编写一个Java程序,通过示例打印字符串中的字符。在下面的示例中,我们使用for循环从头到尾遍历每个字符,并打印给定字符串中的所有字符。在这里,我们使用字符串长度函数来获取字符串长度。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrintStringChars1 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str;
int i;
sc= new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("\n Please Enter any String to Print = ");
str = sc.nextLine();
for(i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
{
System.out.println("The Character at Position " + i + " = " + str.charAt(i));
}
}
}
字符串字符输出
Please Enter any String to Print = Hello
The Character at Position 0 = H
The Character at Position 1 = e
The Character at Position 2 = l
The Character at Position 3 = l
The Character at Position 4 = oJava程序打印字符串中的字符示例2
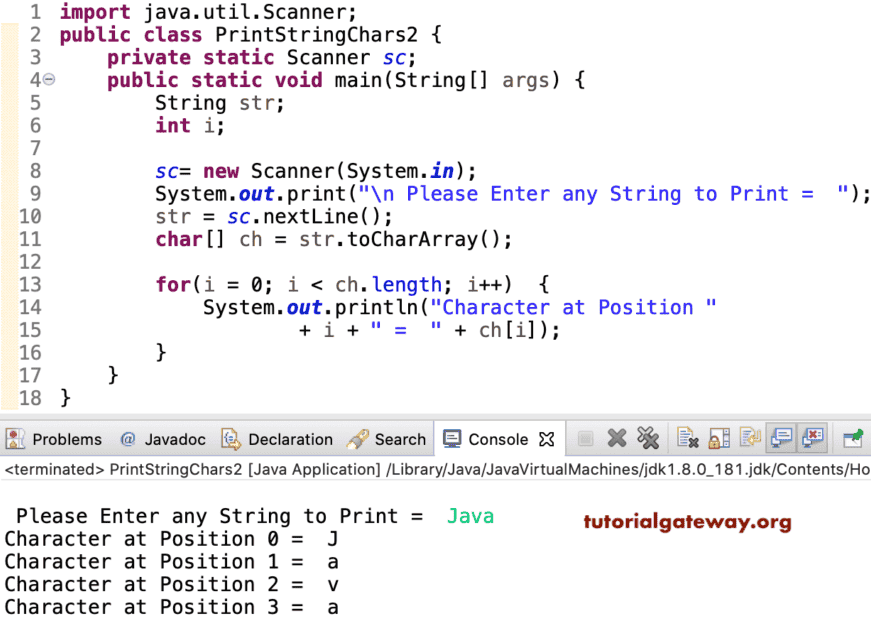
在此示例中,我们使用toCharArray()方法将字符串转换为字符数组。接下来,我们迭代该字符数组并打印字符。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrintStringChars2 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str;
int i;
sc= new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("\n Please Enter any String to Print = ");
str = sc.nextLine();
char[] ch = str.toCharArray();
for(i = 0; i < ch.length; i++)
{
System.out.println("Character at Position " + i + " = " + ch[i]);
}
}
}
下面显示的程序将使用While循环显示字符串中的字符。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrintStringChars3 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str;
int i = 0;
sc= new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("\nPlease Enter any String to Print = ");
str = sc.nextLine();
while(i < str.length())
{
System.out.println("The Character at Position " + i + " = " + str.charAt(i));
i++;
}
}
}
Please Enter any String to Print = learn Java
Character at Position 0 = l
Character at Position 1 = e
Character at Position 2 = a
Character at Position 3 = r
Character at Position 4 = n
Character at Position 5 =
Character at Position 6 = J
Character at Position 7 = a
Character at Position 8 = v
Character at Position 9 = a在此Java打印字符串字符示例中,我们通过创建一个单独的方法来分割代码。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrintStringChars4 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str;
sc= new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("\n Please Enter any String to Print = ");
str = sc.nextLine();
PrintStringCharacters(str);
}
public static void PrintStringCharacters(String str) {
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
{
System.out.println("The Character at Position " + i + " = " + str.charAt(i));
}
}
}
Please Enter any String to Print = Programs
The Character at Position 0 = P
The Character at Position 1 = r
The Character at Position 2 = o
The Character at Position 3 = g
The Character at Position 4 = r
The Character at Position 5 = a
The Character at Position 6 = m
The Character at Position 7 = s这是打印字符串字符的另一个示例。在这里,我们不允许代码打印空字符或单词之间的空格。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrintStringChars5 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str;
sc= new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("\nPlease Enter any String to Print = ");
str = sc.nextLine();
PrintStringCharacters(str);
}
public static void PrintStringCharacters(String str) {
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
{
if(str.charAt(i) != ' ') {
System.out.println("The Character at Position " + i + " = " + str.charAt(i));
}
}
}
}
Please Enter any String to Print = Gateway
The Character at Position 0 = G
The Character at Position 1 = a
The Character at Position 2 = t
The Character at Position 3 = e
The Character at Position 4 = w
The Character at Position 5 = a
The Character at Position 6 = y