Python 赋值运算符便于为声明的变量赋值。等号 (=) 是任何编程语言中最常用的赋值运算符。例如:
i = 10
Python 语言中可用的赋值运算符列表。
| 赋值运算符 | 示例 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| = | x = 25 | 将值25赋给x |
| += | x += 25 | 这与 x = x + 25 相同 |
| -= | x -= 25 | 与 x = x - 25 相同 |
| *= | x *= 25 | 这与 x = x * 25 相同 |
| /= | x /= 25 | 与 x = x / 25 相同 |
| %= | x %= 25 | 这与 x = x % 25 相同 |
| //= | x //= 25 | 与 x = x // 25 相同 |
| **= | x **= 25 | 这与 x = x ** 25 相同 |
| &= | x &= 25 | 这与 x = x & 25 相同 |
| |= | x |= 25 | 这与 x = x | 25 相同 |
| ^= | x ^= 25 | 与 x = x ^ 25 相同 |
| <<= | x <<= 25 | 这与 x = x << 25 相同 |
| >>= | x >>= 25 | 与 x = x >> 25 相同 |
Python 赋值运算符示例
在此示例中,我们使用四个变量:a、Total、x 和 y;它们的值分别为 7、21、9 和 65。接下来,我们使用它们来展示所有赋值运算符的工作功能。
a = 7
Total = 21
Total += a # Using +=
print("The Value of the Total after using += is: ", Total)
Total -= a # Using -=
print("The Value of the Total after using -= is: ", Total)
Total *= a # Using *=
print("The Value of the Total after using *= is: ", Total)
Total //= a # Using //=
print("The Value of the Total after using //= is: ", Total)
Total **= a # Using **=
print("The Value of the Total after using **= is: ", Total)
Total /= a # Using /=
print("The Value of the Total after using /= is: ", Total)
Total %= a # Using %=
print("The Value of the Total after using %= is: ", Total)
x = 9
y = 65
x &= y # Using &=
print("The Value of the x after using &= is: ", x)
x |= 9 # Using |=
print("The Value of the x after using |= is: ", x)
x ^= y # Using ^=
print("The Value of the x after using ^= is: ", x)
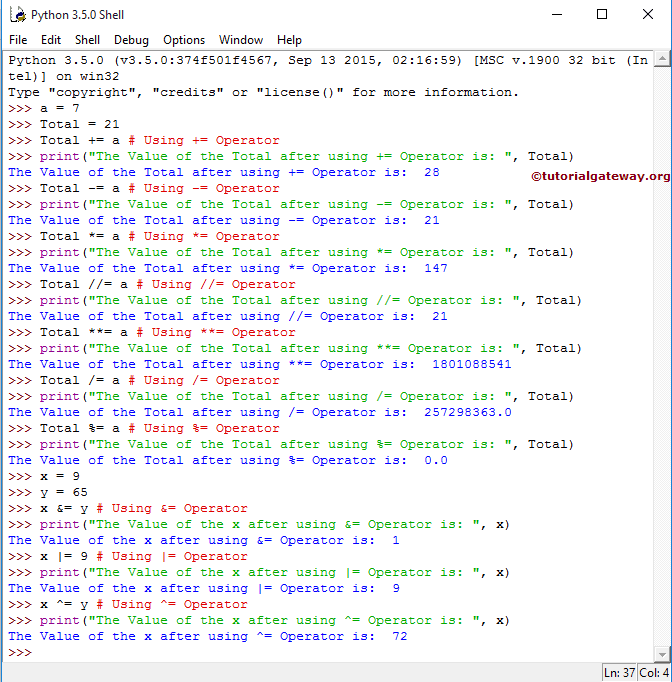
在此示例程序中,我们声明了 2 个整数值,a 和 Total,并分别赋值 7 和 21。
print 语句将显示在 a 和 Total 上使用 Python 赋值运算符后 Total 的输出。让我们看看它们所有功能。
第一个功能:
Total += a # Using +=
print("The Value of the Total after using += is: ", Total)
Total += a 意味着
Total = Total + a ⇒ 21 + 7 = 28
因此,上述 Python print 语句的输出将是 28
第二个赋值运算符的功能是:
Total -= a # Using -=
print("The Value of the Total after using -= is: ", Total)
Total -= a 意味着
Total = Total - a ⇒ 28 - 7 = 21
因此,输出将是 21
第三个功能:
Total *= a # Using *=
print("The Value of the Total after using *= is: ", Total)
Total *= a 意味着
Total = Total * a ⇒ 21 * 7 = 147
因此,输出将是 147
Python 中第四个赋值运算符的功能:
Total //= a # Using //=
print("The Value of the Total after using //= is: ", Total)
Total //= a 表示
Total = Total // a ⇒ 147 // 7 = 21
因此,上述 print 语句的输出将是 21
第五个功能:
Total **= a # Using **=
print("The Value of the Total after using **= is: ", Total)
Total **= a 表示
Total = Total ** a ⇒ 21*21*21 *21*21*21*21 = 1,801,088,541
因此,上述 print 语句的输出将是 1,801,088,541
第六个赋值运算符的功能:
Total /= a # Using /=
>>> print("The Value of the Total after using /= is: ", Total)
Total /= a 意味着
Total = Total / a ⇒ 1,801,088,541 / 7 = 257,298,363
因此,Total /= a 的输出将是 257,298,363
Python 中第七个赋值运算符的功能是:
Total %= a # Using %=
print("The Value of the Total after using %= is: ", Total)
Total %= a 意味着
Total = Total % a ⇒ 257,298,363 % 7 = 0(因为 257,298,363 / 7 的余数 = 0)
在下一行中,我们声明了 2 个整数值 x 和 y,并分别赋值 9 和 65。
x = 9 y = 65
第八个功能:
x &= y # Using &=
print("The Value of the x after using &= is: ", x)
x &= y 表示
x = x & y ⇒ 9 & 65
⇒ 00001001 & 01000001 = 00000001 ⇒ 1
因此,x &= y 的输出是 1。请参阅位运算符
第九个功能:
x |= 9 # Using |=
print("The Value of the x after using |= is: ", x)
x |= 9 表示 x | 9 ⇒ 1 | 9
⇒ 00000001 | 00001001 = 00001001 ⇒ 9
因此,输出将是 9
第十个赋值运算符的功能:
x ^= y # Using ^=
>>> print("The Value of the x after using ^= is: ", x)
x ^= y 表示
x = x ^ y ⇒ 9 ^ 65
⇒ 00001001 ^ 01000001 = 01001000 ⇒ 72
因此,输出将是 72。