编写一个 C 程序,将一个数组传递给函数。或者,如何通过一个实际的例子将数组传递给函数。
在 C 语言中将数组传递给函数的示例
在这个程序中,我们创建了一个函数,它接受一个整型变量并将其作为输出打印。在主程序中,我们使用 for 循环来迭代数组,并将每个元素传递给我们之前创建的函数。
#include<stdio.h>
void PrintArray(int a)
{
printf("Item = %d \n", a);
}
int main()
{
int array[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
PrintArray(array[i]);
}
return 0;
}
输出。请参阅函数按值调用和按引用调用以及 for 循环文章。
Item = 1
Item = 2
Item = 3
Item = 4
Item = 5
Item = 6 如何将完整的数组传递给函数?
您可以直接将数组传递给函数,而不是传递单个数组元素。请参阅C 程序查找元素之和的文章,以理解该程序背后的逻辑。
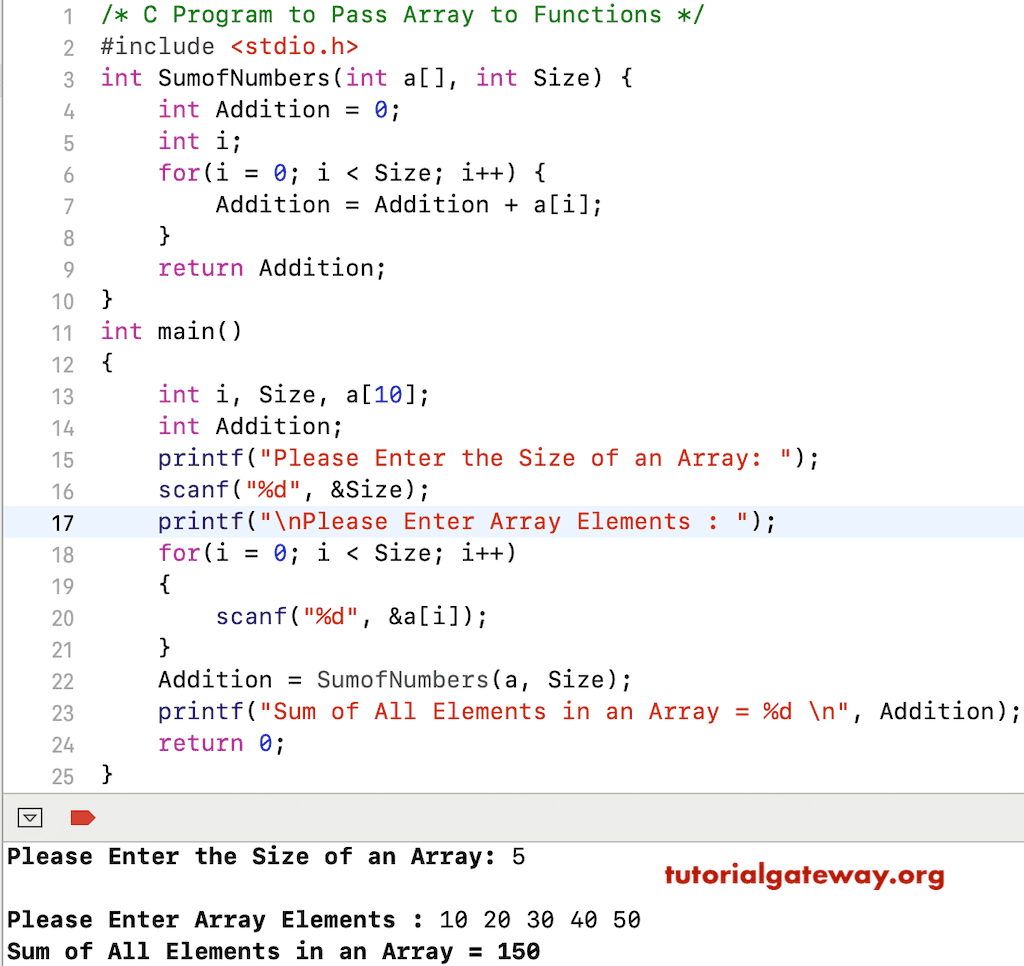
#include<stdio.h>
int SumofNumbers(int a[], int Size)
{
int Addition = 0;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
Addition = Addition + a[i];
}
return Addition;
}
int main()
{
int i, Size, a[10];
int Addition;
printf("Please Enter the Size of an Array: ");
scanf("%d", &Size);
printf("\nPlease Enter Array Elements\n");
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
Addition = SumofNumbers(a, Size);
printf("Sum of All Elements in an Array = %d \n", Addition);
return 0;
}
如何在 C 语言中将数组引用传递给函数?
您可以传递数组元素的引用,而不是传递它本身。我的意思是,直接通过引用调用数组。
#include<stdio.h>
void PrintArray(int *a, int Size)
{
int i;
printf("\n **** Elemenst in this Array are : ****\n");
for (i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
printf(" Element at Array[%d] = %d \n", i, a[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int Array[50], i, Number;
printf("\nPlease Enter Number of elements in an array : ");
scanf("%d", &Number);
printf("Please Enter %d elements of an Array : ", Number);
for (i = 0; i < Number; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &Array[i]);
}
PrintArray(Array, Number);
return 0;
}
Please Enter Number of elements in an array : 5
Please Enter 5 elements of an Array : 10 12 14 23 56
**** Elemenst in this Array are : ****
Element at Array[0] = 10
Element at Array[1] = 12
Element at Array[2] = 14
Element at Array[3] = 23
Element at Array[4] = 56 将多维数组传递给函数
这个程序向您展示了如何将多维数组传递给函数。我建议您参阅查找矩阵中每行之和的文章,以了解该程序背后的逻辑。
#include<stdio.h>
void AddRows(int arr[10][10], int i, int j)
{
int rows, columns;
for(rows = 0; rows < i; rows++)
{
int Sum = 0;
for(columns = 0; columns < j; columns++)
{
Sum = Sum + arr[rows][columns];
}
printf("The Sum of Elements of a Rows in a Matrix = %d \n", Sum );
}
}
int main()
{
int i, j, rows, columns, a[10][10];
printf("Please Enter Number of rows and columns : ");
scanf("%d %d", &i, &j);
printf("Please Enter the Matrix Elements \n");
for(rows = 0; rows < i; rows++)
{
for(columns = 0; columns < j; columns++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[rows][columns]);
}
}
AddRows(a, i, j);
return 0;
}
Please Enter Number of rows and columns : 3 3
Please Enter the Matrix Elements
10 20 30
40 50 60
70 80 90
The Sum of Elements of a Rows in a Matrix = 60
The Sum of Elements of a Rows in a Matrix = 150
The Sum of Elements of a Rows in a Matrix = 240