编写一个 Java 程序来生成随机数,并附带示例。例如,我们可以使用 Math.random 方法、Random 类和 ThreadLocalRandom 类来生成数字。
Java 随机数生成器是 Math 库函数,用于生成并返回零和一之间的伪随机数。Math.random 的基本语法如下所示。
static double random(); //Return Type is Double // In order to use in program: Math.random();
使用 Math 函数生成随机数的 Java 程序
Math 随机数生成器函数返回 0 到 1 之间的伪随机数。在此程序中,我们将使用该函数并显示输出。
package MathFunctions;
public class RandomMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.random());
System.out.println(Math.random());
System.out.println(Math.random());
System.out.println(Math.random());
}
}
random 函数生成的值是从 0(包含)到小于 1。如果观察下面的输出,我们调用了该函数四次,返回了四个不同的值。
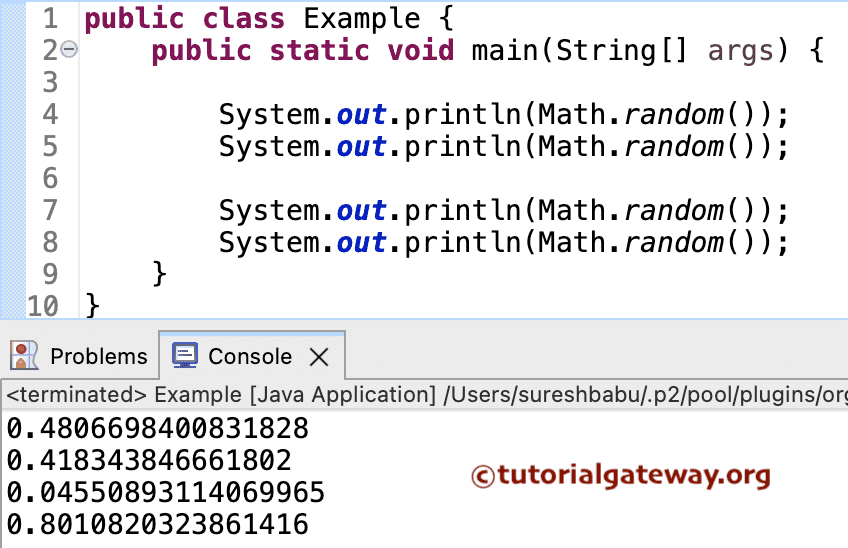
在此示例中,我们使用 Math.random() 方法,该方法生成 0 到 1 之间的双精度随机数。我们还可以通过类型转换来获得所需的数据类型。
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("The First = " + Math.random());
System.out.println("The Second = " + Math.random());
System.out.println("The Third = " + Math.random());
System.out.println("The Fourth = " + Math.random());
}
}
The First = 0.20037158212760142
The Second = 0.0012068894419960952
The Third = 0.18700555955501663
The Fourth = 0.3230234616758232通过使用 Javac Math.random() * (max – min + 1) + min,我们可以生成 min 和 max 值之间的数字。
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
public class Example2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int min = 100, max = 300;
System.out.print("The Doubles between " + min + " and " + max + " = " );
double rand1 = Math.random() * (max - min + 1) + min;
System.out.print(rand1);
System.out.print("\nThe Number between " + min + " and " + max + " = " );
int rand2 = (int)(Math.random() * (max - min + 1) + min);
System.out.print(rand2);
}
}
The Doubles between 100 and 300 = 101.43411590322778
The Number between 100 and 300 = 282使用 for 循环生成随机数的 Java 程序
到目前为止,我们已经生成了一个范围内的单个值。但是,借助 for 循环,我们可以生成范围内的多个值。在此 程序 中,我们将展示如何将随机值存储在数组中。在这里,我们将声明一个双精度类型的数组,并用 Math.random 生成的不同的值填充该数组。
首先,我们声明了一个空的双精度 数组。接下来,我们使用 For 循环迭代数组。在 For 循环中,我们将 i 值初始化为 0。编译器将检查条件 (i < 10)。
以下 Java 随机数生成器函数语句将把值存储在数组中。如果观察代码片段,我们将每个索引位置分配一个值。
编译器将调用 Math 函数 (static double random() ) 来返回 0 到 1 之间的值。
接下来,为了显示数组的值,我们使用了另一个 For 循环 来迭代数组。在 For 循环中,我们将 i 值初始化为 0,编译器将检查条件 (i < myArray.length)。myArray.length 用于查找数组的长度。
在循环内部,Java System.out.println 语句将打印输出。
package MathFunctions;
