
Binary Value of arr2 = 00000010
Binary Value of arr2 = 00000011
Binary Value of arr2 = 00000100
Binary Value of arr2 = 00000101
Binary Value of arr2 = 00000110
Binary Representation of 254 = 11111110
Binary Representation of 253 = 11111101
Binary Representation of 252 = 11111100
Binary Representation of 251 = 11111011
Binary Representation of 250 = 11111010
Binary Representation of 249 = 11111001