如何使用 For 循环、While 循环和函数编写一个 Java 程序对数组执行算术运算,并附带示例。
使用 For 循环执行数组算术运算的 Java 程序
此 Java 程序允许用户输入大小和一维数组元素。接下来,此 Java 程序使用这两个数组执行算术运算,如加法、减法、乘法和除法。
// Java Program to Perform Arithmetic Operations on Array
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayArithmeticOpert1 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int Size, i;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter Number of elements in an array : ");
Size = sc.nextInt();
int [] a = new int[Size];
int [] b = new int[Size];
int [] Addition = new int[Size];
int [] Subtraction = new int[Size];
int [] Multiplication = new int[Size];
int [] Division = new int[Size];
float [] Module = new float[Size];
System.out.print(" Please Enter " + Size + " elements of an Array : ");
for (i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.print(" Please Enter " + Size + " elements of an Array : ");
for (i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
b[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for(i = 0; i < Size; i ++)
{
Addition [i]= a[i] + b[i];
Subtraction [i]= a[i] - b[i];
Multiplication [i]= a[i] * b[i];
Division [i] = a[i] / b[i];
Module [i] = a[i] % b[i];
}
System.out.println("\nAdd\t Sub\t Multi\t Div\t Mod");
for (i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
System.out.print(Addition[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Subtraction[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Multiplication[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Division[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Module[i]+ " \t ");
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
首先,我们声明了 6 个用户指定大小的数组。它们是整型数组 a、b、Addition、Subtraction、Multiplication 和 Module,以及一个浮点型数组 Division。
下面的 For 循环 遍历 a[3] 数组中的每个单元格。for 循环中的条件 (i < Size)) 确保编译器不会超出数组大小。for 循环内的语句将用户输入的数值存储为数组元素,例如 a[0]、a[1]、a[2]。
for (i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
接下来,我们使用另一个 Java For 循环为 b 数组 赋值。
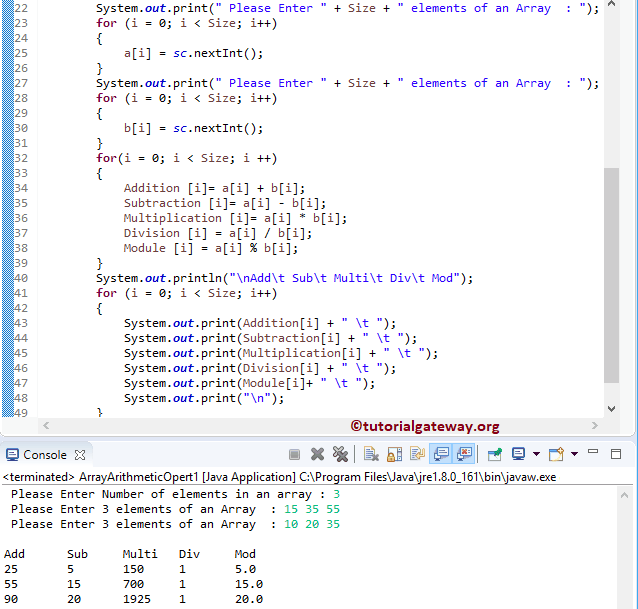
在下一行,我们再用一个 for 循环来遍历每个元素并计算两个数组的加法、减法、乘法、除法和模。从上面的 算术运算 屏幕截图
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
Addition [i] = a[i] + b[i];
Subtraction [i] = a[i] - b[i];
Multiplication [i] = a[i] * b[i];
Division [i] = a[i] / b[i];
Module [i] = a[i] % b[i];
}
用户输入的数组算术运算 Java 程序的值为
a[3] = {15, 35, 55}} 并且
b[3] = {10, 20, 35}}
第一次迭代: for (i = 0; 0 < 3; 0++)
i 的值为 0,条件 (i < 3) 为 True。因此,它开始执行循环内的语句,直到条件失败。
Addition[i] = a[i] + b[i] => a[0] + b[0];
Addition[0] = 15 + 10 = 25
Subtraction[0]= a[0] – b[0]
Subtraction [0] = 15 – 10 = 5
Multiplication[0] = a[0] * b[0]
Multiplication [0] = 15 * 10 = 150
Division[0] = a[0] / b[0]
Division [0] = 15 / 10 = 1
Module[0] = a[0] % b[0]
Module[0] = 15 % 10 = 5
第二次迭代: for (i = 1; 1 < 3; 1++)
i 的值为 1,条件 (i < 3) 为 True。
Addition[1] = a[1] + b[1];
Addition[1] = 35 + 20 = 55
Subtraction[1] = 35 – 20 = 15
Multiplication[1] = 35 * 20 = 700
Division[1] = 35 / 20 = 1
Module[1] = 35 % 20 = 15
第三次迭代: for (i = 2; 2 < 3; 2++)
Addition[2] = a[2] + b[2];
Addition[2] = 55 + 35 = 90
Subtraction[2] = 55 – 35 = 20
Multiplication[2] = 55 * 35 = 1925
Division[2] = 55 / 35 = 1
Module[2] = 55 % 35 = 20
递增后,列值为 3,条件 (i < 3) 失败。因此,它退出循环。
下一个 for 循环,
for (i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
System.out.print(Addition[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Subtraction[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Multiplication[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Division[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Module[i]+ " \t ");
System.out.print("\n");
}
Addition 数组的最终输出为
Addition [3] = {25, 55, 90};
减法数组的最终输出是:
Subtraction [3] = {5, 15, 20};
Multiplication 数组的最终输出为
Multiplication [3] = {150, 700, 1925};
除法数组的最终输出是:
Division [3] = {1.00, 1.00, 1.00};
模数组的最终输出是:
Module [2][3] = { {5, 15, 20};
使用函数的数组算术运算 Java 程序
