使用 switch 语句和 else if 语句编写一个简单的 Java 计算器程序。第一个示例允许输入两个数值和要执行的运算符。
接下来,我们使用 switch 语句根据给定的运算符执行计算。例如,如果我们输入 +,switch 语句将执行加法。在这里,我们还使用 default 语句处理错误的运算符,以通知用户输入错误。
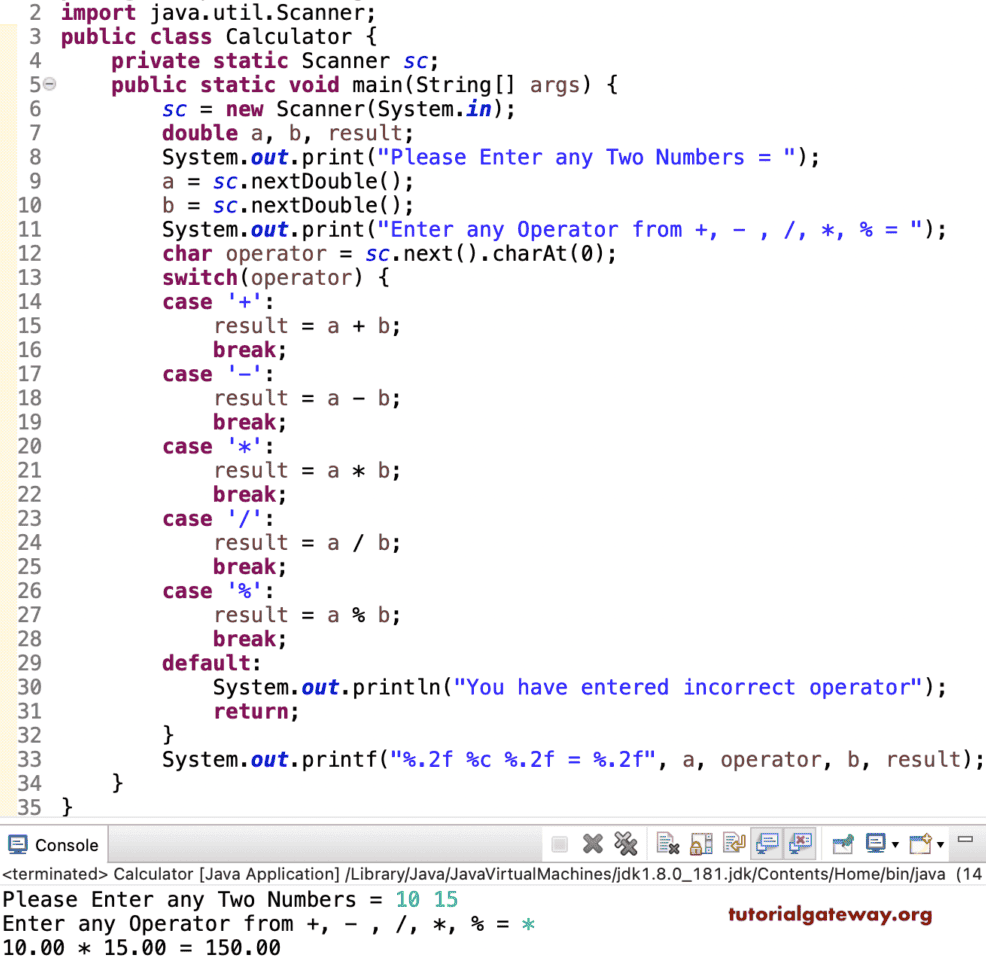
package SimpleNumberPrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Calculator {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
double a, b, result;
System.out.print("Please Enter any Two Numbers = ");
a = sc.nextDouble();
b = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter any Operator from +, - , /, *, % = ");
char operator = sc.next().charAt(0);
switch(operator) {
case '+':
result = a + b;
break;
case '-':
result = a - b;
break;
case '*':
result = a * b;
break;
case '/':
result = a / b;
break;
case '%':
result = a % b;
break;
default:
System.out.println("You have entered incorrect operator");
return;
}
System.out.printf("%.2f %c %.2f = %.2f", a, operator, b, result);
}
}
让我输入一个错误的符号。
Please Enter any Two Numbers = 11 4
Enter any Operator from +, - , /, *, % = #
You have entered incorrect operator使用 else if 编写 Java 计算器程序
在这个示例中,我们用else if 条件替换了 switch 语句,以创建一个简单的计算器。
package SimpleNumberPrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example2 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
double a, b, result = 0;
System.out.print("Please Enter any Two Numbers = ");
a = sc.nextDouble();
b = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter any Operator from +, - , /, *, % = ");
char operator = sc.next().charAt(0);
if(operator == '+') {
result = a + b;
}
else if(operator == '-') {
result = a - b;
}
else if(operator == '*') {
result = a * b;
}
else if(operator == '/') {
result = a / b;
}
else if(operator == '%') {
result = a % b;
}
else {
System.out.println("You have entered incorrect operator");
}
System.out.printf("%.2f %c %.2f = %.2f", a, operator, b, result);
}
}
Please Enter any Two Numbers = 20 32
Enter any Operator from +, - , /, *, % = -
20.00 - 32.00 = -12.00这个简单的计算器程序与上面的示例相同。但是,我们为每个计算创建了一个单独的函数。在实际应用中,最好创建一个包含这些方法的独立类,并创建该类的一个实例以便在主程序中调用它们。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] xrgs) {
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
double x, y, result = 0;
System.out.print("Enter Two Numbers = ");
x = sc.nextDouble();
y = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter anyy opt from +, - , /, *, % = ");
char opt = sc.next().charAt(0);
if (opt == '+') {
result = add(x, y);
} else if (opt == '-') {
result = sub(x, y);
} else if (opt == '*') {
result = mul(x, y);
} else if (opt == '/') {
result = div(x, y);
} else if (opt == '%') {
result = mod(x, y);
} else {
System.out.println("You have entered incorrect option");
}
System.out.printf("%.2f %c %.2f = %.2f", x, opt, y, result);
}
static double add(double x, double y) {
return x + y;
}
static double sub(double x, double y) {
return x - y;
}
static double mul(double x, double y) {
return x * y;
}
static double div(double x, double y) {
return x / y;
}
static double mod(double x, double y) {
return x % y;
}
}
Enter Two Numbers = 22
8
Enter anyy opt from +, - , /, *, % = %
22.00 % 8.00 = 6.00