C 语言编程中的 If Else 语句是 If 语句(我们在之前的文章中讨论过)的扩展。我们已经了解了 If 条件,它只在给定条件为真时执行语句。而当条件为假时,它不会执行代码。
在现实世界中,我们希望在条件不成立时也能执行某些操作。为此,我们使用 If Else 语句。在这里,当条件不成立时,else 块将执行其代码块。让我们看看 If Else 的语法。
C If Else 语句语法
该编程语言中 If Else 语句的基本语法如下:
if (Test condition)
{
//The condition is TRUE then these will be executed
True statements;
}
else
{
//The condition is FALSE then these will be executed
False statements;
}
当上述结构中的测试条件评估为真时,将执行真代码块。当条件为假时,将执行假代码块。If Else 语句的流程图如下所示。
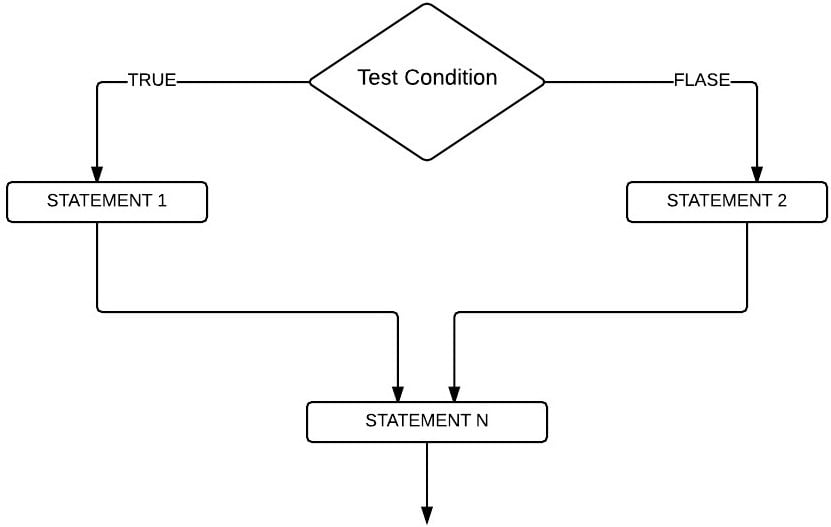
C 语言中 If Else 语句的示例
在这个程序中,我们将放置 4 个不同的 printf 行。如果条件为真,我们将打印 2 个独立的行。当条件为假时,程序将打印另外 2 行。
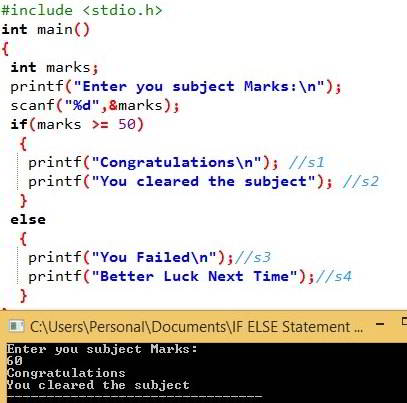
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int marks;
printf("Enter you subject Marks:\n");
scanf("%d",&marks);
if(marks >= 50)
{
printf("Congratulations\n"); //s1
printf("You cleared the subject"); //s2
}
else
{
printf("You Failed\n");//s3
printf("Better Luck Next Time");//s4
}
return 0;
}
分析:用户输入他的分数,如果分数大于或等于 50,则 s1 和 s2 将被打印。例如,如果分数小于 50,则 s3 和 s4 将作为输出被打印。
输出 1:让我们输入 60 作为分数。这意味着表达式为真。
让我们输入 30 作为分数。条件被评估为假。
Enter you subject Marks:
30
You Failed
Better Luck Next Time
评论已关闭。