此 Java 程序与第一个示例相同。但我们使用了一个单独的方法来对一维数组元素执行算术运算。
// Java Program to Perform Arithmetic Operations on Array
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayArithmeticOpert3 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int Size, i = 0, j = 0;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter Number of elements in an array : ");
Size = sc.nextInt();
int [] a = new int[Size];
int [] b = new int[Size];
System.out.print(" Please Enter " + Size + " elements of an Array : ");
while(i < Size)
{
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
i++;
}
System.out.print(" Please Enter " + Size + " elements of an Array : ");
while(j < Size )
{
b[j] = sc.nextInt();
j++;
}
ArithmeticOpertioons(a, b, Size);
}
public static void ArithmeticOpertioons(int a[], int b[], int Size)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
int [] Addition = new int[Size];
int [] Subtraction = new int[Size];
int [] Multiplication = new int[Size];
int [] Division = new int[Size];
float [] Module = new float[Size];
while(i < Size)
{
Addition [i]= a[i] + b[i];
Subtraction [i]= a[i] - b[i];
Multiplication [i]= a[i] * b[i];
Division [i] = a[i] / b[i];
Module [i] = a[i] % b[i];
i++;
}
System.out.println("\nAdd\t Sub\t Multi\t Div\t Mod");
while(j < Size )
{
System.out.print(Addition[j] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Subtraction[j] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Multiplication[j] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Division[j] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Module[j]+ " \t ");
System.out.print("\n");
j++;
}
}
}
Java 数组算术运算输出
Please Enter Number of elements in an array : 5
Please Enter 5 elements of an Array : 10 20 30 40 50
Please Enter 5 elements of an Array : 2 15 28 14 75
Add Sub Multi Div Mod
12 8 20 5 0.0
35 5 300 1 5.0
58 2 840 1 2.0
54 26 560 2 12.0
125 -25 3750 0 50.0 使用 While 循环的数组算术运算 Java 程序
此 程序 与上面相同,但我们使用 Java While 循环 来对数组元素执行算术运算。
// Java Program to Perform Arithmetic Operations on Array
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayArithmeticOpert2 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int Size, i;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter Number of elements in an array : ");
Size = sc.nextInt();
int [] a = new int[Size];
int [] b = new int[Size];
System.out.print(" Please Enter " + Size + " elements of an Array : ");
for (i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.print(" Please Enter " + Size + " elements of an Array : ");
for (i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
b[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
ArithmeticOpertioons(a, b, Size);
}
public static void ArithmeticOpertioons(int a[], int b[], int Size)
{
int i;
int [] Addition = new int[Size];
int [] Subtraction = new int[Size];
int [] Multiplication = new int[Size];
int [] Division = new int[Size];
float [] Module = new float[Size];
for(i = 0; i < Size; i ++)
{
Addition [i]= a[i] + b[i];
Subtraction [i]= a[i] - b[i];
Multiplication [i]= a[i] * b[i];
Division [i] = a[i] / b[i];
Module [i] = a[i] % b[i];
}
System.out.println("\nAdd\t Sub\t Multi\t Div\t Mod");
for (i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
System.out.print(Addition[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Subtraction[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Multiplication[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Division[i] + " \t ");
System.out.print(Module[i]+ " \t ");
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
Java 数组算术运算输出
Please Enter Number of elements in an array : 4
Please Enter 4 elements of an Array : 12 48 89 63
Please Enter 4 elements of an Array : 89 16 128 43
Add Sub Multi Div Mod
101 -77 1068 0 12.0
64 32 768 3 0.0
217 -39 11392 0 89.0
106 20 2709 1 20.0