如何使用For循环、While循环、指针、函数、引用传递和递归编写C语言查找数字阶乘的程序。它用符号“!”表示。阶乘是所有小于等于该数且大于0的数的乘积。
n! = n * (n-1) * (n -2) * …….* 1。例如,5的阶乘表示为5! = 5 *4 * 3 * 2 * 1 = 120
使用For循环查找数字阶乘的C语言程序
此阶乘程序允许用户输入任何整数值。通过使用此值,此C语言程序使用For循环查找数字的阶乘。
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i, n;
long fac = 1;
printf("Please Enter any number to Find Factorial = ");
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
fac = fac * i;
}
printf("\nFactorial of %d = %ld\n", n, fac);
return 0;
}
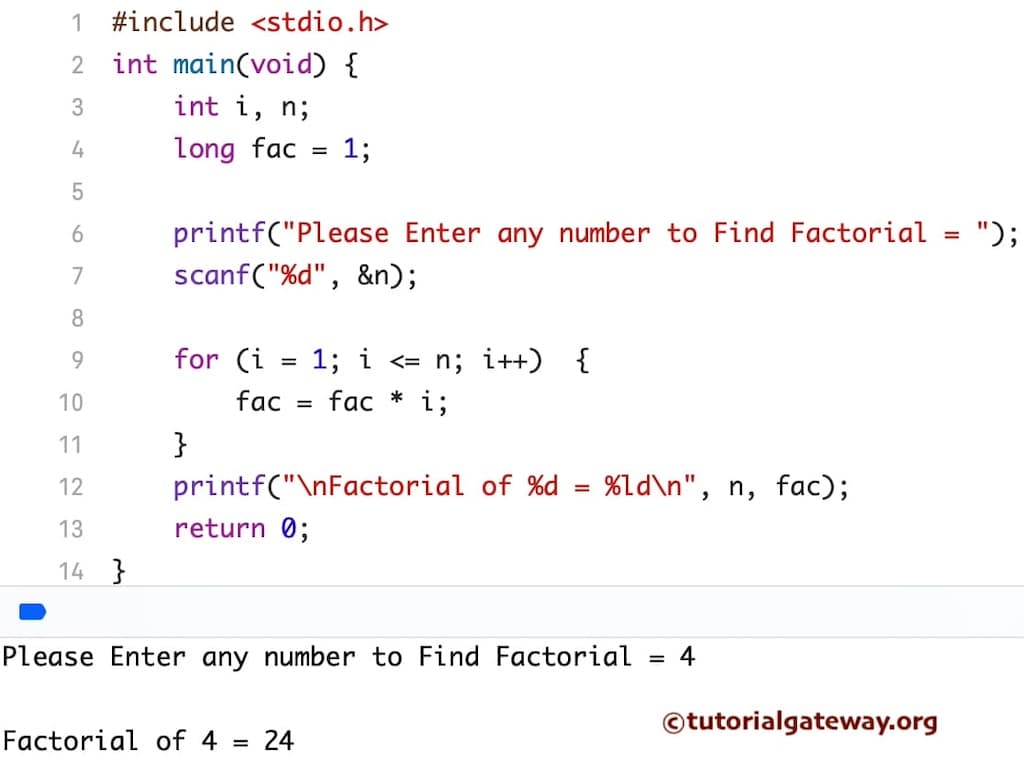
在此C语言查找数字阶乘的示例中,我们声明了两个整数变量 i 和 number。我们还声明了一个长整型变量并将值1赋给了它。
尽管我们计算整数变量,但我们将输出声明为长整型变量。因为当我们为大整数计算阶乘时,结果肯定会超出整数限制。
第一个C语言编程printf语句将要求用户输入自己的整数值进行计算。scanf语句会将用户输入的值赋给Number变量。
在For循环中,我们将整数I的值初始化为1,并且(i <= Number)条件将在条件失败时帮助循环终止。
在上例中,用户输入了一个整数4,用于查找阶乘数字程序。
第一次迭代
i = 1, Factorial= 1 and Number= 4 – 这意味着 (i <= Number) 为真
Factorial = Factorial * i => 1 *1 = 1
i++ 表示 i 将变为 2
第二次迭代
i = 2, Factorial= 1 and Number= 4 – 这意味着 (2 <= 4) 为真
Factorial = 1 *2 = 2
i++ 表示 i 将变为 3
C语言查找数字阶乘程序第三次迭代
i = 3, Factorial= 2 and Number= 4 – 这意味着 (3 <= 4) 为真
Factorial= 2 *3 = 6
i++ 表示 I 将变为 4
第四次迭代
i = 4, Factorial= 6 and Number= 4 – 这意味着 (4 <= 4) 为真
