Python 支持文件处理。我的意思是,Python 编程语言提供了各种函数,允许我们创建文件、打开文件、读取数据和向文件写入数据。
与其他语言不同,Python 编程语言处理文件的方式不同。它根据数据将文件视为文本或二进制,并且每行必须以行尾字符(如换行符、逗号等)终止。
它提供了一个重要的函数 `open` 来处理文件。`File open` 函数接受两个参数:`file_name` 和 `mode`。此文件 `open` 函数的语法是
f_open = open(“File_Name”, “mode”)
在上面的 Python 文件处理语法中,`mode` 是一个可选参数。打开文件有四种不同的模式。
- r – 表示读取模式,是打开文件的默认模式。它打开一个现有文件进行读取,如果没有这样的文档,则会抛出错误。
- r+ – 这是用于读写模式。
- a – 表示追加。如果文件存在,它会打开该文件并将数据追加到现有内容。如果文件不存在,它会创建一个指定名称的新文件。
- w – 表示写入模式。它以写入模式打开文件以进行处理,并用新内容覆盖现有内容。如果文件不存在,它会创建一个新文件。
- x – 用于创建新文件。如果文件已存在,则会抛出错误。
- 除了这些模式,你还可以指定文件必须处理的数据类型。我的意思是二进制数据或文本模式。
- t – 文本模式,是默认模式。
- b – 二进制模式。
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt")
上面的文件处理代码等同于 `f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "rt")`
Python 文件操作示例
以下示例列表有助于创建新文件、打开、重命名和删除文件。接下来,向其中写入文本、关闭、追加、写入和读取可用选项。为了演示大多数这些文件方法,包括读写,我们使用下面的 txt 文本示例。
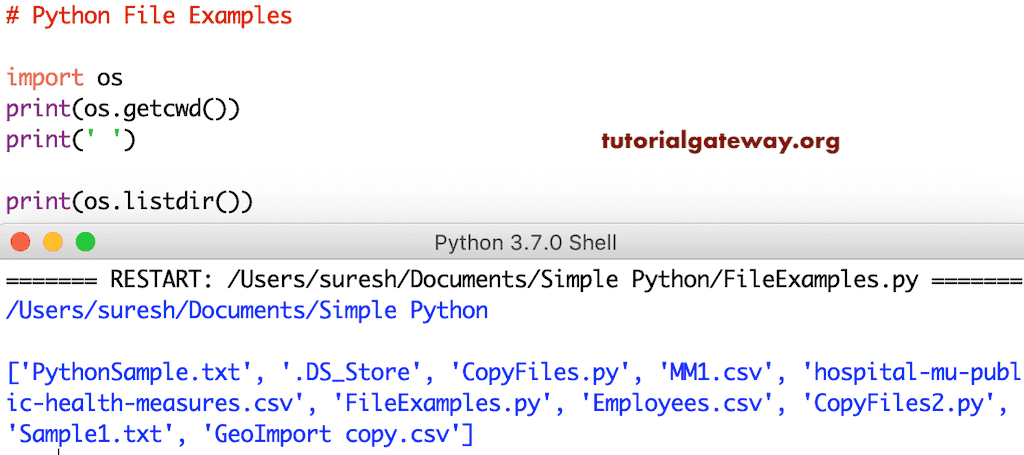
Python `listdir` 函数显示当前目录中的所有文件
在这种语言中,你可以通过指定名称或完整路径来打开文件。完整名称会在当前工作目录中打开文件。但是,你可以使用任何目录中的完整路径访问文档。在我们开始之前,让我使用 `listdir` 函数获取当前目录中的列表。
import os
print(os.getcwd())
print(' ')
print(os.listdir())
打开文件
你可以在这种编程语言中通过指定名称或完整路径来打开文件。
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt")
或者使用完整路径
f_open = open("C:/users/Document/PythonSample.txt")
Python 读取文件
文件读取函数用于读取文件内部的数据。这是一个简单的 Python 示例,它以读取模式打开一个示例 txt。接下来,我们使用 `read` 函数读取该 txt 内的数据。
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_open.read())
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python Tutorial
Welcome to Tutorial Gateway
File Examples
带参数的文件读取函数
在处理字符串数据时,你可以使用带参数的文件读取函数来限制它返回的字符数。例如,`read(5)` 读取前五个字符,或者 `read(10)` 读取前 10 个字符。
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_open.read(5))
print(f_open.read(2))
读取所需字符输出
Hello
Wo第一个 `read` 语句打印前五个字符。接下来,`read` 打印接下来的两个。如果你想打印前 10 个,那么你必须关闭并重新打开它。
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_open.read(5))
