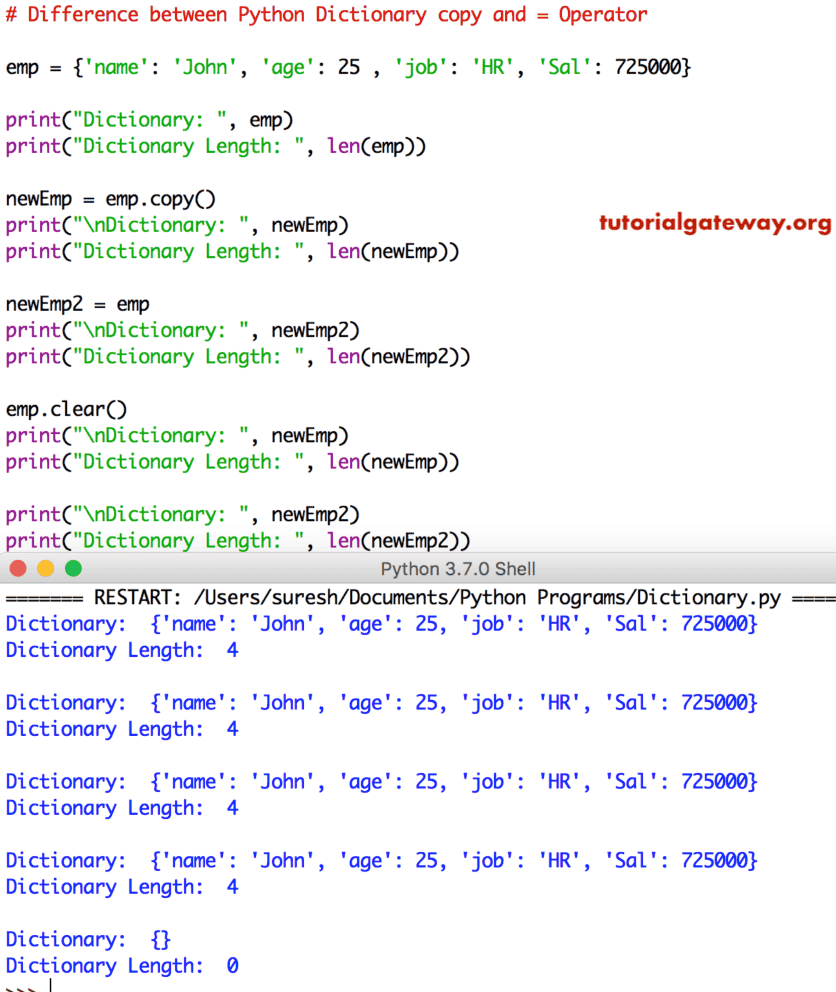
在本节中,我们将通过实际示例讨论 Python 字典复制与 = 运算符之间的区别。Python 字典复制(浅拷贝)将字典项复制到一个全新的字典中。而 = 运算符则创建现有字典的一个实例。
Python 字典复制与 = 运算符之间的区别 示例 1
在此示例中,我们展示了如何使用这两个选项将字典项复制到一个新字典中。如您所见,这两个 Python 代码都给出了相同的结果。
# Difference between Python Dictionary copy and = Operator
emp = {'name': 'John', 'age': 25 , 'job': 'HR', 'Sal': 725000}
print("Dictionary: ", emp)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(emp))
newEmp = emp.copy()
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp))
newEmp2 = emp
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp2)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp2))
字典复制与 = 运算符的输出
Dictionary: {'name': 'John', 'age': 25, 'job': 'HR', 'Sal': 725000}
Dictionary Length: 4
Dictionary: {'name': 'John', 'age': 25, 'job': 'HR', 'Sal': 725000}
Dictionary Length: 4
Dictionary: {'name': 'John', 'age': 25, 'job': 'HR', 'Sal': 725000}
Dictionary Length: 4区分字典复制与 = 运算符 示例 2
在此程序中,我们使用 字典清空 函数从 字典 中删除项。如果您仔细观察,当我们从 emp 中删除项时,newEmp2 也返回一个空集。
# Difference between Python Dictionary copy and = Operator
emp = {'name': 'John', 'age': 25 , 'job': 'HR', 'Sal': 725000}
print("Dictionary: ", emp)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(emp))
newEmp = emp.copy()
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp))
newEmp2 = emp
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp2)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp2))
emp.clear()
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp))
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp2)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp2))