Factorial = 6 * 4 = 24
i++ 表示 i 将变为 5 – 这意味着 (5 <= 4) 为假。因此,For循环将终止。
最后一个printf语句将打印用户输入整数的输出。在printf语句中,第一个%d代表Number,第二个%d代表输出。
printf("Factorial of %d = %d\n", Number, Factorial);
使用While循环查找数字阶乘的C语言程序
这个使用while循环查找数字阶乘的程序允许您输入任何整数值。通过使用该值,它将找到并返回结果。
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int Num, i = 1;
long Fc = 1;
printf("\n Please Enter any value \n");
scanf("%d", &Num);
while (i <= Num)
{
Fc = Fc * i;
i++;
}
printf("Factorial of %d = %d\n", Num, Fc);
return 0;
}
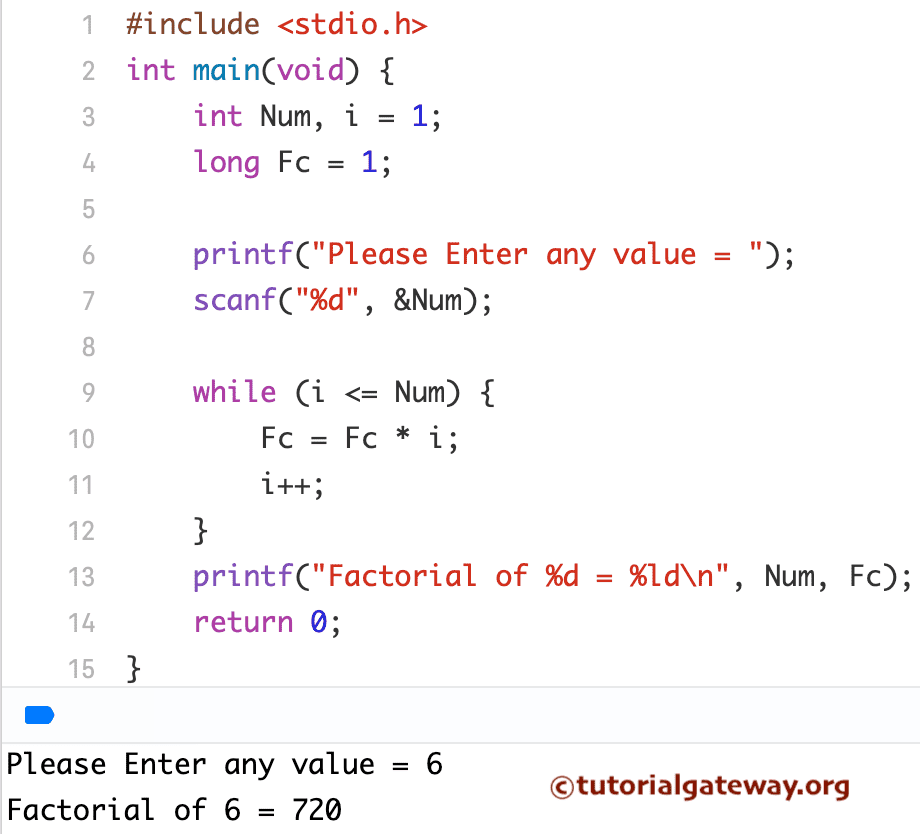
我们在上面的示例中用While循环替换了For循环。如果您不理解While循环程序,请参考这里的While循环文章:While循环。
使用指针查找数字阶乘的C语言程序
此程序将使用指针查找给定数字的阶乘。我建议您在此示例之前参考指针文章。它将帮助您理解指针和指针变量的概念。
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i, Num, *P;
long Fct = 1;
printf("\n Please Enter any \n");
scanf("%d", & Num);
P = &Num;
for (i = 1; i <= *P; i++)
{
Fct = Fct * i;
}
printf("\nFact of %d Using Normal Variable = %d\n", Num, Fct);
printf("Fact of %d Using Pointer Variable = %d\n", *P, Fct);
return 0;
}
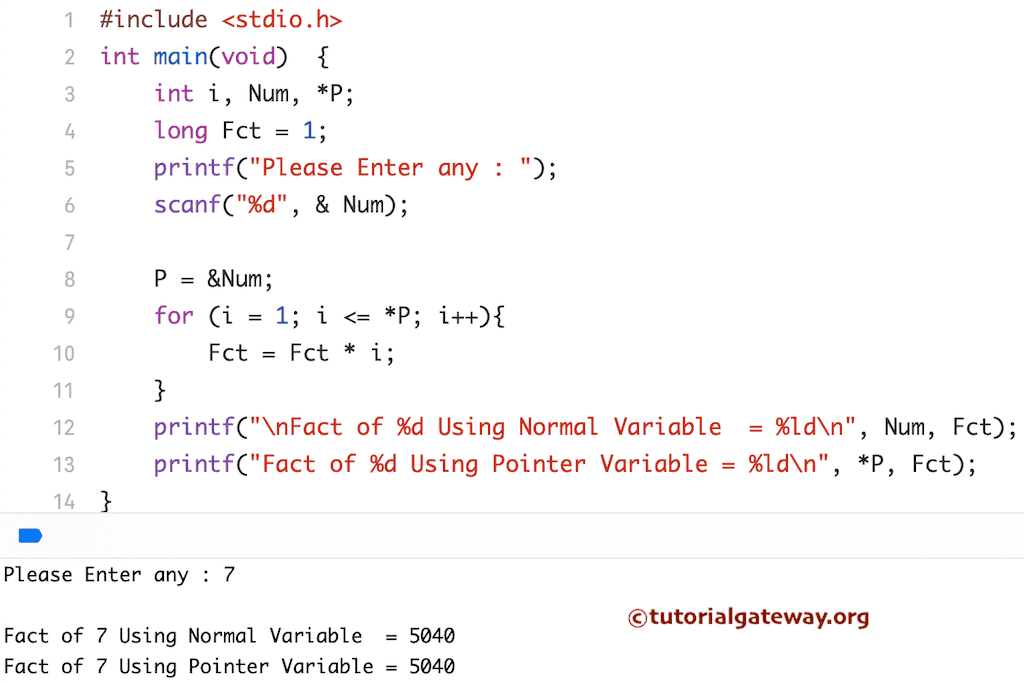
在此程序中,我们将Number变量的地址赋给了指针变量的地址。这里,P是我们已经声明的指针变量的地址(*P)。我们都知道,&Number是Number的地址。
