如何用C语言和实际例子编写一个使用冒泡排序来排序数组的程序?下面这个冒泡排序程序使用嵌套的 For 循环将一维数组元素按升序排序。
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[100], number, i, j, temp;
printf("\n Please Enter the total Number of Elements : ");
scanf("%d", &number);
printf("\n Please Enter the Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < number; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for(i = 0; i < number - 1; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < number - i - 1; j++)
{
if(a[j] > a[j + 1])
{
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
printf("\n List Sorted in Ascending Order : ");
for(i = 0; i < number; i++)
{
printf(" %d \t", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
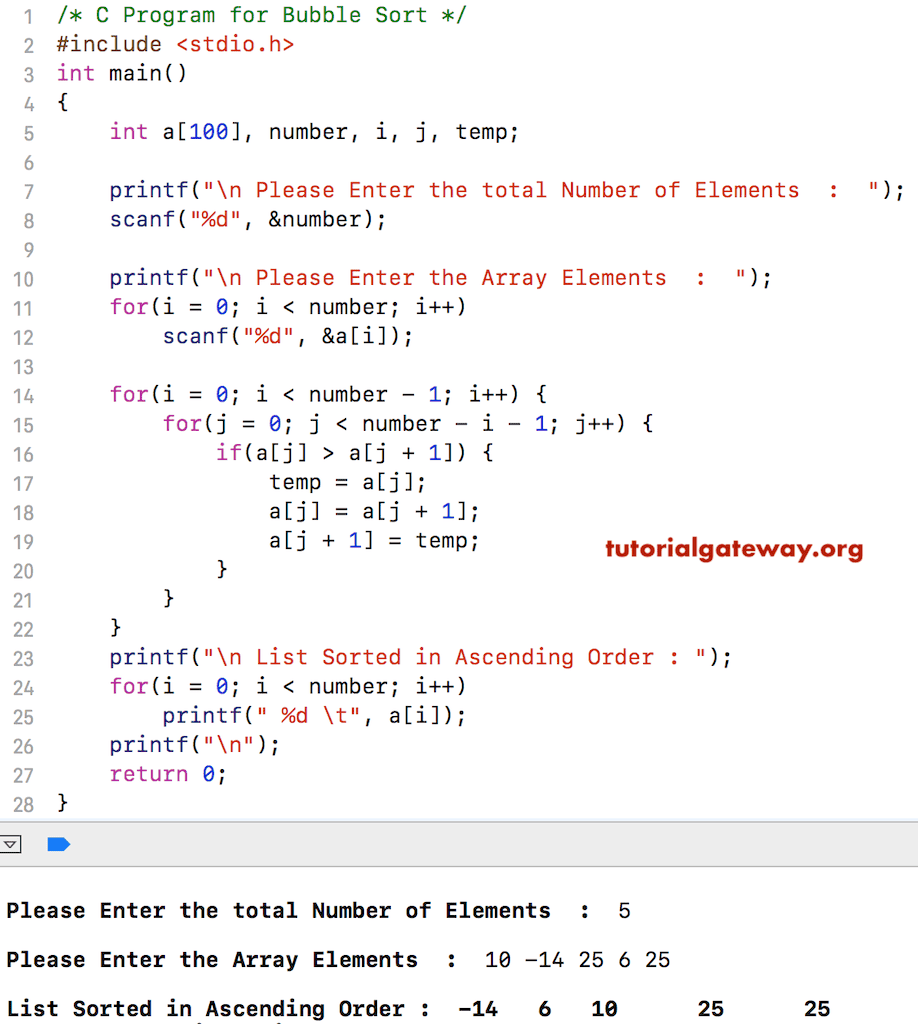
在这里,For 循环将确保数字在 0 和 一维数组的最大大小值之间。
第一个 For 循环 – 第一次迭代: for(i = 0; 0 < 4; 0++)
条件为真,因此它将进入第二个 for 循环
第二个 For 循环 – 第一次迭代: for(j = 0; 0 < 5-0-1; 0++)
For 循环内的条件为真。因此,编译器将进入 If 语句
if(a[0] > a[1]) => if(10 > -14) – 表示条件为真
temp = 10
a[j] = a[j + 1] => a[0] = a[1] => a[0] = -14
a[j + 1] = temp => a[1] = 10
现在数组将是 -14 10 25 6 25。接下来,j 将增加 1。
第二个 For 循环 – 第二次迭代: for(j = 1; 1 < 5 – 0 – 1; 1++)
For 循环条件为真,编译器将进入 If 语句
if(10 > 25) – 表示条件为假。对其余 C 编程迭代执行相同操作
使用 While 循环的 C 语言冒泡排序程序
这个冒泡排序程序与上面的相同。但是,我们用 While 循环替换了 for 循环,以使用冒泡排序来组织数组元素
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[100], number, i, j, temp;
printf("\n Please Enter the total Number of Elements : ");
scanf("%d", &number);
printf("\n Please Enter the Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < number; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
i = 0;
while(i < number - 1) {
j = 0;
while(j < number - i - 1) {
if(a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
j++;
}
i++;
}
printf("\n List in Ascending Order : ");
for(i = 0; i < number; i++)
printf(" %d \t", a[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Please Enter the total Number of Elements : 6
Please Enter the Array Elements : 10 20 -30 20 5 15
List in Ascending Order : -30 5 10 15 20 20 使用函数的 C 冒泡排序程序
这个冒泡排序 程序与第一个示例相同。不过,我们分离了使用 函数通过冒泡排序组织数组元素的逻辑。
#include <stdio.h>
void bubFunc(int a[], int number) {
int i, j, temp;
for(i = 0; i < number - 1; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < number - i - 1; j++) {
if(a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[100], size, i;
printf("\n Please Enter the total Elements : ");
scanf("%d", &size);
printf("\n Please Enter the Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
bubFunc(arr, size);
printf("\n List in Ascending Order : ");
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf(" %d \t", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Please Enter the total Elements : 4
Please Enter the Array Elements : 3 -2 1 0
List in Ascending Order : -2 0 1 3 使用指针的 C 语言冒泡排序程序
在这个冒泡排序程序示例中,我们创建了一个额外的函数,并使用 指针来 交换两个数字。其余与上面相同
#include <stdio.h>
void Swap(int *x, int *y)
{
int Temp;
Temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = Temp;
}
void bubFunc(int a[], int number) {
int i, j, temp;
for(i = 0; i < number - 1; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < number - i - 1; j++) {
if(a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
Swap(&a[j], &a[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[100], size, i;
printf("\n Please Enter the total Elements : ");
scanf("%d", &size);
printf("\n Please Enter the Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
bubFunc(arr, size);
printf("\n Array in Ascending Order : ");
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf(" %d \t", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Please Enter the total Elements : 6
Please Enter the Array Elements : 10 20 30 -12 20 5
Array in Ascending Order : -12 5 10 20 20 30