编写一个 Java 程序,使用 While 循环、For 循环、函数和递归来打印斐波那契数列。斐波那契数列是按以下顺序显示的数字:0、1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34……
使用 While 循环的 Java 斐波那契数列程序
此程序使用 while 循环,允许输入一个正整数。然后,此程序使用 While 循环显示从 0 到给定数字的斐波那契数列。
package AdvancedSeries;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FibonacciSeries {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Number, i = 0, First_Value = 0, Second_Value = 1, Next;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please Enter any integer Value: ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
while(i < Number) {
if(i <= 1) {
Next = i;
}
else {
Next = First_Value + Second_Value;
First_Value = Second_Value;
Second_Value = Next;
}
System.out.println(Next);
i++;
}
}
}
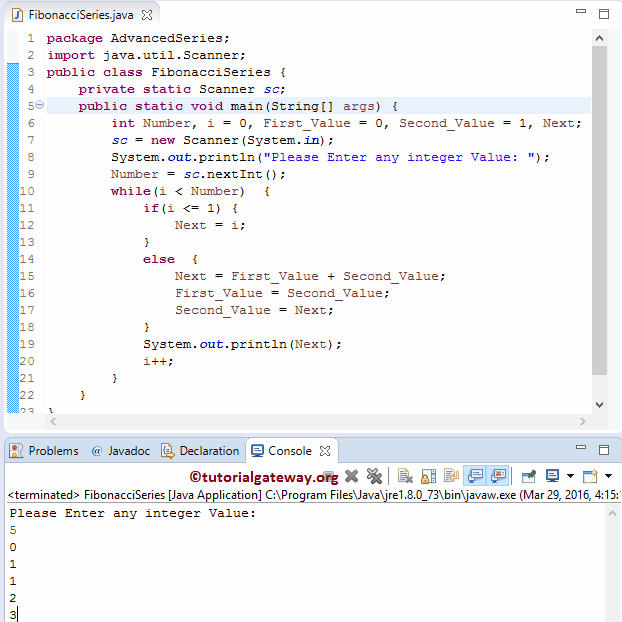
让我们逐次查看此斐波那契数列程序中 while 循环的工作原理。数字 = 5,我们知道 i = 0,第一个值 = 0,第二个值 = 1
在此程序中,While 循环从 0 开始,并迭代到给定值。在 While 循环内,我们在此 编程 中使用了 If Else 语句。
第一次迭代
- While (0 < 5) 为 TRUE。因此,程序将开始执行 while 循环内的语句。
- While 循环内的条件 if (0 <= 1) 为 TRUE。因此,Next = 0,编译器将退出 if 语句块。
- Print 语句 System.out.println(Next) 将打印值 0
- 最后,i 递增到 1。请参考 递增和递减运算符 文章。
第二次迭代
- While (1 < 5) 为 TRUE。
- if (1 <= 1) 为 TRUE。因此,它打印 1
- i 将递增到 1
Java 斐波那契数列程序第三次迭代
- While (2 < 5) 为 TRUE。
- if (2 <= 1) 为 FALSE。因此,else 块内的语句将开始执行。
- Next = First_Value + Second_Value ==> 0 + 1 = 1
- First_Value = Second_Value = 1
- Second_Value = Next = 1
- 接下来,它打印 1,i 递增 1。
第四次迭代
- While (3 < 5) 为 TRUE。
- if (3 <= 1) 为 FALSE。