P = &Num;
在For循环中,我们将i值与指针变量*P进行比较,而不是与Number变量进行比较。
这里,*P表示指针变量中的值。
使用函数查找数字阶乘的C语言程序
此程序允许用户输入任何整数值。用户输入的值将被传递给我们创建的函数。在此用户定义函数中,此程序使用For循环查找数字的阶乘。
#include <stdio.h>
long CaclFtr(int);
int main()
{
int Nm;
long Fc = 1;
printf("\n Please Enter any number \n");
scanf("%d", &Nm);
Fc = CaclFtr(Nm);
printf("Factorial of %d = %d\n", Nm, Fc);
return 0;
}
long CaclFtr(int Nm)
{
int i;
long Fc = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= Nm; i++)
{
Fc = Fc * i;
}
return Fc;
}

在此数字阶乘示例中,由于函数CaclFtr()将返回长整型值作为输出,因此我们将函数调用赋值给长整型变量。
Factorial = CaclFtr(Nc);
当编译器在main()函数中到达CaclFtr(Nc)行时,编译器将立即跳转到下面的函数。
long CaclFtr(int Nc)
我们已经在上面的程序示例中解释了逻辑。
最后一行以return语句结束。这意味着每次我们从main()或任何子函数调用CaclFtr()函数时,它都会返回值。
使用递归查找数字阶乘的C语言程序
此程序允许您输入任何整数值。用户输入的值将被传递给我们创建的函数。在此用户定义函数中,此程序以递归方式查找数字的阶乘。
在此示例之前,请参考C语言的递归文章。它将帮助您理解递归概念。
#include <stdio.h>
long CalFct(int);
int main()
{
int Num;
long Fact = 1;
printf("\n Please Enter any \n");
scanf("%d", &Num);
Fact = CalFct(Num);
printf("\nFactorial of %d = %d\n", Num, Fact);
return 0;
}
long CalFct(int Num)
{
if (Num == 0 || Num == 1)
return 1;
else
return Num * CalFct(Num -1);
