在 C 编程语言中,如何使用 fputs 将字符数组或字符串数据写入文件?fputs 函数用于将一个字符数组写入指定的流。要逐个字符写入,请使用 fputc 函数。
C 编程语言中 fputs 的语法如下所示。
int fputs(const char *str, FILE *stream)
或者我们可以简单地写成
int fputs(string, <File Pointer>)
在上面的 fputs 函数代码片段中:
- char:请指定您想要写入文件的字符数组。
- stream:请指定一个指向 FILE 对象的指针。或者说,一个持有地址和操作模式的文件指针。
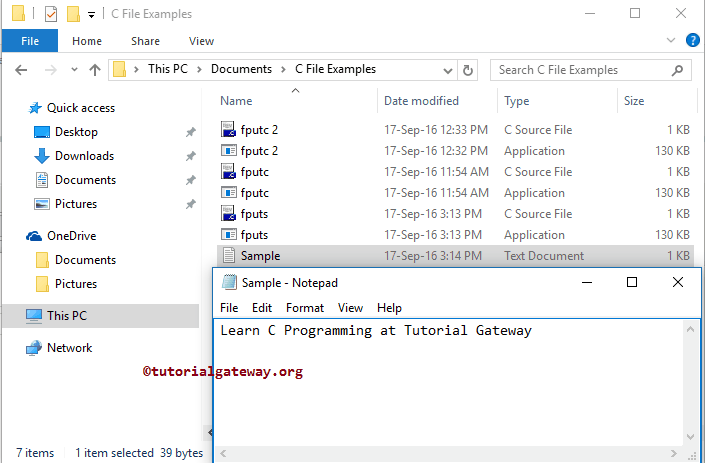
我们将使用以下指定的文件来演示这个 fputs 函数。从下面的截图中,您可以看到 sample.txt 文件位于我们的“文档”文件夹中,并且是空的。
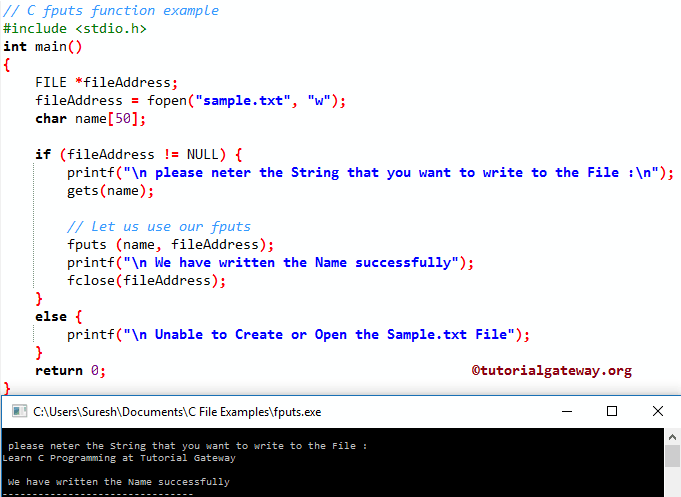
C fputs 函数示例
fputs 函数用于将字符数组写入用户指定的文件。这个 C 程序将帮助您理解这一点。
提示:在使用 fputs 函数之前,您必须包含 #include<stdio.h> 头文件。
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fileAddress;
fileAddress = fopen("sample.txt", "w");
char name[50];
if (fileAddress != NULL) {
printf("\n please neter the String that you want to write to the File :\n");
gets(name);
// Let us use our fputs
fputs (name, fileAddress);
printf("\n We have written the Name successfully");
fclose(fileAddress);
}
else {
printf("\n Unable to Create or Open the Sample.txt File");
}
return 0;
}
在这个 fputs 函数示例中,我们首先创建了文件指针,然后以写入模式指定了文件。请参考 fputc 函数 的文章。
提示:在这个 C 程序中,我们没有提及文件名的完整路径,因为我的应用程序和 txt 文件位于同一位置。如果您的情景不同,请提供完整路径。
FILE *fileAddress;
fileAddress = fopen("sample.txt", "w");
下面的 If 语句 检查我们是否成功打开了 sample.txt。
if (fileAddress != NULL) {
以下语句要求用户输入他想写入 sample.txt 的字符串,我们使用 Gets 函数读取用户输入。
printf("\n please neter the String that you want to write to the File :\n");
gets(name);
接下来,我们使用 C fputs 函数将用户指定的字符串写入 sample.txt。
fputs (name, fileAddress);
然后,我们关闭了 C 编程 文件指针。
fclose(fileAddress);
让我们打开文本文件,看看我们是否成功返回了字符。