在 SQL Server 中,当处理大量数据集(或海量记录)时,我们可能需要将中间结果存储在临时查询中。这样,我们就可以进一步访问它们。SQL Server 提供了多种选项来实现这一目标:CTE、临时表、派生表和表变量。让我们通过实际示例了解 SQL Server 中 CTE、临时表、派生表和表变量的区别。
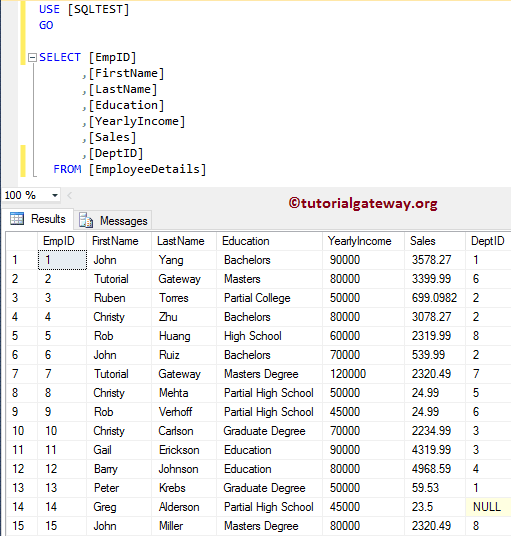
对于此 SQL CTE、临时表、派生表示例,我们使用数据库中的两个表(员工详细信息和部门)。Employee Details 表中的数据是
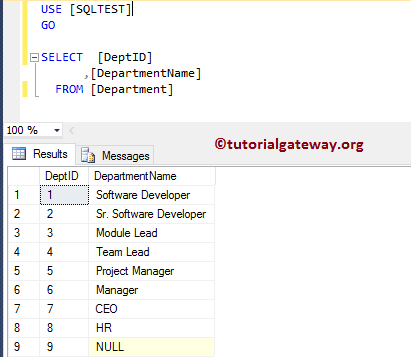
Department 表中已有的数据是
CTE、临时表、派生表和表变量之间的区别
在本节中,我们的目标是显示每个部门的总员工人数。以及销售额和他们的总年薪。我们将使用的 SQL 查询的基本结构包含
- 我们将使用内部联接从 Employees 和 Department 表中选择列。
- 并且,我们使用GROUP BY来聚合列。我建议您访问聚合函数文章。
- 最后,我们使用 CTE、表变量、临时表、派生表来过滤数据。
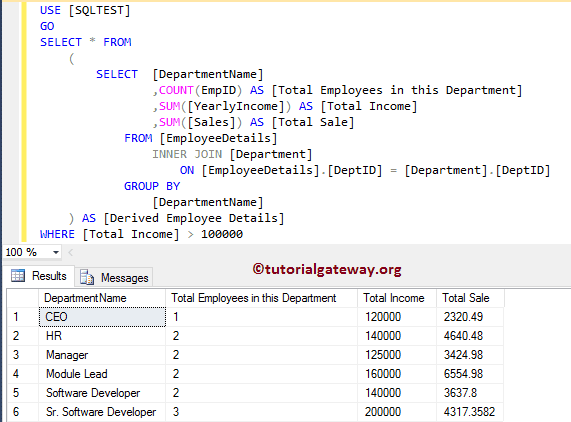
派生表示例
我们将使用派生列来实现我们的目标。我建议您参考派生表文章来理解查询。
-- Difference between CTE, Temp Tables, Derived tables , and Table variable SELECT * FROM ( SELECT [DepartmentName] ,COUNT(EmpID) AS [Total Employees in this Department] ,SUM([YearlyIncome]) AS [Total Income] ,SUM([Sales]) AS [Total Sale] FROM [EmployeeDetails] INNER JOIN [Department] ON [EmployeeDetails].[DeptID] = [Department].[DeptID] GROUP BY [DepartmentName] ) AS [Derived Employee Details] WHERE [Total Income] > 100000
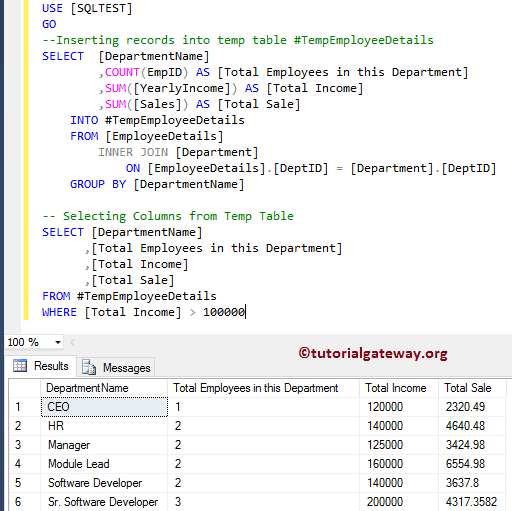
SQL 临时表示例
我们将使用临时表来实现我们的目标。首先,我们使用Insert Into Statement将记录插入到本地临时表中。接下来,我们将选择该临时表中的所有记录,其总收入大于 100000。我建议您参考临时表文章来理解查询。
--Inserting records into temp table #TempEmployeeDetails
SELECT [DepartmentName]
,COUNT(EmpID) AS [Total Employees in this Department]
,SUM([YearlyIncome]) AS [Total Income]