}
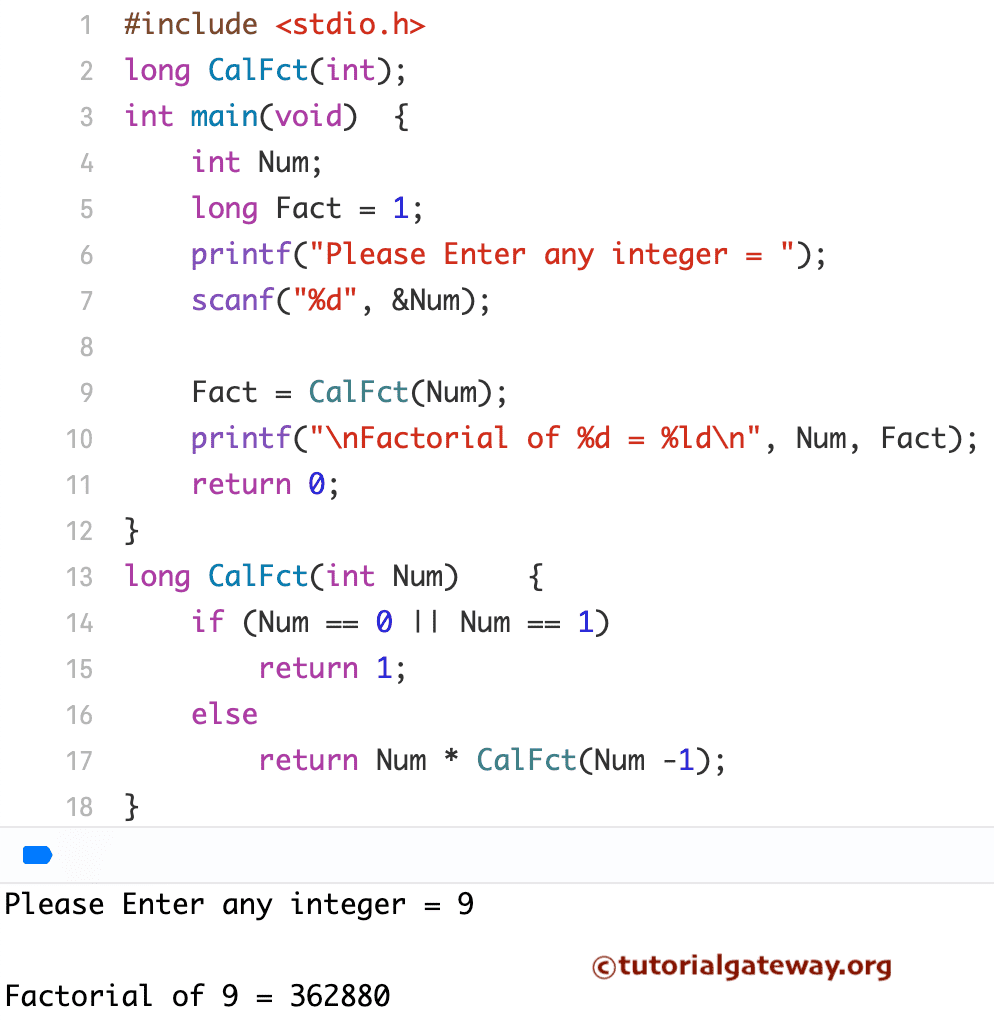
在此程序的自定义函数中,
long CalFct(int Num)
If语句将检查给定的数字是否等于0或等于1。
- 如果条件为真,函数将返回1。
- 并且,如果条件为真,函数将递归地返回Num * (Num -1)。
在此数字阶乘示例中,用户输入的值为9。这意味着第一个If语句失败,所以,
Fact = Num * CalFct (Num -1);
= 9 * CalFct (9 -1)
= 9 * CalFct (8)
= 9 * 8 * CalFct (7)
= 9 * 8 * 7 * CalFct (6)
= 9 * 8 * 7 * 6 * CalFct (5)
= 9 * 8 * 7 * 6 * 5 * CalFct (4)
= 9 * 8 * 7 * 6 * 5 * 4 * CalFct (3)
= 9 * 8 * 7 * 6 * 5 * 4 * 3 * CalFct (2)
= 9 * 8 * 7 * 6 * 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * CalFct (1)
= 9 * 8 * 7 * 6 * 5 * 4 * 3 * 2
= 362880
使用引用传递查找数字阶乘的C语言程序
这允许用户输入任何整数值。而不是用户输入的值,而是将变量的地址传递给我们创建的函数。在此用户定义函数中,此程序使用For循环和引用传递查找数字的阶乘。
在此程序示例之前,请参考按值传递和按引用传递文章。它将帮助您理解按值传递和按引用传递的概念之间的区别。
#include <stdio.h>
long CalFct(int *);
int main()
{
int Num;
long Fact = 1;
printf("\n Please Enter any value \n");
scanf("%d", &Num);
Fact = CalFct(&Num);
printf("Factorial of %d = %d\n", Num, Fact);
return 0;
}
long CalFct(int *Num)
{
int i;
long Fact = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= *Num; i++)
{
Fact = Fact * i;
}
return Fact;
}
Please Enter any value
8
Factorial of 8 = 40320