Java cos 函数是 Math 函数之一,用于计算指定表达式的三角余弦。在开始 cos 程序之前,让我们先来看一下三角余弦函数背后的数学公式,如下所示:
cos(x) = 邻边长度 / 斜边长度。
Java 编程语言中 Math.cos 的基本语法如下所示。
static double cos(double number); //Return Type is Double // In order to use in program: Math.cos(double number);
数字:可以是您想计算余弦值的数字或有效的数值表达式。
- 如果数字参数是正数或负数,则函数将返回余弦值。
- 如果数字参数不是数字,则 Math.cos 函数将返回 NaN。
如何在 Java 中使用 math cos?
此函数将返回介于 -1 和 1 之间的值。我们使用 math cos 函数来查找正数和负数的三角余弦值。并使用此函数显示输出。
package TrigonometricFunctions;
public class CosMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double x = Math.cos(1.96 - 4.65 + 2.98);
System.out.println("Cosine value = " + x);
System.out.println("\nCosine value of Positive Number = " + Math.cos(10.25));
System.out.println("Cosine value of Positive Number= " + Math.cos(2.28));
System.out.println("\nCosine value of Negative Number = " + Math.cos(-4.85));
System.out.println("Cosine value of Negative Number = " + Math.cos(-7.95));
double m = Math.toRadians(30);
System.out.println("\nCosine value of Negative Number = " + Math.cos(m));
}
}
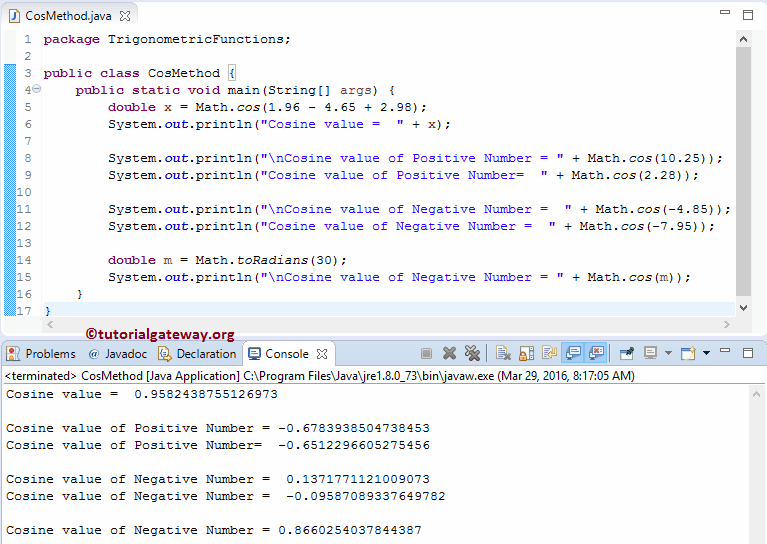
首先,我们声明了一个 Double 类型的变量 x,并直接在该表达式上使用了 Math.cos 函数。这里,我们使用 System.out.println 语句将结果作为输出打印出来。
double x = Math.cos(1.96 - 4.65 + 2.98);
System.out.println("Cosine value = " + x);
Math.cos(1.96 – 4.65 + 2.98)
==> Math.cos (0.29) ==> 0.95
接下来,我们直接在正双精度值上使用了 Math.cos 函数。
System.out.println("\nCosine value of Positive Number = " + Math.cos(10.25));
System.out.println("Cosine value of Positive Number= " + Math.cos(2.28));
这里,我们直接在负双精度值上使用了 Java math cos 函数。
System.out.println("\nCosine value of Negative Number = " + Math.cos(-4.85));
System.out.println("Cosine value of Negative Number = " + Math.cos(-7.95));
接下来,我们声明了一个 Double 类型的变量并赋值。然后,我们使用 Math.toRadians 函数将 30 转换为等效的弧度。然后,Java System.out.println 语句将结果作为输出打印出来。
double m = Math.toRadians(30);
System.out.println("\nCosine value of Negative Number = " + Math.cos(m));
Java cos 数组示例
在此 Java 程序中,我们将计算批量数据的余弦值。在这里,我们将声明一个双精度类型的数组并计算数组元素的余弦值。
package TrigonometricFunctions;
public class CosMethodOnArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double [] myArray = {0, 1, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 120, 180, 240, 360};
for (int i = 0; i < myArray.length; i++) {
System.out.format("Cosine value of Array Element %.2f = %.4f\n", myArray[i], Math.cos(myArray[i]));
}
}
}
Cosine value of Array Element 0.00 = 1.0000
Cosine value of Array Element 1.00 = 0.5403
Cosine value of Array Element 30.00 = 0.1543
Cosine value of Array Element 45.00 = 0.5253
Cosine value of Array Element 60.00 = -0.9524
Cosine value of Array Element 75.00 = 0.9218
Cosine value of Array Element 90.00 = -0.4481
Cosine value of Array Element 120.00 = 0.8142
Cosine value of Array Element 180.00 = -0.5985
Cosine value of Array Element 240.00 = 0.3258
Cosine value of Array Element 360.00 = -0.2837我们使用 For Loop 来迭代数组。在 Cosine For Loop 中,我们将 i 初始化为 0。接下来,只要条件 (i < myArray.length) 为真,编译器就会执行。
提示:myArray.length 用于查找数组的长度。
for (int i = 0; i < myArray.length; i++) {
在这里,我们在 System.out.format 语句中直接使用了 cos 函数。这里,它将调用 Math 方法(static double cos(double number))来查找相应的余弦值并打印输出。
System.out.format("Cosine value of Array Element %.2f = %.4f\n", myArray[i], Math.cos(myArray[i]));
注意:要查找单个项的余弦值,请使用:Math.cos(myArray[index_position])
如何在 Java ArrayList 中使用 cos
在此 Java 程序中,我们将声明一个双精度类型的 ArrayList 并计算列表元素的余弦值。
package TrigonometricFunctions;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CosMethodOnArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Double> myList = new ArrayList<Double>(5);
myList.add(15.45);
myList.add(65.64);
myList.add(95.60);
myList.add(120.75);
myList.add(140.68);
myList.add(180.98);
for (double x : myList) {
System.out.format("Cosine of %.2f = %.4f \n", x, Math.cos(x));
}
}
}
Cosine of 15.45 = -0.9669
Cosine of 65.64 = -0.9449
Cosine of 95.60 = 0.2168
Cosine of 120.75 = 0.2000
Cosine of 140.68 = -0.7702
Cosine of 180.98 = 0.3320 在此 math cos 函数示例中,我们使用 For Loop 来迭代 ArrayList 中的双精度值。
for (double x : myList) {
编译器将调用 cos Math 函数(static double cos(double x))来查找相应的余弦值并打印输出。
System.out.format("Cosine value of ArrayList Item %.2f = %.4f \n", x, Math.cos(x));
提示:请参考 acos 函数以查找指定表达式的反正余弦。