,SUM([Sales]) AS [Total Sale]
INTO #TempEmployeeDetails
FROM [EmployeeDetails]
INNER JOIN [Department]
ON [EmployeeDetails].[DeptID] = [Department].[DeptID]
GROUP BY [DepartmentName]
-- Selecting Columns from Temp Table
SELECT [DepartmentName]
,[Total Employees in this Department]
,[Total Income]
,[Total Sale]
FROM #TempEmployeeDetails
WHERE [Total Income] > 100000
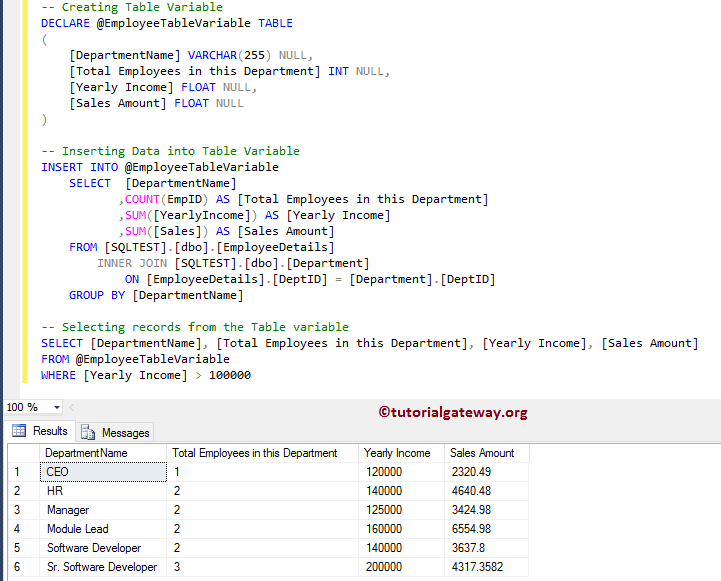
SQL 表变量示例
这次我们将使用表变量来实现我们的目标。首先,我们声明了一个表变量。接下来,我们使用Insert Into Statement将记录插入到该表变量中。最后,我们将从表变量中选择所有记录,其总收入大于 100000。我建议您参考表变量来理解查询。
-- Creating Table Variable
DECLARE @EmployeeTableVariable TABLE
(
[DepartmentName] VARCHAR(255) NULL,
[Total Employees in this Department] INT NULL,
[Yearly Income] FLOAT NULL,
[Sales Amount] FLOAT NULL
)
-- Inserting Data into Table Variable
INSERT INTO @EmployeeTableVariable
SELECT [DepartmentName]
,COUNT(EmpID) AS [Total Employees in this Department]
,SUM([YearlyIncome]) AS [Yearly Income]
,SUM([Sales]) AS [Sales Amount]
FROM [SQLTEST].[dbo].[EmployeeDetails]
INNER JOIN [SQLTEST].[dbo].[Department]
ON [EmployeeDetails].[DeptID] = [Department].[DeptID]
GROUP BY [DepartmentName]
-- Selecting records from the Table variable
SELECT [DepartmentName], [Total Employees in this Department], [Yearly Income], [Sales Amount]
FROM @EmployeeTableVariable
WHERE [Yearly Income] > 100000
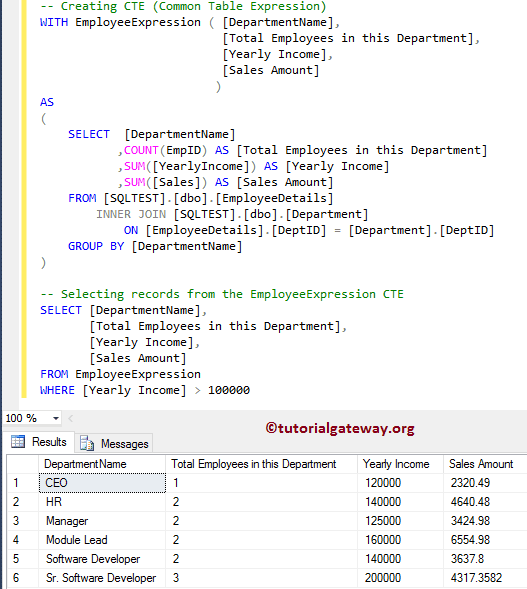
SQL 公用表表达式示例
