Python 的 math 库提供了各种函数和常量/属性,允许我们执行数学功能。与其他全局对象、属性和函数不同,Python math 库对象中的属性和函数是静态的。因此,我们可以像访问 pi 这样的数学属性和像 abs(number) 这样的函数。
Python math 对象属性
Python math 库模块中提供了属性或常量的列表。
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| math.e | 它返回欧拉数 e,约等于 2.71828 |
| math.pi | 它返回圆周率值,约等于 3.14 |
| math.inf | 此属性返回正无穷大。您可以使用 -math.INF 返回负无穷大。 |
| math.nan | 它返回“非数字”作为输出。 |
Python 数学函数
Python 数学函数列表可在 math 库中找到。请点击以下链接查看可用方法的教程。
| Python 数学函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ceil(x) | 它返回大于或等于指定表达式或数字的最小整数。 |
| copysign(x) | 此函数查找第一个参数的绝对值。它返回绝对值和第二个参数中指定的符号。 |
| fabs(x) | 给定数字的绝对值 |
| factorial(x) | 它查找指定表达式或特定数字的阶乘。 |
| floor(x) | 小于或等于指定数字的最大整数值。 |
| fmod(x, y) | 此 Python math 函数计算指定给定参数的模数。 |
| frexp(x) | 它以对 (m, e) 的形式返回 x 的尾数和指数,其中 m 是浮点值,e 是整数值。 |
| fsum(Iterable) | 计算并返回迭代器(元组和列表)的总和 |
| gcd(x, y) | 此函数返回两个给定参数的最大公约数。 |
| isclose(x, y) | 如果两个参数彼此接近,则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE |
| isfinite(x) | 用于检查给定数字/表达式既不是无穷大(正或负)也不是 NaN。如果给定数字既不是无穷大也不是 NaN(非数字),则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE。 |
| isinf(x) | 检查给定数字是否为无穷大(正或负)。如果数字是无穷大,则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE |
| isnan(x) | 此数学函数检查给定数字是否为 NaN(非数字)。如果给定数字是 NaN,则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE |
| round(x) | 它是一个常规函数(不是 Math 模块函数)。它将指定的表达式或特定数字四舍五入到最接近的整数。 |
| ldexp(x, i) | 此内置方法返回 x * (2**i)。它也被称为 frexp 方法的逆。 |
| modf(x) | 将给定值分为两个参数:分数部分作为第一个参数,整数值作为第二个参数。 |
| trunc(x) | 从指定表达式中删除小数位并返回整数值 |
Python math 幂和对数函数
以下是 math 库中可用的幂和对数函数列表。
| 幂和对数方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| exp(x) | 它计算 E 的幂,其中 E 是欧拉数,约等于 2.71828。 |
| expm1(x) | 它计算 E 的幂(其中 E 是欧拉数,约等于 2.71828)并从中减去一。 |
| log(x, base) | 此幂和对数函数查找以 E 为底的数字的对数值。 |
| log2(x) | 以 E 为底的数字的对数值。 |
| log10(x) | 以 E 为底的给定数字的对数值。 |
| pow(x) | 此幂和对数函数计算指定表达式的幂 |
| sqrt(x) | 指定的 Python 表达式或单个数字的平方根 |
Python 三角函数
以下是 math 库中可用的三角函数列表。
| 三角方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| acos(x) | 它返回给定数字的反余弦值 |
| asin(x) | 此三角函数返回给定数字的反正弦值 |
| atan(x) | 数字的反正切值 |
| atan2(y, x) | 它返回从 X 轴到指定点 (y, x) 的角度(以弧度为单位)。 |
| cos(x) | 此三角函数返回数字的余弦值 |
| hypot(x, y) | 它根据指定索引从字符串中提取字符 |
| sin(x) | 给定数字的正弦值 |
| tan(x) | 给定数字的正切值 |
Python 双曲函数
双曲三角函数允许我们对双曲线而不是圆执行以下数学函数。
| 双曲方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| acosh(x) | 它返回给定数字的双曲反余弦(反双曲余弦)值 |