public class RandomMethodInArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double [] myArray = new double[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
myArray[i] = Math.random();
}
//Displaying Result
for (int i = 0; i < myArray.length; i++) {
System.out.println("Array Element = " + myArray[i]);
}
}
}
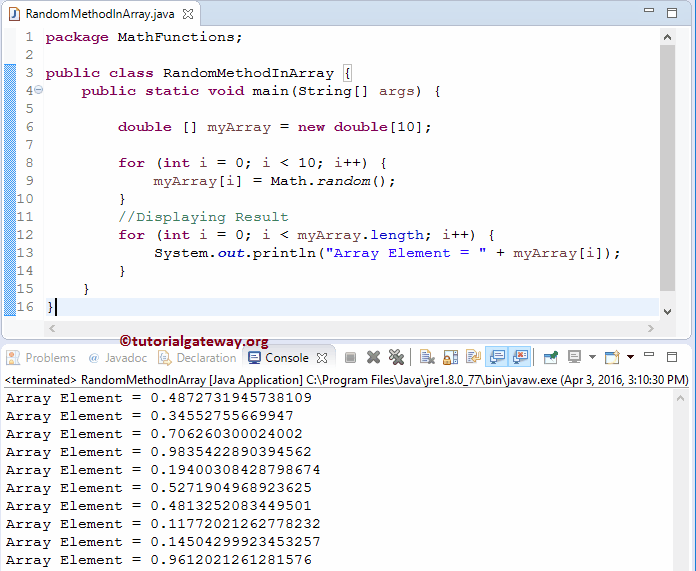
这是生成随机数数组的另一个示例。
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int min = 10, max = 100;
System.out.println("Ten Numbers between " + min + " and " + max);
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
int rdNum = (int)(Math.random() * (max - min + 1) + min);
System.out.print(rdNum + " ");
}
System.out.println("\nTwenty Numbers between 100 and 250");
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
int rdNum = (int)(Math.random() * (250 - 100 + 1) + 100);
System.out.print(rdNum + " ");
}
}
}
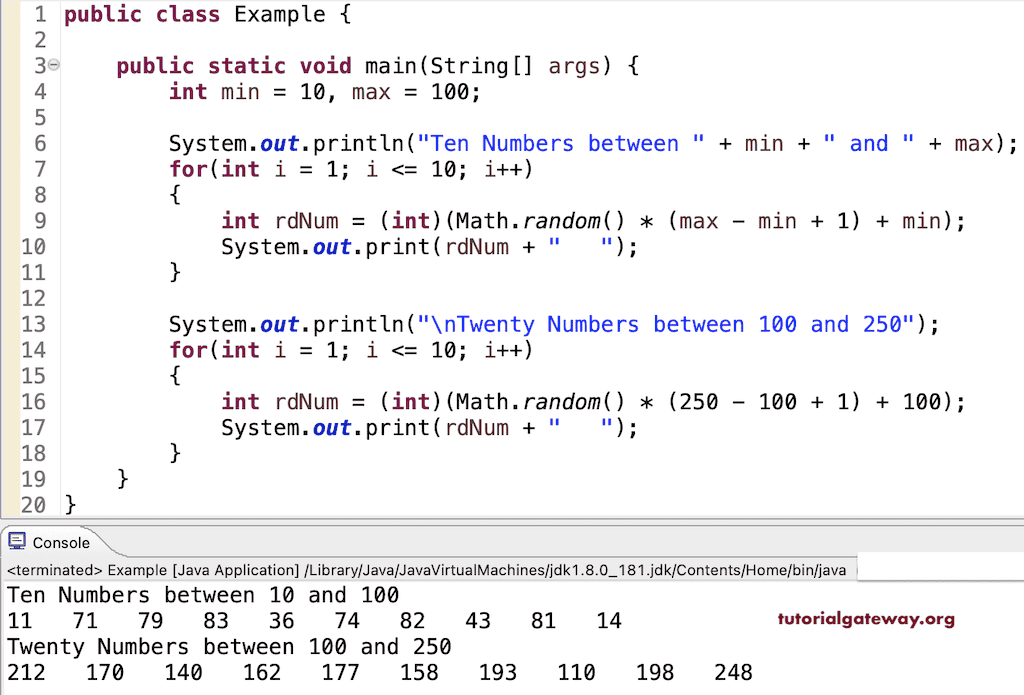
使用 Random 类生成随机数的 Java 程序
此类 Random 具有生成数字的不同方法。它们是:
- nextInt() – 生成 0 到 -1 之间的值
- nextInt(maxValue)
- nextFloat() – 返回 0.0 到 1.0 之间的值
- nextDouble() – 返回 0.0 到 1.0 之间的值
- nextLong()
- nextBoolean()
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
import java.util.Random;
public class Example4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random rand = new Random();
System.out.println("Integer Values");
System.out.println(rand.nextInt());
System.out.println(rand.nextInt(20));
System.out.println(rand.nextInt(100));
System.out.println("Double Values");
System.out.println(rand.nextDouble());
System.out.println(rand.nextDouble());
System.out.println("Float Values");
System.out.println(rand.nextFloat());
System.out.println(rand.nextFloat());
System.out.println("Long Values");
System.out.println(rand.nextLong());
System.out.println(rand.nextLong());
}
}
Integer Values
1907114976
4
34
Double Values
0.9425130257739933
0.35445514266974565
Float Values
0.26128042
0.47151804
Long Values
1983140345491940719
8269807721314480176在此示例中,我们使用 for 循环生成了十个整数类型的随机数,最大值为 100。
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
import java.util.Random;
public class Example5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random rand = new Random();
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
