Java format 方法是 String 方法之一,用于使用用户指定的格式和参数返回一个格式化后的字符串。本文将通过示例展示如何编写 String format 方法。其基本语法如下所示。
Java String format 方法语法
该编程语言提供了两种不同的方法来格式化给定的字符串。以下方法接受两个参数:第一个参数是我们想要应用的格式,第二个参数是说明符引用的参数。
public static String format (String format, Object.. args); // It will return String as output //In order to use in program String.format (String format, Object.. args);
以下 Java string.format 方法接受三个参数:第一个参数是我们想要应用的区域设置,第二个参数是我们想要应用的格式。第三个参数是说明符引用的 args。
public static String format (locale l, String format, Object.. args); //In order to use in program String.format (locale l, String format, Object.. args);
- Locale(区域设置):这是我们在过程中想要应用的区域设置。如果区域设置为 NULL,则不应用本地化。
- Format(格式):请指定字符串。例如,%d、%f、%s 等。
- Args(参数):由格式说明符引用的参数。如果我们指定了更多参数,则会忽略多余的参数。
IllegalFormatException(非法格式异常):如果字符串包含非法语法,则会抛出此错误。非法语法可能包括:
- 当说明符与给定参数不兼容时。
- 或者当我们指定了不足的参数时。
NullPointerException(空指针异常):如果格式为 NULL。
提示:如果我们省略 Locale 参数,则 Javac 将采用系统默认的本地化。
Java String.format 示例
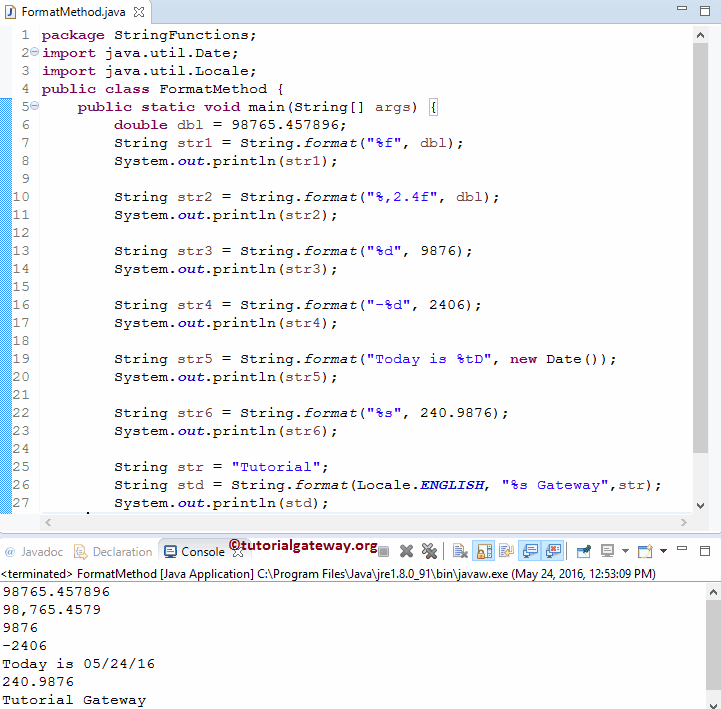
在此 程序中,我们使用 String 方法通过用户指定的格式更改给定对象。在此示例程序中,第一个语句将用户指定的双精度值更改为浮点数。
Java 中的第三个 String 函数代码会将 9876 的值格式化为正整数。下一个语句会将 2406 的值格式化为负整数。然后,我们使用了数据值。
以下语句将 240.9876 的值格式化为 String 数据。最后一个语句使用的是指定的区域设置(即 ENGLISH)。
package StringFunctions;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
public class FormatMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double dbl = 98765.457896;
String str1 = String.format("%f", dbl);
System.out.println(str1);
String str2 = String.format("%,2.4f", dbl);
System.out.println(str2);
String str3 = String.format("%d", 9876);
System.out.println(str3);
String str4 = String.format("-%d", 2406);
System.out.println(str4);
String str5 = String.format("Today is %tD", new Date());
System.out.println(str5);
String str6 = String.format("%s", 240.9876);
System.out.println(str6);
String str = "Tutorial";
String std = String.format(Locale.ENGLISH, "%s Gateway",str);
System.out.println(std);
}
}