| asinh(x) | 此双曲函数返回给定数字的双曲反正弦(反双曲正弦)值 |
| atanh(x) | 给定数字的双曲反正切(反双曲正切)值 |
| cosh(x) | 给定数字的双曲余弦值 |
| sinh(x) | 它返回给定数字的双曲正弦值 |
| tanh(x) | 给定数字的双曲正切值 |
Python 角度数学函数
以下是 math 库中可用的角度函数列表。
| 角度方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| degrees(x) | 它将指定的角度从弧度转换为度数。 |
| radians(x) | 此角度函数将指定的角度从度数转换为弧度。 |
Python 特殊数学函数
以下是 math 库中可用的特殊函数列表。
| 特殊 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| erf(x) | 它返回指定值处的误差。 |
| erfc(x) | 此特殊函数返回互补误差函数。或者我们可以简单地说,1 – erf(x) |
| gamma(x) | 它返回指定值处的 Gamma。 |
| lgamma(x) | 此特殊函数返回指定值处 Gamma 函数的自然对数。 |
Python math 函数示例
以下示例帮助您理解这些数学函数。
常量示例
在此常量示例中,我们使用 math 库中可用的常量列表。它们是 pi、e、tau、inf 和 nan。
import math as td
print('pi Constant - Pi = ', td.pi)
print('pi Constant - Degrees of Pi = ', td.degrees(td.pi))
print('\ne Constant - e = ', td.pi)
print('e Constant - Degrees of e = ', td.degrees(td.e))
print('\ntau Constant - tau = ', td.tau)
print('tau Constant - Degrees of tau = ', td.degrees(td.tau))
print('\ninf Constant - Positive Infinity = ', td.inf)
print('inf Constant - Negative Infinity = ', -td.inf)
print('\nNaN Constant - Not a Number = ', td.nan)
pi Constant - Pi = 3.141592653589793
pi Constant - Degrees of Pi = 180.0
e Constant - e = 3.141592653589793
e Constant - Degrees of e = 155.74607629780772
tau Constant - tau = 6.283185307179586
tau Constant - Degrees of tau = 360.0
inf Constant - Positive Infinity = inf
inf Constant - Negative Infinity = -inf
NaN Constant - Not a Number = nanPython math 函数 – fabs、ceil、floor、factorial
在此示例中,我们将使用 fabs 查找绝对值,并使用 copysign 更改符号。接下来,我们使用 ceil 和 floor 查找天花板值和地板值。在最后一条语句中,我们使用 factorial 函数查找给定值的阶乘。
import math as mh
x = 10.98
y = 30.22
z = -40.95
print('FABS - Absolute Value of z = ', mh.fabs(z))
print('FABS - Absolute Value of -124.897 = ', mh.fabs(-124.897))
print('\ncopysign of x, z = ', mh.copysign(x, z))
print('copysign of z, x = ', mh.copysign(z, x))
print('\nCEIL - Ceiling of x = ', mh.ceil(x))
print('CEIL - Ceiling of y = ', mh.ceil(y))
print('\nFLOOR - Floor of x = ', mh.floor(x))
print('FLOOR - Floor of y = ', mh.floor(y))
print('\nFactorial of 3 = ', mh.factorial(3))
print('Factorial of 5 = ', mh.factorial(5))
FABS - Absolute Value of z = 40.95
FABS - Absolute Value of -124.897 = 124.897
copysign of x, z = -10.98
copysign of z, x = 40.95
CEIL - Ceiling of x = 11
CEIL - Ceiling of y = 31
FLOOR - Floor of x = 10
