编写一个 Java 程序,使用 for 循环打印数组中的第 K 个元素。
package NumPrograms;
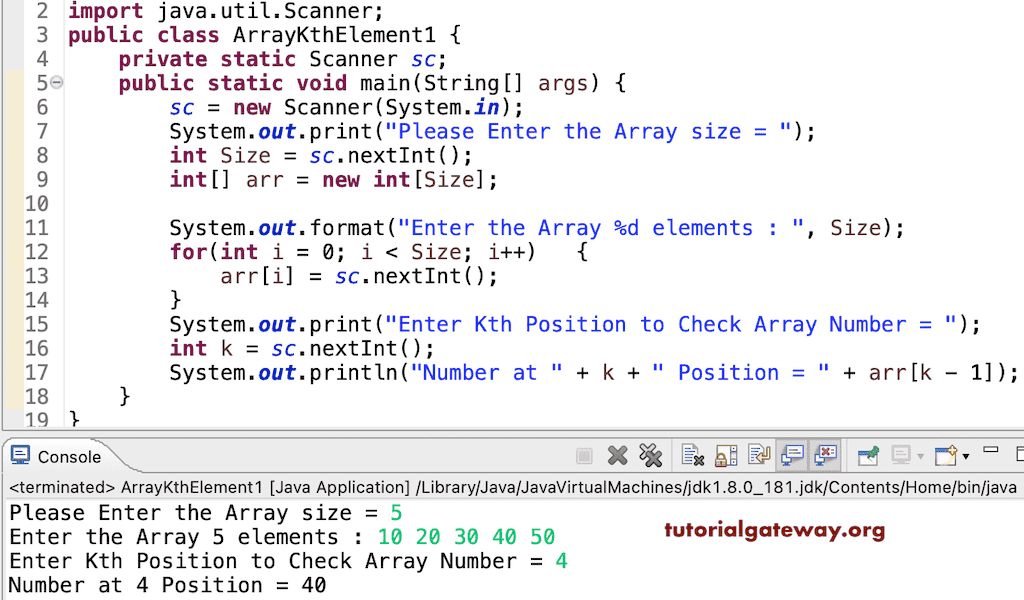
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayKthElement1 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Please Enter the Array size = ");
int Size = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[Size];
System.out.format("Enter the Array %d elements : ", Size);
for(int i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.print("Enter Kth Position to Check Array Number = ");
int k = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Number at " + k + " Position = " + arr[k - 1]);
}
}
此程序使用 while 循环打印给定数组中的第 K 个元素。在此 Java 示例中,我们使用了一个额外的 if else 语句来检查该值是否在数组范围内。
package NumPrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example2 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Please Enter the size = ");
int Size = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[Size];
System.out.format("Enter the %d elements : ", Size);
int i = 0;
while(i < Size)
{
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
i++;
}
System.out.print("Enter Kth Position to Check Array Number = ");
int k = sc.nextInt();
if(k <= Size)
{
System.out.println("Number at " + k + " Position = " + arr[k - 1]);
}
else
{
System.out.println("The Kth Position is Out of Range");
}
}
}
Please Enter the size = 8
Enter the 8 elements : 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Enter Kth Position to Check Array Number = 6
Number at 6 Position = 60