- Next = 1 + 1 = 2
- First_Value = Second_Value = 1
- Second_Value = Next = 2
- 打印 2。
- i 将递增 1。
第五次迭代
- While (4 < 5) 为 TRUE。
- if (4 <= 1) 为 FALSE。
- Next = 1 + 2 = 3
- First_Value = Second_Value = 2
- Second_Value = Next = 3
- 接下来,它打印 3 并将 i 递增 1。
第六次迭代:While (5 < 5) 为 FALSE。因此,程序将退出 while 循环。Next 值的最终输出为 0 1 1 2 3
使用 For 循环的 Java 斐波那契数列程序
此程序使用 For 循环 显示从 0 到给定数字的斐波那契数列。下面的代码与上面的代码相同。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FSUsingFor {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Number, i, First_Value = 0, Second_Value = 1, Next;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please Enter any integer Value: ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
for(i = 0; i < Number; i++) {
if(i <= 1) {
Next = i;
}
else {
Next = First_Value + Second_Value;
First_Value = Second_Value;
Second_Value = Next;
}
System.out.println(Next);
}
}
}

使用函数的 Java 斐波那契数列程序
此示例使用函数显示从 0 到给定数字的数字。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FSUsingFunctions {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Number;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please Enter any integer Value: ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
Fibsr(Number);
}
public static void Fibsr(int Number) {
int i, First_Value = 0, Second_Value = 1, Next;
for(i = 0; i < Number; i++) {
if(i <= 1) {
Next = i;
}
else {
Next = First_Value + Second_Value;
First_Value = Second_Value;
Second_Value = Next;
}
