编写一个 Java 程序,使用临时变量和不使用临时变量或第三个变量来交换两个数字。我们将为此程序使用临时变量、算术运算符和位运算符。
此 Java 程序允许用户输入两个整数值。通过使用第三个变量和赋值运算符,此示例交换了这两个数字。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a, b, temp;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter the First : ");
a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print(" Please Enter the Second : ");
b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("\n Before : a = " + a + " and b = " + b);
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
System.out.println("\n After : a = " + a + " and b = " + b);
}
}
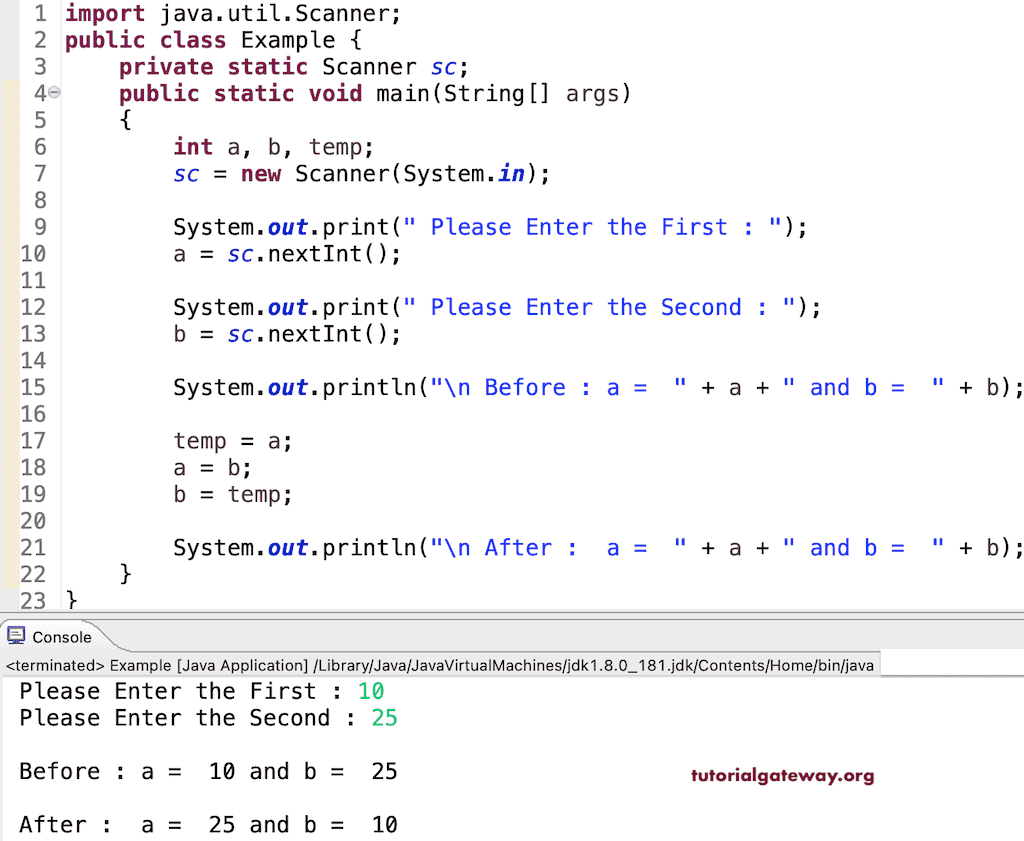
在上面使用临时变量交换两个数字的示例中,我们将 a = 10 和 b = 25 分配给了变量。
Temp = a – 这意味着将 a 的值赋给 Temp 变量。
Temp = 10
a = b – 将 b 的值赋给变量 a。
a = 25
b = Temp – 将 Temp 的值赋给 b。
b = 6
Java 程序不使用临时变量交换两个数字
在此示例中,我们不使用临时或第三个变量来交换两个数字,而是使用 算术运算符 来执行加法和减法。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example2 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a, b;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter the First value : ");
a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print(" Please Enter the Second value : ");
b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("\n Before : a = " + a + " and b = " + b);
a = a + b;
b = a - b;
a = a - b;
System.out.println("\n After : a = " + a + " and b = " + b);
}
}
使用算术运算符的结果。
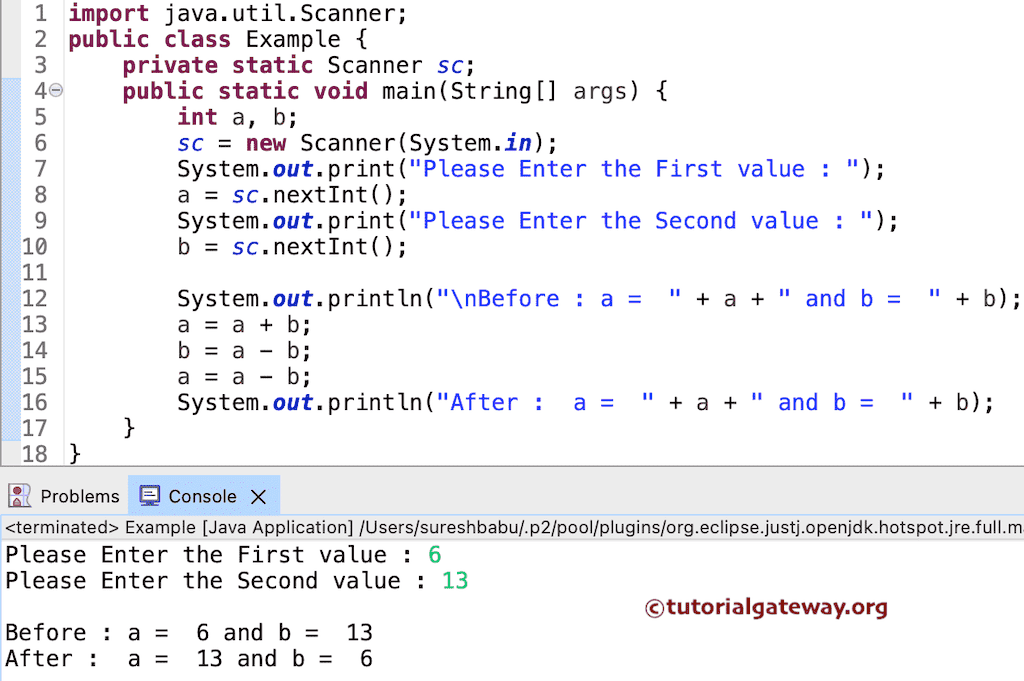
用户输入的值为 a = 6 和 b = 13
a = a + b
