编写一个 Java 程序,按字母顺序对字符串进行排序。此示例允许输入大小和字符串项。接下来,我们使用 Array sort 函数按字母顺序对单词或字符串数组进行排序。
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SortStringArrAlphabetically1 {
private static Scanner sc;
private static Scanner sc2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
sc2 = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the Total Strings you enter = ");
int Size = sc.nextInt();
String str[] = new String[Size];
System.out.format("Enter %d Strings one by one\n", Size);
for(int i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
str[i] = sc2.nextLine();
}
Arrays.sort(str);
System.out.format("\nAfter Sorting the String Alphabetically\n");
for(String s: str)
{
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
}
}
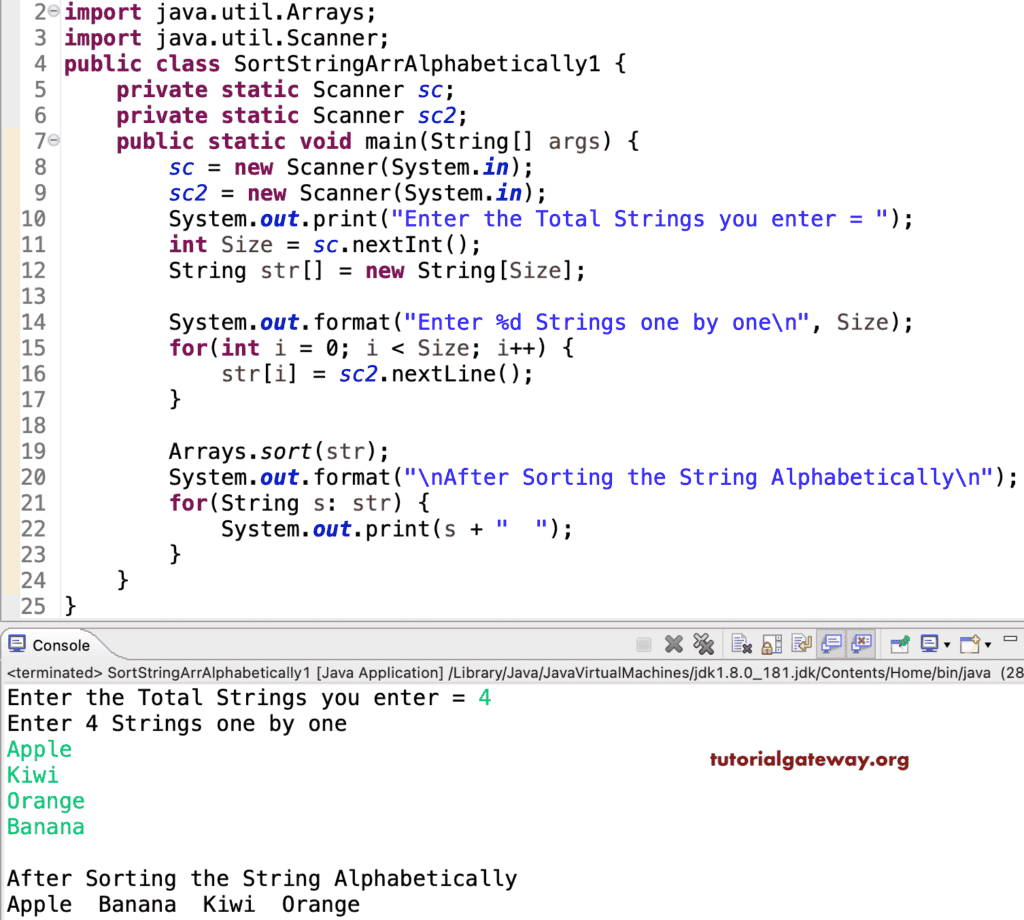
使用 for 循环按字母顺序对字符串进行排序的 Java 程序
在此 示例 中,我们使用 for 循环从头到尾迭代字符串数组,并比较每个单词。我们使用临时变量根据结果移动它们的位置。
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example2 {
private static Scanner sc;
private static Scanner sc2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Size, i, j;
String temp;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
sc2 = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the Total Words you enter = ");
Size = sc.nextInt();
String str[] = new String[Size];
System.out.format("Enter %d Sentences one by one\n", Size);
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
str[i] = sc2.nextLine();
}
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
for(j = i + 1; j < Size; j++)
{
if(str[i].compareTo(str[j]) > 0)
{
temp = str[i];
str[i] = str[j];
str[j] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.format("\nAfter Sorting the String Alphabetically\n");
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
System.out.print(str[i] + " ");
}
}
}
Enter the Total Words you enter = 5
Enter 5 Sentences one by one
banana
kiwi
apple
usa
canada
After Sorting the String Alphabetically
apple banana canada kiwi usa