FLOOR - Floor of y = 30
Factorial of 3 = 6
Factorial of 5 = 120Python math 函数 – fmod、frexp、fsum、gcd
在此示例中,我们使用了 fmod、frexp、fsum 和 gcd,并带有不同的值。
import math as gm
print('FMOD - Mod of 2 and 3 = ', gm.fmod(2, 3))
print('FMOD - Mod of 225.55 and 5.5 = ', gm.fmod(222.55, 5.5))
print('\nFREXP - Mantissa and Exponent Value of 5 = ', gm.frexp(5))
print('FREXP - Mantissa and Exponent Value of -9 = ', gm.frexp(-9))
print('\nFSUM - Sum of Tuple Items = ', gm.fsum((10, 20, 30, 40)))
print('FSUM - Sum of List Items = ', gm.fsum([5, 22, 35, 9]))
print('\nGCD of two 10 and 2 = ', gm.gcd(10, 2))
print('GCD of two 100 and 15 = ', gm.gcd(100, 15))
FMOD - Mod of 2 and 3 = 2.0
FMOD - Mod of 225.55 and 5.5 = 2.5500000000000114
FREXP - Mantissa and Exponent Value of 5 = (0.625, 3)
FREXP - Mantissa and Exponent Value of -9 = (-0.5625, 4)
FSUM - Sum of Tuple Items = 100.0
FSUM - Sum of List Items = 71.0
GCD of two 10 and 2 = 2
GCD of two 100 and 15 = 5Python math 函数 – round、ldexp、modf、trunc、remainder
在此数学函数示例中,我们使用了 round、ldexp、mode、trunc 和 remainder。
import math as at
print('ROUND - Rounded Number 100.98763 = ', round(100.9876, 2))
print('ROUND - Rounded Number 125.932832 = ', round(125.932832, 3))
print('\nLDEXP - LDEXP (FREXP inverse) Number of 4, 5 = ', at.ldexp(4, 5))
print('LDEXP - LDEXP (FREXP inverse) Number of -9, 2 = ', at.ldexp(-9, 2))
print('\nMODF - Modf (Divided 1 to 2) Number of 100 = ', at.modf(100))
print('MODF - Modf (Divided 1 to 2) Number of 120.98 = ', at.modf(120.98))
print('\nTRUNC - Truncated Number 100.98763 = ', at.trunc(100.9876))
print('ROUND - Truncated Number 125.932832 = ', at.trunc(-125.932832))
print('\nRemainder of 29 and 5 = ', at.remainder(20, 5))
print('Remainder of 10 and 3 = ', at.remainder(10, 3))
ROUND - Rounded Number 100.98763 = 100.99
ROUND - Rounded Number 125.932832 = 125.933
LDEXP - LDEXP (FREXP inverse) Number of 4, 5 = 128.0
LDEXP - LDEXP (FREXP inverse) Number of -9, 2 = -36.0
MODF - Modf (Divided 1 to 2) Number of 100 = (0.0, 100.0)
MODF - Modf (Divided 1 to 2) Number of 120.98 = (0.980000000000004, 120.0)
TRUNC - Truncated Number 100.98763 = 100
ROUND - Truncated Number 125.932832 = -125
Remainder of 29 and 5 = 0.0
Remainder of 10 and 3 = 1.0对数函数示例
在此 Python 对数函数示例中,我们使用 math exp、expm1 来获取 exp 值。接下来,我们使用 log、log2 和 log10 来获取自然对数值、以 2 为底的对数值和以 10 为底的对数值。然后我们使用 pow 查找 x 的 y 次方和 sqrt 查找数字的平方根。