System.out.print(rand.nextInt(100) + 1 + " ");
}
}
}
9 45 62 84 18 2 10 33 28 60 使用 ThreadLocalRandom 生成随机数的 Java 程序
我们还可以使用 ThreadLocalRandom 在范围内生成随机数。nextInt()、nextDouble() 和 nextLong() 接受最小值和最大值限制。
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
public class Example6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Integer Values");
System.out.println(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt());
System.out.println(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(20));
System.out.println(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100, 500));
System.out.println("Double Values");
System.out.println(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble());
System.out.println(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble(50));
System.out.println(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble(30, 50));
System.out.println("Float Values");
System.out.println(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextFloat());
System.out.println(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextFloat());
System.out.println("Long Values");
System.out.println(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong());
System.out.println(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong(40));
System.out.println(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong(400, 600));
}
}
Integer Values
536433268
17
105
Double Values
0.35695024289926547
29.875628014935078
45.29405097588917
Float Values
0.62107533
0.9211104
Long Values
-1523132321353307594
4
542此程序使用了 ThreadLocalRandom 和 for 循环。
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
public class Example7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int min = 100, max = 300;
System.out.println("Ten Numbers are");
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
System.out.print(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100) + 1 + " ");
}
System.out.println("\nFifteen Numbers are");
for(int i = 0; i < 15; i++)
{
int rdNum = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(min, max);
System.out.print(rdNum + " ");
}
}
}
Ten Numbers are
10 88 47 68 41 79 45 74 1 41
Fifteen Numbers are
262 187 267 255 255 265 136 201 228 255 166 156 115 291 169