System.out.println(Next);
}
}
}
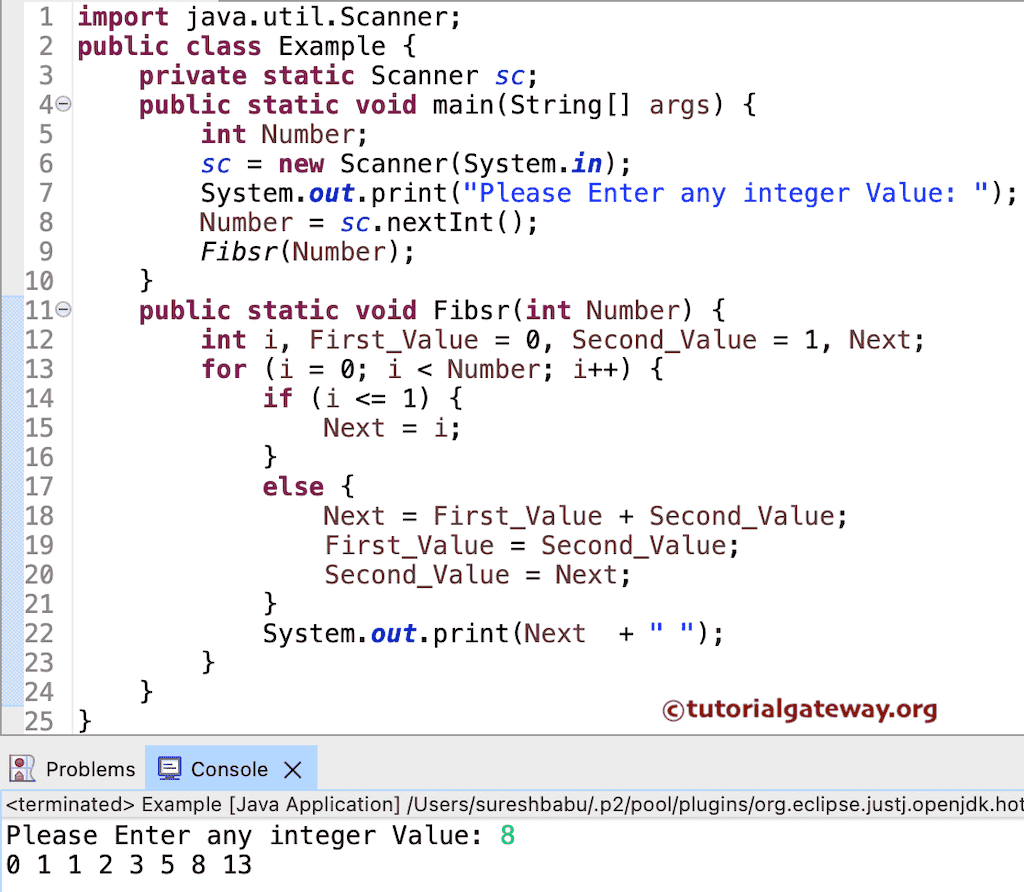
在此 程序 中,当编译器到达 Fibsr(Number) 行时,它会跳转到下面的函数
public static void Fibsr(int Number) {
使用递归打印斐波那契数列的 Java 程序
此斐波那契数列程序使用递归和 OOPS 显示从 0 到 N 的数字。在此示例中,我们将首先创建一个具有递归反转整数方法的类。
public class CalFib {
public int fns(int Number) {
if(Number == 0)
return 0;
else if (Number == 1)
return 1;
else
return (fns(Number - 2) + fns(Number - 1));
}
}
在 Main 中,我们将创建该类的实例并调用方法。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FSUsingRecusrsion {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Number, i;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please Enter any integer Value: ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
CalFib fib = new CalFib();
for(i = 0; i < Number; i++) {
System.out.println(fib.fns(i));
}
}
}
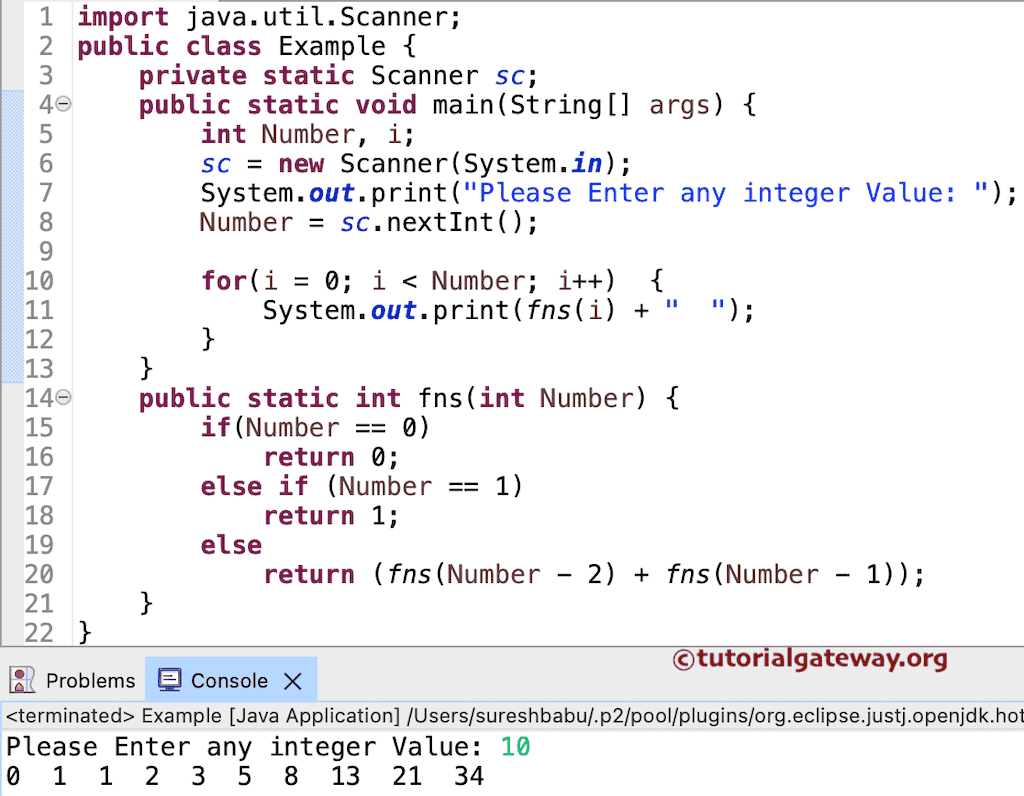
在此斐波那契数列程序类中,我们定义了一个函数。它接受整数值并返回整数值。
public int fns(int Number) {
让我们看看上面指定函数内的 Else If 语句
- if (Number == 0) 如果为 TRUE,则函数返回零值。
- if (Number == 1) – 如果为 TRUE,则函数返回一值。
- 如果数字大于 1,则执行 else 块内的语句。
我们在 Else 块内递归调用函数以显示结果。
return (fns(Number - 2)+ fns(Number - 1));
例如,Number = 2
==> (fns(Number – 2) + fns(Number – 1))
==> (fns(2 – 2) + fns(2 – 1)),这意味着
(fns (0)+ fns(1))
==> return (0 + 1) = return 1。
Main 类分析
在程序主类中,我们首先创建了类的实例/创建了类的对象。
CalFib fib = new CalFib();
接下来,我们声明一个 For 循环,并在 for 循环内调用 fns(int Number) 方法。在这里,System.out.println 语句将打印输出。
for(i = 0; i < Number; i++) {
System.out.println(fib.fns(i));
}