这次我们将使用公用表表达式(或 CTE)来实现我们的目标。首先,我们创建一个 CTE。接下来,我们将从该 CTE 中选择所有记录,其总收入大于 100000。我建议您参考Server CTE来理解查询。
-- Creating CTE (Common Table Expression)
WITH EmployeeExpression ( [DepartmentName],
[Total Employees in this Department],
[Yearly Income],
[Sales Amount]
)
AS
(
SELECT [DepartmentName]
,COUNT(EmpID) AS [Total Employees in this Department]
,SUM([YearlyIncome]) AS [Yearly Income]
,SUM([Sales]) AS [Sales Amount]
FROM [SQLTEST].[dbo].[EmployeeDetails]
INNER JOIN [SQLTEST].[dbo].[Department]
ON [EmployeeDetails].[DeptID] = [Department].[DeptID]
GROUP BY [DepartmentName]
)
-- Selecting records from the EmployeeExpression CTE
SELECT [DepartmentName],
[Total Employees in this Department],
[Yearly Income],
[Sales Amount]
FROM EmployeeExpression
WHERE [Yearly Income] > 100000
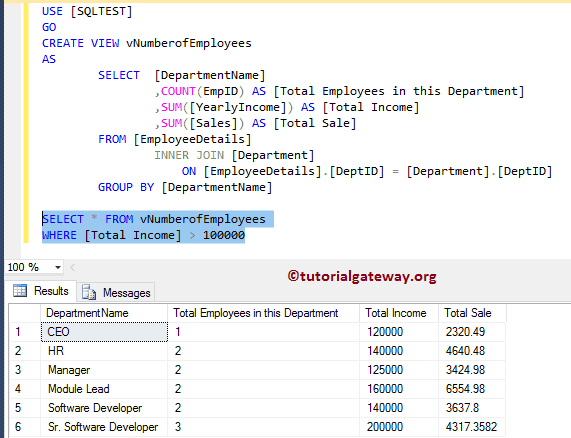
SQL 视图示例
您还可以使用视图来实现我们的目标。首先,我们创建一个视图,该视图从两个表中选择所有匹配的记录以及聚合。接下来,我们将从视图中选择所有记录,其总收入大于 100000。请参考视图来了解查询。
--Creating a View
CREATE VIEW vNumberofEmployees
AS
SELECT [DepartmentName]
,COUNT(EmpID) AS [Total Employees in this Department]
,SUM([YearlyIncome]) AS [Total Income]
,SUM([Sales]) AS [Total Sale]
FROM [EmployeeDetails]
INNER JOIN [Department]
ON [EmployeeDetails].[DeptID] = [Department].[DeptID]
GROUP BY [DepartmentName]
-- Selecting Records from vNumberofEmployees View
SELECT * FROM vNumberofEmployees
WHERE [Total Income] > 100000