编写一个 Java 程序,通过示例查找二次方程的根。二次方程的数学表示为 ax²+bx+c = 0。二次方程有两个根,它们完全取决于判别式。如果判别式 > 0,则该方程有两个不同的实根。
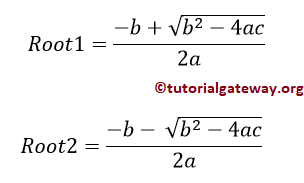
如果判别式 < 0,则存在两个不同的复根。
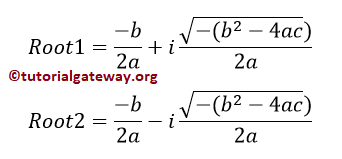
如果判别式 = 0,则存在两个相等且实有的根。
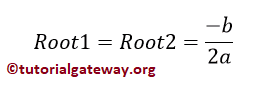
使用 If Else 查找二次方程根的 Java 程序
此 Java 程序允许用户输入 a、b 和 c 的三个值。接下来,此程序使用 If Else 语句返回二次方程的根。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double a, b, c;
double r1, r2, i, d;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter the Values of a, b, c of Quadratic Equation : ");
a = sc.nextDouble();
b = sc.nextDouble();
c = sc.nextDouble();
d = (b * b) - (4 * a *c);
if(d > 0)
{
r1 = (-b + Math.sqrt(d) / (2 * a));
r2 = (-b - Math.sqrt(d) / (2 * a));
System.out.println("\n Two Distinct Real Roots Exists: r1 = " + r1 + " and r2 = " + r2);
}
else if(d == 0)
{
r1 = r2 = -b / (2 * a);
System.out.println("\n Two Equal and Real Roots Exists: r1 = " + r1 + " and r2 = " + r2);
}
else if(d < 0)
{
r1 = r2 = -b / (2 * a);
i = Math.sqrt(-d) / (2 * a);
System.out.println("\n Two Distinct Complex Roots Exists: r1 = " +
r1 + " + " + i + " and r2 = " + r2 +" - " +i);
}
}
}
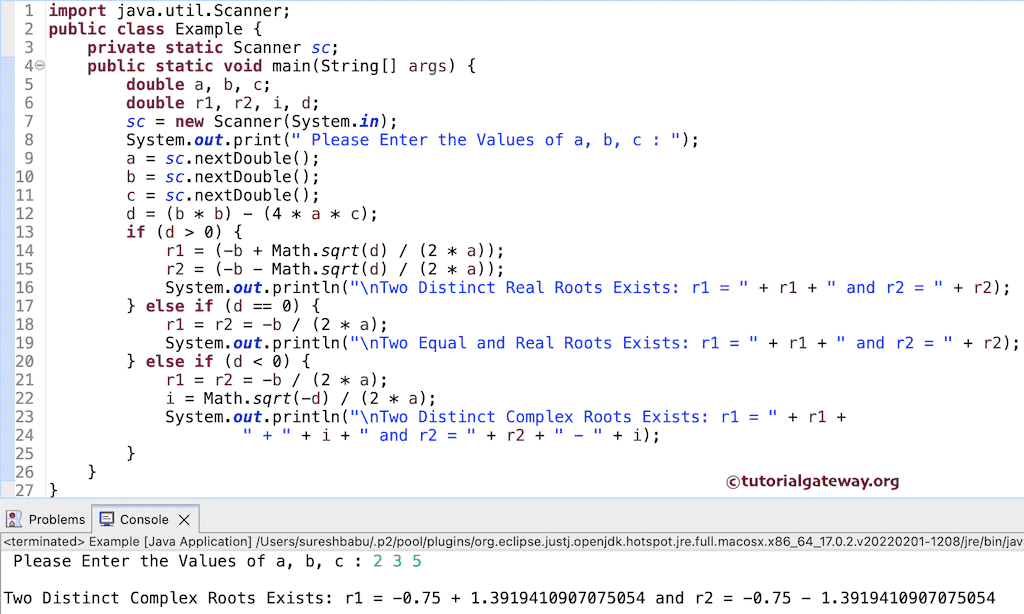
用户在此 Java 程序中输入的值是 2、3 和 5,用于查找二次方程的根。这意味着 a = 2,b = 3,c = 5,方程为 2x²+3x+5 = 0。
d = (b * b) – (4 * a *c) => (3 * 3) – (4 * 2 * 5)
d = (9) – (40) = -31
这意味着 d < 0。因此 r1 = r2 = -b / (2 * a) => -3 / (2 * 2)。
r1 = r2 = -0.75
i = sqrt(-d) / (2 * a)
= sqrt(- -31) / (2 * 2) => 5.567 / 4
i = 1.3919
r1= r1 + i = -0.75 + 1.3919
r2= r2 – i = -0.75 – 1.3919
使用 Switch Case 查找二次方程根的 Java 程序
此程序与上述程序相同,用于显示二次方程的根,但这次我们使用的是 Switch Case。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class QuadraticEquation2 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double a, b, c;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter the Values of a, b, c of Quadratic Equation : ");
a = sc.nextDouble();
b = sc.nextDouble();
c = sc.nextDouble();
QuadraticEquation(a, b, c);
}
public static void QuadraticEquation(double a, double b, double c)
{
double root1, root2, imaginary, discriminant;
discriminant = (b * b) - (4 * a *c);
if(discriminant > 0)
{
root1 = (-b + Math.sqrt(discriminant) / (2 * a));
root2 = (-b - Math.sqrt(discriminant) / (2 * a));
System.out.println("\n Two Distinct Real Roots Exists: root1 = " + root1 + " and root2 = " + root2);
}
else if(discriminant == 0)
{
root1 = root2 = -b / (2 * a);
System.out.println("\n Two Equal and Real Roots Exists: root1 = " + root1 + " and root2 = " + root2);
}
else if(discriminant < 0)
{
root1 = root2 = -b / (2 * a);
imaginary = Math.sqrt(-discriminant) / (2 * a);
System.out.println("\n Two Distinct Complex Roots Exists: root1 = " + root1 +
" + " + imaginary + " and root2 = " + root2 +" - " +imaginary);
}
}
}
Please Enter the Values of a, b, c of Quadratic Equation : 10 15 -25
Two Distinct Real Roots Exists: root1 = -13.25 and root2 = -16.75用户在此 Java 程序中输入 10、15 和 -25。这意味着 a = 10,b = 15,c = -25,二次方程为 10x²+15x-25 = 0。
判别式 = (b * b) – (4 * a *c) => (15 * 15) – (4 * 10 *(-25))
= 225 + 1000 = 1225
这意味着判别式 > 0,因此
root1 = (-b + sqrt(判别式) / (2 * a))
= (-15 + sqrt(1225) / (2 * 10)) => (-15 + 35 / (20))
= -15 + 1.75 = -13.25
root2 = (-b – sqrt(判别式) / (2 * a))
= (-15 – sqrt(1225) / (2 * 10)) => (-15 – 35 / (20))
= -15 – 1.75 = -16.75