Java 的 codePointAt 方法是 String 方法之一,用于返回指定索引位置的字符的 Unicode。本文将通过示例展示如何在 Java 编程语言中使用 codePointAt 方法。该函数的索引位置从 0 开始,而不是 1。
Java 编程语言中 codePointAt 的基本语法如下所示。
public int codePointAt(int Index_Position) //In order to use in program String_Object.codePointAt(int Index_Position)
- String_Object:请指定有效的 String 对象。
- Index_Position:请指定所需字符的索引位置。
codePointAt 函数将返回指定 Index_Position 的 String_Object 中字符的 Unicode 值。如果我们指定的索引位置超出范围或为负值,codePointAt 函数将抛出错误。
Java codePointAt 示例
字符串 codePointAt 方法返回指定索引位置的字符的 Unicode 值。在此 Java 程序中,我们将查找相同内容。
package StringFunctions;
public class CodePointAt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Learn Free Java Tutorial";
int a = str.codePointAt(0);
int b = str.codePointAt(8);
int c = str.codePointAt(14);
int d = str.codePointAt(str.length()- 1);
System.out.println( "Unicode Vlaue of Character at Index position 0 = " + a);
System.out.println( "Unicode Vlaue of Character at Index position 8 = " + b);
System.out.println( "Unicode Vlaue of Character at Index position 14 = " + c);
System.out.println( "Unicode Vlaue of Character at Last Index position = " + d);
}
}
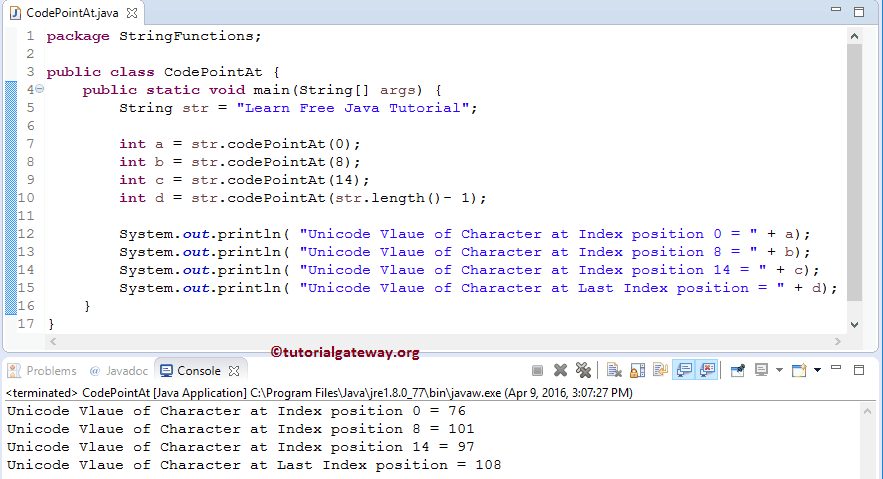
在此 Java codePointAt 方法示例中,我们声明了 String 变量并使用第一个语句为其赋值。
以下 Java 三条语句将查找索引位置为 0、8、14 的字符。然后将这些字符的 Unicode 值赋给整数变量 a、b 和 c。
int a = str.codePointAt(0); int b = str.codePointAt(8); int c = str.codePointAt(14);
如果您观察到上面的屏幕截图,str.codePointAt(0) 返回 76。这是因为我们都知道索引位置 0 处的字符是 L,根据 ASCII 表,L 的 Unicode 值是 76。您应该将空格算作一个字符。
在下一行,我们使用 length 函数来计算字符串长度。
int d = str.codePointAt(str.length()- 1);
从上面的 String 方法代码片段中,我们从字符串长度中减去一,因为字符串的长度是从 1 到 n 计算的,而索引位置是从 0 开始到 n-1 结束。以下四个 System.out.println 语句将打印输出。