a = 6 + 13 = 19
b= a-b = 19 – 13 = 6
a = a-b = 19 – 6 = 13
两个数字的最终值:a = 13 和 b = 6
注意:我们可以通过乘法和除法方法来交换两个数字。但是,如果我们处理较大的整数值或其中任何一个为 0,它可能会产生奇怪的值。
使用按位 OR 运算符交换两个数字
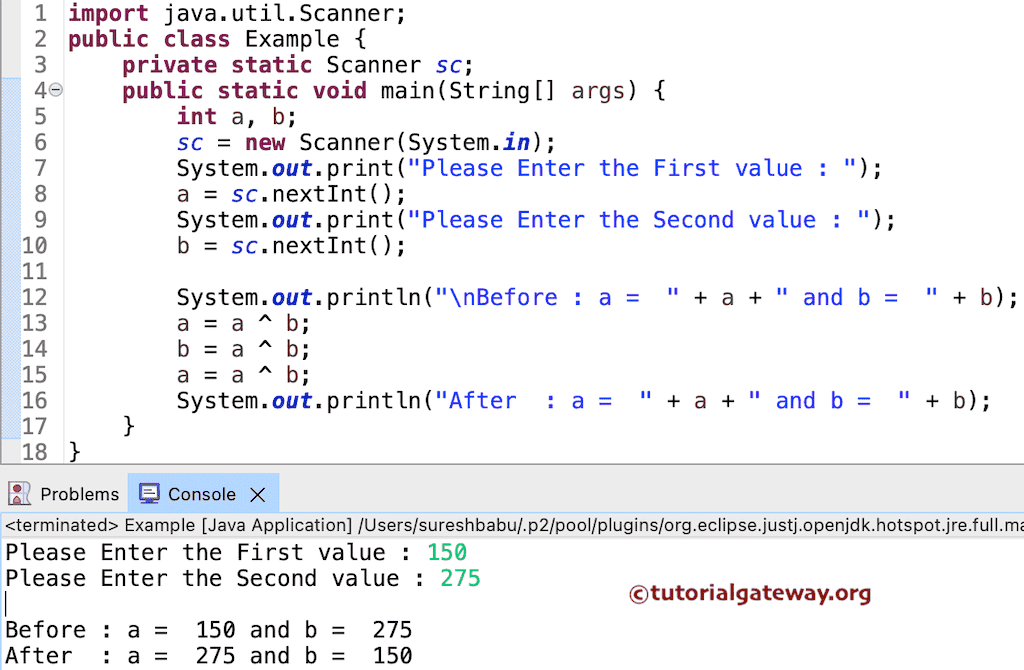
在此示例中,我们将使用 按位运算符 XOR,而不是使用临时变量来交换两个数字。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example3 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a, b;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter the First value : ");
a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print(" Please Enter the Second value : ");
b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("\n Before : a = " + a + " and b = " + b);
a = a ^ b;
b = a ^ b;
a = a ^ b;
System.out.println("\n After : a = " + a + " and b = " + b);
}
}
输出
Java 使用函数交换两个数字的程序
此 程序 与第一个 Java 临时变量示例相同。但是,我们将逻辑分离并将其放置在一个单独的方法中。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example4 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a, b;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter the First value : ");
a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print(" Please Enter the Second value : ");
b = sc.nextInt();
swfunc(a, b);
}
public static void swfunc(int a, int b)
{
int temp;
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
System.out.println("\n After : a = " + a + " and b = " + b);
}
}
Please Enter the First value : 12
Please Enter the Second value : 95
After : a = 95 and b = 12