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_open.read(8))
Hello
HelloWor使用 For 循环读取 Python 文件
你还可以使用循环按顺序读取所有数据。例如,下面的示例使用 For 循环 读取此 txt 中可用的每一行。
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
for char in f_open:
print(char)
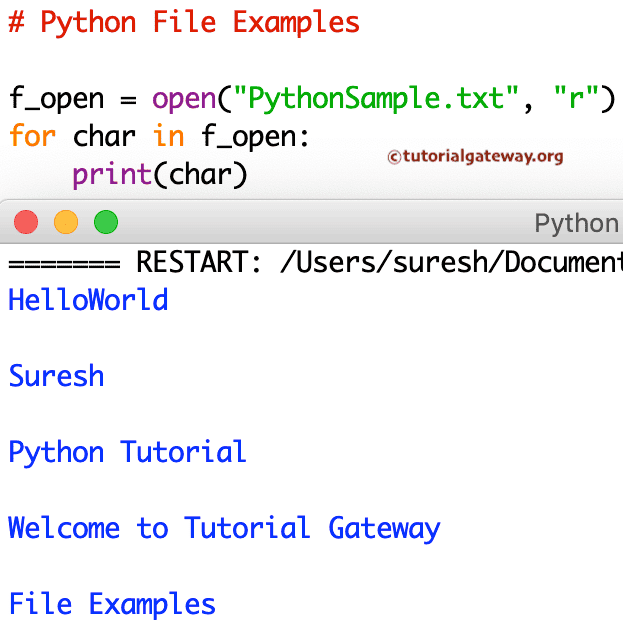
在此文件读取示例中,`for` 循环遍历示例文本中的完整文本并打印每一行。
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
for line in f_open:
print(line, end = '')
For 循环读取已打开的文件。
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python Tutorial
Welcome to Tutorial Gateway
File Examples
Python 文件 `readline` 函数
`readline` 函数读取行尾字符之前的完整行。此示例打开一个文件并从中读取第一行。
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readline())
HelloWorld
>>> 如果你想读取两行,那么调用 `readline` 函数两次,依此类推。让我打印三行。
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readline())
print(f_sample.readline())
print(f_sample.readline())
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python Tutorial你可以使用此 `readline` 函数读取或打印所需的行。下面的 `readline` 函数代码从文本文件中打印第二行。如果你将 `readline` 函数与参数一起使用,那么它的行为与带参数的 `read` 函数相同。我的意思是,`readline(2) = read(2)`
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readline(2))
print()
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.read(2))
文件 `readline` 与 `read` 函数输出
He
He使用 `readlines` 函数读取文件
在这种语言中,我们还有一个名为 `readlines()` 的函数。它从给定文本中读取数据,并以列表格式打印所有数据。它用适当的分隔符分隔每一行。
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readlines())
['HelloWorld\n', 'Suresh\n', 'Python Tutorial\n', 'Welcome to Tutorial Gateway\n', 'File Examples\n']Python 关闭文件函数
关闭文件函数关闭一个已经打开的文件。尽管它有一个垃圾收集器来关闭它们,但你不应该完全依赖它。始终关闭打开的文件是一个好习惯。在这里,我们打开它,读取一行,然后关闭它。
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readline())
f_sample.close()
HelloWorld
让我从那个已关闭的 txt 中打印另一行。
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readline())
f_sample.close()
print(f_sample.readline())
你可以注意到 shell 抛出的错误。