import math as th
print('exp of 5 = ', th.exp(5))
print('exp of -3 = ', th.exp(-3))
print('\nexpm1 of 8 = ', th.expm1(8))
print('expm1 of -5 = ', th.expm1(-5))
print('\nLOG - logarithmic of 5 = ', th.log(5))
print('LOG - logarithmic of 100 Base 2 = ', th.log(100, 2))
print('\nLOG2 - logarithmic of 120 Base 2 = ', th.log2(120))
print('\nLOG10 - logarithmic of 150 Base 10 = ', th.log2(150))
print('\nPOW - 2 Power 3 = ', th.pow(2, 3))
print('POW - 5 Power 4 = ', th.pow(5, 4))
print('\nSQRT - Square Root of 25 = ', th.sqrt(25))
print('SQRT - Square Root of 19 = ', th.sqrt(19))
exp of 5 = 148.4131591025766
exp of -3 = 0.049787068367863944
expm1 of 8 = 2979.9579870417283
expm1 of -5 = -0.9932620530009145
LOG - logarithmic of 5 = 1.6094379124341003
LOG - logarithmic of 100 Base 2 = 6.643856189774725
LOG2 - logarithmic of 120 Base 2 = 6.906890595608519
LOG10 - logarithmic of 150 Base 10 = 7.22881869049588
POW - 2 Power 3 = 8.0
POW - 5 Power 4 = 625.0
SQRT - Square Root of 25 = 5.0
SQRT - Square Root of 19 = 4.358898943540674三角函数 cos、sin、tan、acos、asin、atan、atan2、hypot
在此 Python 三角函数示例中,我们将使用 sin、cos 和 tan 查找正弦、余弦和正切值。接下来,我们使用 acos、asin、atan 和 atan2 查找反余弦、反正弦和反正切值。在最后一条语句中,我们使用了 hypot
import math as mt
print('COS - Cosine of 10 = ', mt.cos(10))
print('COS - Cosine of -15 = ', mt.cos(-15))
print('\nSIN - Sine of 3 = ', mt.sin(3))
print('SIN - Sine of -5 = ', mt.sin(-5))
print('\nTAN - Tangent of 9 = ', mt.tan(9))
print('TAN - Tangent of -3 = ', mt.tan(-3))
print('\nACOS - Arc Cosine of 1 = ', mt.acos(1))
print('ACOS - Arc Cosine of -0.78 = ', mt.acos(-0.78))
print('\nASIN - Arc Sine of 1 = ', mt.asin(1))
print('ASIN - Arc Sine of -2 = ', mt.asin(-0.42))
print('\nATAN - Arc Tangent of 0.72 = ', mt.atan(0.72))
print('ATAN - Arc Tangent of -2.71 = ', mt.atan(-2.71))
print('\nATAN2 - Tangent of 2, 5 = ', mt.atan2(2, 5))
print('\nHYPOT - Hypot Value of 2, 3 = ', mt.hypot(2, 3))
COS - Cosine of 10 = -0.8390715290764524
COS - Cosine of -15 = -0.7596879128588212
SIN - Sine of 3 = 0.1411200080598672
SIN - Sine of -5 = 0.9589242746631385
TAN - Tangent of 9 = -0.4523156594418099
TAN - Tangent of -3 = 0.1425465430742778
ACOS - Arc Cosine of 1 = 0.0
ACOS - Arc Cosine of -0.78 = 2.4654621440291318
ASIN - Arc Sine of 1 = 1.5707963267948966
ASIN - Arc Sine of -2 = -0.43344532006988595
