如何编写一个 Java 程序来打印字符的 ASCII 值?在此编程中,每个字符都有其自己的 ASCII 值(它只是一个整数)。当我们为变量分配一个字符时,存储的不是它本身,而是该字符的 ASCII 值。例如,'A' 的 ASCII 值是 65。
Java 程序打印字符的 ASCII 值示例
在此程序中,用户请求输入任何字母。接下来,此程序显示该特定字符的 ASCII 值。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ASCIIofCharacter {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
char ch;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter any Character : ");
ch = sc.next().charAt(0);
//Assigning the Character to Integer value
int num1 = ch;
// You can also Type cast the Character Value to convert it into Integer value
int num2 = (int)ch;
System.out.println("\n The ASCII value of a given character " + ch + " = " + num1);
System.out.println("\n The ASCII value of a given character " + ch + " = " + num2);
// Type casting directly inside the system.out.println
System.out.println("\n The ASCII value of a given character " + ch + " = " + (int)ch);
}
}
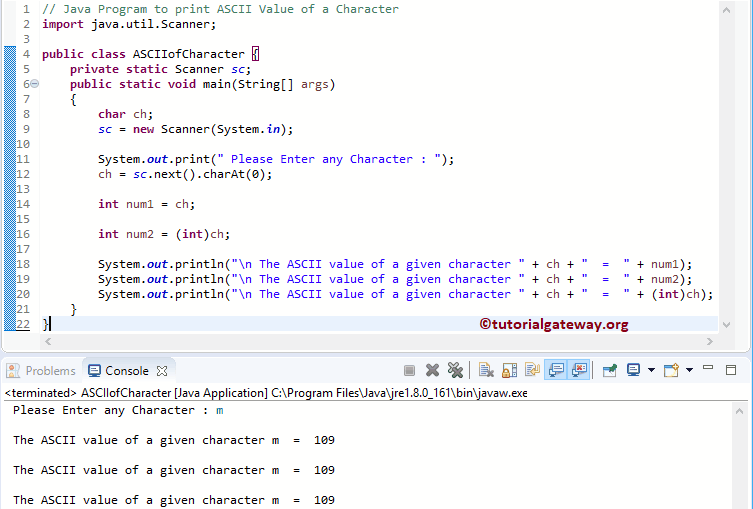
这次我们插入了单词。尽管这是一个单词,但这个 Java 程序由于 sc.next().charAt(0) 仅接受第一个字母。它读取索引位置 0 处的字母。请参考ASCII 表文章以了解 ASCII 字符及其十进制、十六进制和八进制数字的列表。
Please Enter any Character : Tutorial
The ASCII value of a given character T = 84
The ASCII value of a given character T = 84
The ASCII value of a given character T = 84