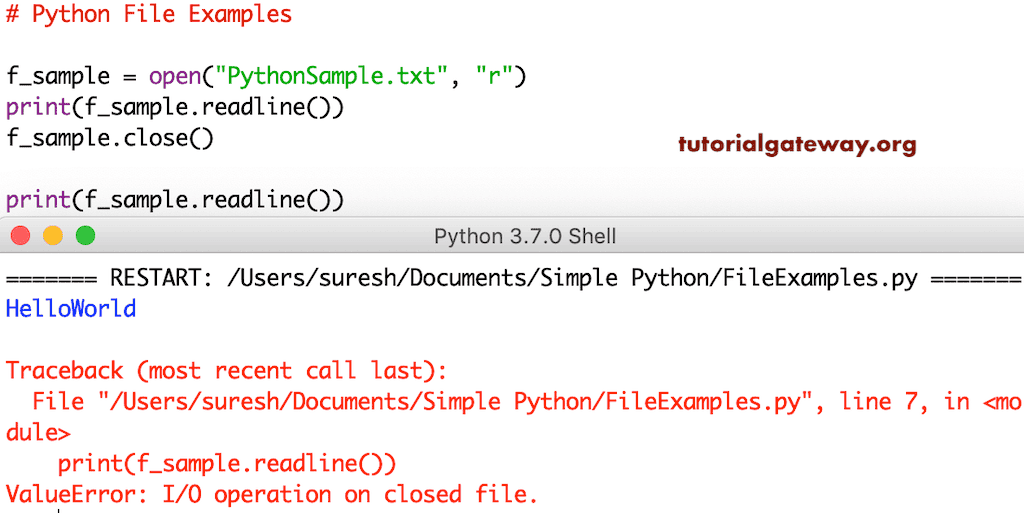
上面的程序显示了 `close` 方法的使用。但是,不建议使用我们上面展示的方式。
在实际操作中,你必须使用 `with` 语句来正确关闭打开的文件。或者,有些人说,我们可以使用 `try finally` 块。我们将向你展示这两种方法。
在 Python 文件操作中使用 `try finally`
try:
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.read())
finally:
f_sample.close()
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python Tutorial
Welcome to Tutorial Gateway
File Examples文件 `with` 语句
`with` 语句确保此语句打开的每个文件都已关闭,无论是否存在错误。
with open("PythonSample.txt", "r") as f_sample:
print(f_sample.read())
f_sample.close()
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python Tutorial
Welcome to Tutorial Gateway
File Examples`with` 语句不只是关闭文件对象。你可以使用此 `with` 语句以任何模式打开文件。我的意思是,你可以使用它来读取数据、写入数据等。
最重要的是,我们在需要执行多个语句的操作中使用它。此语句将它们保存在一个块中,以便我们可以在该块中编写多个语句,例如读取和写入文件。
with open("PythonSample.txt", "w") as f_sample:
f_sample.write("First Line")
f_sample.close()
with open("PythonSample.txt", "r") as f_sample:
print(f_sample.read())
f_sample.close()
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python Tutorial
Welcome to Tutorial Gateway
File Examples
>>>Python 写入文件
它提供了 `write` 方法来向文件写入内容或数据。在我们进入 `write` 函数示例之前,我假设你还记得我之前说过的。你必须使用追加模式的 `a` 或写入模式的 `w`。
此示例以写入模式打开示例文本并写入欢迎消息。接下来,我们打开它以打印数据。
f_demo = open("PythonSample.txt", "w")
f_demo. write("Welcome to Tutorial gateway")
f_demo.close()
# Let me open and check
f_demo = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_demo.read())
Welcome to Tutorial gateway这次,我们使用 `write` 方法写入多行代码。
f_writedemo = open("PythonSample.txt", "w")
f_writedemo. write("Python")
f_writedemo. write("\nTutorial gateway")
f_writedemo. write("\nHappy Coding!")
f_writedemo. write("\nHi \nHello \nCheers")
f_writedemo.close()
# Let me open it and check
f_writedemo = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_writedemo.read())
Python
Tutorial gateway
Happy Coding!