ATAN - Arc Tangent of 0.72 = 0.6240230529767569
ATAN - Arc Tangent of -2.71 = -1.2172930308235297
ATAN2 - Tangent of 2, 5 = 0.3805063771123649
HYPOT - Hypot Value of 2, 3 = 3.6055512754639896Python math 三角函数 cosh、sinh、tanh、acosh、asinh、atanh
在此数学示例中,我们使用双曲三角函数。首先,我们使用 cosh、sinh 和 tanh 查找双曲余弦、正弦和正切值。接下来,acosh、asinh 和 atanh 查找双曲反余弦、反正弦和双曲反正切值。
import math as ma
print('COSH - Hyperbolic Cosine of 2 = ', ma.cosh(2))
print('COSH - Hyperbolic Cosine of -1 = ', ma.cosh(-1))
print('\nSINH - Hyperbolic Sine of 3 = ', ma.sinh(3))
print('SINH - Hyperbolic Sine of -5 = ', ma.sinh(-5))
print('\nTANH - Hyperbolic Tangent of 1 = ', ma.tanh(1))
print('TANH - Hyperbolic Tangent of -3 = ', ma.tanh(-3))
print('\nACOSH - Hyperbolic Arc Cosine of 10 = ', ma.acosh(10))
print('ACOSH - Hyperbolic Arc Cosine of 30.78 = ', ma.acosh(30.78))
print('\nASINH - Hyperbolic Arc Sine of 15 = ', ma.asinh(15))
print('ASINH - Hyperbolic Arc Sine of -25 = ', ma.asinh(-25))
print('\nATANH - Hyperbolic Arc Tangent of 0.57 = ', ma.atanh(0.57))
print('ATANH - Hyperbolic Arc Tangent of -0.71 = ', ma.atanh(-0.71))
COSH - Hyperbolic Cosine of 2 = 3.7621956910836314
COSH - Hyperbolic Cosine of -1 = 1.5430806348152437
SINH - Hyperbolic Sine of 3 = 10.017874927409903
SINH - Hyperbolic Sine of -5 = -74.20321057778875
TANH - Hyperbolic Tangent of 1 = 0.7615941559557649
TANH - Hyperbolic Tangent of -3 = -0.9950547536867305
ACOSH - Hyperbolic Arc Cosine of 10 = 2.993222846126381
ACOSH - Hyperbolic Arc Cosine of 30.78 = 4.119748326708938
ASINH - Hyperbolic Arc Sine of 15 = 3.4023066454805946
ASINH - Hyperbolic Arc Sine of -25 = -3.9124227656412556
ATANH - Hyperbolic Arc Tangent of 0.57 = 0.6475228448273728
ATANH - Hyperbolic Arc Tangent of -0.71 = -0.8871838632580928角度和特殊函数 – degrees、radians、gamma
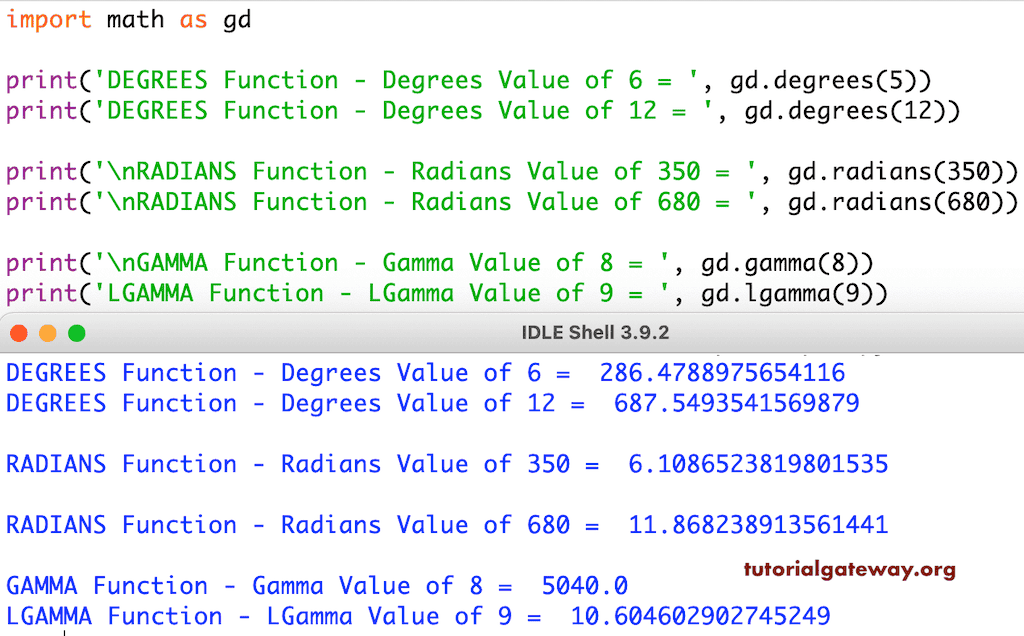
在此 Python math 角度函数示例中,我们使用 degrees 和 radians 将度数转换为弧度,反之亦然。接下来,我们使用 gamma 和 lgamma 返回 gamma 值。
import math as gd
print('DEGREES Function - Degrees Value of 6 = ', gd.degrees(5))
print('DEGREES Function - Degrees Value of 12 = ', gd.degrees(12))
print('\nRADIANS Function - Radians Value of 350 = ', gd.radians(350))
print('\nRADIANS Function - Radians Value of 680 = ', gd.radians(680))
print('\nGAMMA Function - Gamma Value of 8 = ', gd.gamma(8))
print('LGAMMA Function - LGamma Value of 9 = ', gd.lgamma(9))