Hi
Hello
Cheers
>>>我们从一开始就一直在处理这个 txt。然而,这个 `write` 函数删除了所有内容并返回了这个欢迎消息。
`write` 方法接受一个列表作为参数,因此你可以一次性写入列表中的项目。我的意思是,无需使用多个 `write` 函数。
f_writelinesdemo = open("PythonSample.txt", "w")
text = ["First Line\n", "Second Line\n", "Third Line\n", "Fourth Line"]
f_writelinesdemo. writelines(text)
f_writelinesdemo.close()
# Let me open and check
f_writelinesdemo = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_writelinesdemo.read())
First Line
Second Line
Third Line
Fourth Line
>>>追加文件
我们正在以追加模式打开文件,并检查写入 hello 消息后会发生什么。
f_demo = open("PythonSample.txt", "a")
f_demo. write("\nHell World!")
f_demo.close()
# Let me open the file and check
f_demo = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_demo.read())
First Line
Second Line
Third Line
Fourth Line
Hell World!
>>>如何使用 Python 中的 For 循环写入文件?
你还可以使用 `for` 循环写入多行信息。在这里,我们以示例方式在 Sample10 文本中写入 10 行。
f_loopdemo = open("Sample10.txt", "w")
for i in range(1, 11):
f_loopdemo.write("This is the %d Line\n" %(i))
f_loopdemo.close()
# Let me open the file and check
f_loopdemo = open("Sample10.txt", "r")
print(f_loopdemo.read())
使用 for 循环写入文件输出
This is the 1 Line
This is the 2 Line
This is the 3 Line
This is the 4 Line
This is the 5 Line
This is the 6 Line
This is the 7 Line
This is the 8 Line
This is the 9 Line
This is the 10 Line
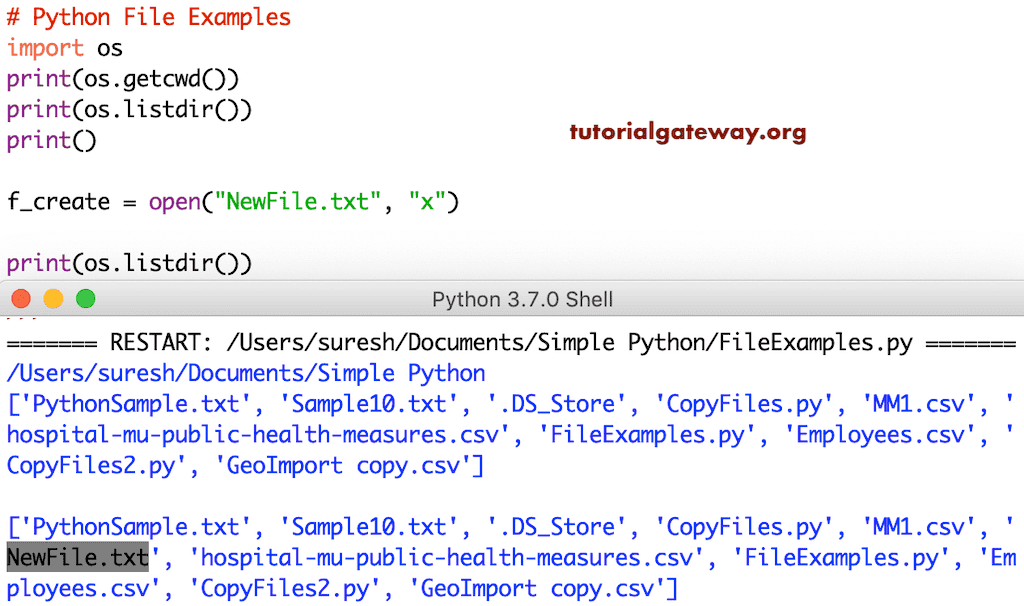
在 Python 中创建新文件
到目前为止,我们一直在使用现有文件。但是,你可以使用读取方法创建自己的文件。为此,你必须使用 `x` 来创建新文件,或者使用 `a` 模式,或者使用 `w` 模式。这三种模式都会创建一个新文件,但最后两种有所不同。
f_create = open("NewFile.txt", "x")
让我创建另一个文件并向其中写入一些内容。这样,你就可以看到新文件和文本。这个程序创建了一个 Sample1 文本文件,写入一个字符串,然后关闭它。接下来,我们以读取模式打开该文件并从中打印数据。
f_create = open("Sample1.txt", "x")
f_create.write("Python Program")
f_create.close()
# Open the Sample1 file
f_create = open("Sample1.txt", "r")
print(f_create.read())
它使用 `w` 作为写入模式来创建一个新文件并向其中写入一些内容。
f_wcreate = open("Sample2.txt", "x")
f_wcreate.write("Python Tutorial")
f_wcreate.close()
# Open the Sample1
f_wcreate = open("Sample2.txt", "r")
print(f_wcreate.read())
Python Tutorial
>>>`open` 函数与 `a` 模式 – 追加模式。
f_acreate = open("Sample3.txt", "x")
f_acreate.write("Tutorial Gateway")
f_acreate.close()
# Open the Sample1
f_acreate = open("Sample3.txt", "r")
print(f_acreate.read())
Tutorial Gateway
>>>如何在 Python 中重命名文件?
你必须导入 `os` 模块才能重命名目录中的文件。在 `os` 模块中,我们有一个函数可以帮助我们重命名目录中已有的文件。
让我使用这种编程语言中的文件重命名函数将 Sample2.txt 重命名为 NewSample.txt。接下来,我们打开重命名后的文件以查看其中的数据。
import os
os.rename("Sample2.txt", "NewSample.txt")
f_sample = open("NewSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.read())
Python Tutorial
>>>如何在 Python 中删除文件?
要删除文件,你必须导入 `os` 模块。在 `os` 模块中,我们有一个 `remove` 函数,可以帮助我们从 目录 中删除文件。让我使用此文件 `remove` 函数来删除我们之前创建的 Sample3.txt。
import os
os.remove("Sample3.txt")

它运行得很完美;但是,如果你尝试删除一个不存在的文件,它会抛出错误。让我删除我们之前删除的 Sample3.txt。
当你运行时,它会抛出错误:`FileNotFoundError:[Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'Sample3.txt'`。为了避免这类错误,建议检查文件是否存在。
import os
if os.path.exists("Sample3.txt"):
os.remove("Sample3.txt")
else:
print("Hey! No such file exists")
Hey! No such file exists
>>>Python 文件 `seek` 和 `tell` 函数
这是查找指针位置的两个函数。
- tell():它告诉你当前指针位置。
- seek():将指针位置设置到特定位置。
with open("PythonSample.txt", "r") as f_sample:
print("Pointer Initial Position : ", f_sample.tell())
print(f_sample.read())
print("Current Pointer Position : ", f_sample.tell())
f_sample.seek(22)
print("\n Current File Position : ", f_sample.tell())
f_sample.close()
Pointer Initial Position : 0
First Line
Second Line
Third Line
Fourth Line
Hell World!
Current Pointer Position : 57
Current File Position : 22
>>>文件属性
这种编程语言提供了以下文件属性来获取你正在处理的文件的信息。
- name:它返回文件的名称。
- mode:你以什么模式打开?例如,r 模式,w 模式等。
- closed:如果给定的文件已关闭,则返回 `True`,否则返回 `False`。
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_open.read())
print('\nName = ', f_open.name)
print('Mode = ', f_open.mode)
print('closed? = ', f_open.closed)
f_open.close()
print('\closed? = ', f_open.closed)
Pointer Initial Position : 0
First Line
Second Line
Third Line
Fourth Line
Hell World!
Name = PythonSample.txt
Mode = r
closed? = False
closed? = True
>>>